- Business & Enterprise
- Education, Learning & Skills
- Energy & Environment
- Financial Services
- Health & Wellbeing
- Higher Education
- Work & Welfare
- Behavioural insights
- Business Spotlight – IFF’s business omnibus
- Customer experience research
- Customer satisfaction measurement
- National statistics and complex surveys
- Stakeholder research
- Tenant satisfaction measures
- Our approach
- Trusted partner
- Equality, diversity & inclusion at IFF
- Sustainability at IFF
- Charity giving
- Meet the team
- News & resources
- Case studies

How to write an effective research brief
Whether you’re launching a simple survey or planning a large-scale project the quality of your brief will hugely impact on the value you get from the research. While it can take a little time and effort creating a research brief, it will undoubtedly be time well spent – getting you better results and return on your investment and saving you valuable resources on further clarification. At best, a poor brief will be a time drain on you and your team. At worst, the findings will fail to meet your objectives, costing you time and money.
We’ve seen a lot of research briefs over the years. Some of which have been well thought through and clear, helping us prepare a detailed proposal and deliver an effective project and subsequent results. And others which have been not so good, lacking clarity or detail.
Using this experience, we’ve put together a ‘how to’ guide on writing an effective research brief, to help you ensure success on your next project.
1. Preparation is key
As with any project, before you start it’s crucial you think through what you want and need to deliver. Here are some things you should consider:
- Why are you conducting the research? What exactly are you looking to understand?
- Who are you looking to understand better? Who do you need to speak to answer your research questions?
- Who are your internal stakeholders? Have you discussed the project needs with the people in your organisation who will use the findings or who are invested in the research?
- How will the findings be used?
- When do you need the findings?
- Have you agreed a budget with either your procurement team, or the relevant person in your organisation?
2. Be clear on your objectives
This is one of the most important parts of your brief to convey to the reader what you want out of the project and ensure you get results which deliver.
Projects should have around three or four overarching aims which set out what the project ultimately wants to achieve.
These might be things like:
- Assess the impact of……
- Examine views of…..
- Evaluate the effectiveness of….
In addition to project objectives, you should also include the key questions you want the research to answer. These should support you in meeting the aims of the research.
For example, if the project aim is to assess the impact of an intervention, your research questions might include:
- Who did the intervention target?
- What did the project deliver?
- What elements were successful, and why?
- What were the main enablers and barriers?
3. Remember your audience
Research agencies or organisations who will be responding to your brief might not know anything about your business. So, make sure you include enough background information in your brief to enable them to understand your needs and deliver effectively. And avoid use of jargon or acronyms which could lead to errors or confusion.
4. Structure your research brief
Before you start to populate your brief it’s worth considering all the information and sections you need to include, to structure your thinking and ensure you don’t miss anything important.
This might include some, or all, of the following:
- Background info
- Introduction
- Aims and objectives
- Research Question(s)
- Issues / Risks
- Methodology
- Timing and Outputs
- Project Management
5. Make it thorough, yet succinct
While it’s crucial to include all the relevant information to enable bidders to respond effectively, no one wants to read reams and reams of information. To avoid the key information getting lost in the details use annexes to add supplementary information which could be useful.
6. Consider how prescriptive you want to be on the methodology
The extent to which you want to specify the methodology will depend on the project you aim to deliver. There are benefits and risks to being overly prescriptive or offering free reign. If you outline in precise detail how you want the research to be conducted, you will hamper any original ideas from those invited to tender and might limit the impact on the research. Whereas, if you’re less prescriptive, allowing room for creativity, you risk not getting the project or results you want, or receiving proposals on a scale which you can’t resource.
Generally, it is useful to allow those invited to tender some scope to develop the methodology they propose to use. Exceptions might be where previous work has to be very precisely replicated or some other very precise commitment about the nature of findings has been given to stakeholders.
7. Define your timelines
As a minimum, you need to include when you want the project to start and end. But you should also include the timetable for procurement. When planning this, don’t underestimate the time and resource needed to run a procurement exercise. Make sure your evaluators are available when you need them and have enough time blocked out in their diary.
You’ll likely also want to include milestones for when you expect outputs to be delivered, such as deadlines for a draft report (providing opportunity for review and feedback) and the final report; allowing sufficient time between the two to enable your stakeholders to consult, for you to feedback and for the contractor to revise the report.
8. Set expectations on cost
You will most likely have budgetary constraints, with a figure for what you are prepared to spend. To save you and your bidders time, and to set realistic expectations, you should include an indication within your brief. This will prevent you receiving proposals which are way out of the ballpark; enable bidders to plan a project which delivers on (or at least close to) budget; and will prevent any nasty surprises, further down the line.
By following these tips you’ll be well on your way to creating an effective research brief which delivers on time and on budget.
If you’d like more guidance download our “step-by-step” guide, which includes a template and information for what to include in each section to ensure success.
Download the guide now.
- Scroll to top
- Light Dark Light Dark

Cart review
No products in the cart.
7 Essential Steps: How to Write a Research Brief That Gets Results
- Author Survey Point Team
- Published February 17, 2024

In this blog, we’ll explore seven essential steps to learn how to write a research brief that not only guides your project but also resonates with your audience. Research briefs are the unsung heroes of successful projects. Whether you’re a seasoned researcher or a newbie, crafting a well-structured brief can significantly impact the quality of your work.
Crafting a research brief that yields results is crucial. Explore the seven essential steps to write an effective research brief, ensuring success in your projects. Learn from experts and avoid common pitfalls.
Embarking on a research journey requires a well-crafted roadmap. A research brief serves as the compass, guiding you through the intricate terrain of data and insights. In this article, we will explore the seven essential steps to create a research brief that not only meets but exceeds expectations, ensuring the desired results.
Table of Contents
The Importance of Research Briefs
Why Research Briefs Matter
Research briefs are the cornerstone of successful projects. They set the tone, define objectives, and guide researchers toward meaningful outcomes. A well-structured brief not only saves time but also ensures the collected data aligns with the project goals.
How to Write a Research Brief: Understanding Your Objective
Defining Clear Research Goals
The first step in creating a research brief is understanding the project’s objective. Clearly define what you aim to achieve, ensuring every subsequent decision aligns with this overarching goal. Clarity at this stage is paramount.
Target Audience Analysis
Identifying and Understanding Your Audience
Knowing your audience is key to effective communication. Dive deep into demographic details, preferences, and behaviors. Tailor your research brief to resonate with the intended audience, enhancing its impact.
Crafting a Clear Research Question
Formulating Effective Research Queries
A well-defined research question is the compass that guides your entire project. Craft a question that is clear, concise, and directly aligns with your objectives. This foundational step ensures focused and purposeful research.
Literature Review
Building a Solid Foundation
Before venturing into uncharted territories, review existing literature. This not only provides valuable insights but also prevents redundancy. Acknowledge the work of others and identify gaps your research can fill.
Research Methodology
Choosing the Right Approach
Selecting the appropriate research methodology is pivotal. Whether qualitative or quantitative, the chosen approach should align with your objectives. Justify your choice, considering the nature of your research question.
How to Write a Research Brief: Data Collection
Ensuring Quality Information
Collecting data is where the rubber meets the road. Implement a robust data collection strategy, ensuring the information gathered is relevant, accurate, and aligns with your research question. Quality over quantity is the mantra.
Analysis and Interpretation
Extracting Meaningful Insights
Analysis is the heart of research. Interpret the collected data, drawing meaningful conclusions. Your insights should directly contribute to answering your research question and, consequently, achieving your objective.
Crafting a Compelling Title
Making Your Research Brief Stand Out
A captivating title is the first impression your research brief makes. It should be concise, intriguing, and reflective of the study’s essence. Crafting a compelling title sets the stage for your audience’s engagement.
The Power of Effective Communication
Conveying Your Message Clearly
Beyond the data, effective communication is crucial. Present your findings in a clear, concise manner. Utilize visuals, charts, and graphs to enhance understanding. Make your research brief accessible to a broad audience.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid
Mistakes That Can Derail Your Research
Avoiding common pitfalls is as important as following the right steps. Identify and steer clear of potential pitfalls that could compromise the integrity and effectiveness of your research brief. Learn from others’ mistakes to enhance your own success.
Real-life Success Stories
Learnings from Notable Research Briefs
Drawing inspiration from successful research briefs can provide valuable insights. Explore real-life success stories, understand the strategies employed, and apply these lessons to elevate the impact of your own research briefs.
How to Write a Research Brief: FAQ
Can I write multiple research questions? Certainly, but ensure they all align with your main objective. Quality over quantity is crucial in research.
How do I choose between qualitative and quantitative methods? Consider the nature of your research question. Qualitative methods delve into depth, while quantitative methods focus on breadth.
Is a literature review necessary for all research briefs? Yes, a literature review establishes the context for your research and prevents duplication of efforts.
How do I make my title captivating? A captivating title is concise, intriguing, and reflective of your study’s essence. Use language that sparks curiosity.
What are common pitfalls in research briefs? Common pitfalls include unclear objectives, biased data collection, and inadequate analysis. Be vigilant to avoid these pitfalls.
Can I use the same research methodology for every project? Adapt your research methodology to align with each project’s unique objectives. There’s no one-size-fits-all approach.
Wrapping Up the Research Brief Journey In conclusion, crafting a research brief that gets results requires a strategic approach. By following the seven essential steps outlined in this article, you can navigate the complexities of research with confidence. Remember, a well-prepared brief not only guides your journey but ensures the destination is one of success.
Survey Point Team
Related posts.

- Posted by Survey Point Team
How K12 Data Analytics Can Help You Achieve Your School’s Goals in 2024

Discover Why Data Science is Right for You: 7 Compelling Reasons to Dive In Today

Python vs R for Data Analysis: Which One Should Learn in 2024?

Reference management. Clean and simple.
Getting started with your research paper outline
Levels of organization for a research paper outline
First level of organization, second level of organization, third level of organization, fourth level of organization, tips for writing a research paper outline, research paper outline template, my research paper outline is complete: what are the next steps, frequently asked questions about a research paper outline, related articles.
The outline is the skeleton of your research paper. Simply start by writing down your thesis and the main ideas you wish to present. This will likely change as your research progresses; therefore, do not worry about being too specific in the early stages of writing your outline.
A research paper outline typically contains between two and four layers of organization. The first two layers are the most generalized. Each layer thereafter will contain the research you complete and presents more and more detailed information.
The levels are typically represented by a combination of Roman numerals, Arabic numerals, uppercase letters, lowercase letters but may include other symbols. Refer to the guidelines provided by your institution, as formatting is not universal and differs between universities, fields, and subjects. If you are writing the outline for yourself, you may choose any combination you prefer.
This is the most generalized level of information. Begin by numbering the introduction, each idea you will present, and the conclusion. The main ideas contain the bulk of your research paper 's information. Depending on your research, it may be chapters of a book for a literature review , a series of dates for a historical research paper, or the methods and results of a scientific paper.
I. Introduction
II. Main idea
III. Main idea
IV. Main idea
V. Conclusion
The second level consists of topics which support the introduction, main ideas, and the conclusion. Each main idea should have at least two supporting topics listed in the outline.
If your main idea does not have enough support, you should consider presenting another main idea in its place. This is where you should stop outlining if this is your first draft. Continue your research before adding to the next levels of organization.
- A. Background information
- B. Hypothesis or thesis
- A. Supporting topic
- B. Supporting topic
The third level of organization contains supporting information for the topics previously listed. By now, you should have completed enough research to add support for your ideas.
The Introduction and Main Ideas may contain information you discovered about the author, timeframe, or contents of a book for a literature review; the historical events leading up to the research topic for a historical research paper, or an explanation of the problem a scientific research paper intends to address.
- 1. Relevant history
- 2. Relevant history
- 1. The hypothesis or thesis clearly stated
- 1. A brief description of supporting information
- 2. A brief description of supporting information
The fourth level of organization contains the most detailed information such as quotes, references, observations, or specific data needed to support the main idea. It is not typical to have further levels of organization because the information contained here is the most specific.
- a) Quotes or references to another piece of literature
- b) Quotes or references to another piece of literature
Tip: The key to creating a useful outline is to be consistent in your headings, organization, and levels of specificity.
- Be Consistent : ensure every heading has a similar tone. State the topic or write short sentences for each heading but avoid doing both.
- Organize Information : Higher levels of organization are more generally stated and each supporting level becomes more specific. The introduction and conclusion will never be lower than the first level of organization.
- Build Support : Each main idea should have two or more supporting topics. If your research does not have enough information to support the main idea you are presenting, you should, in general, complete additional research or revise the outline.
By now, you should know the basic requirements to create an outline for your paper. With a content framework in place, you can now start writing your paper . To help you start right away, you can use one of our templates and adjust it to suit your needs.
After completing your outline, you should:
- Title your research paper . This is an iterative process and may change when you delve deeper into the topic.
- Begin writing your research paper draft . Continue researching to further build your outline and provide more information to support your hypothesis or thesis.
- Format your draft appropriately . MLA 8 and APA 7 formats have differences between their bibliography page, in-text citations, line spacing, and title.
- Finalize your citations and bibliography . Use a reference manager like Paperpile to organize and cite your research.
- Write the abstract, if required . An abstract will briefly state the information contained within the paper, results of the research, and the conclusion.
An outline is used to organize written ideas about a topic into a logical order. Outlines help us organize major topics, subtopics, and supporting details. Researchers benefit greatly from outlines while writing by addressing which topic to cover in what order.
The most basic outline format consists of: an introduction, a minimum of three topic paragraphs, and a conclusion.
You should make an outline before starting to write your research paper. This will help you organize the main ideas and arguments you want to present in your topic.
- Consistency: ensure every heading has a similar tone. State the topic or write short sentences for each heading but avoid doing both.
- Organization : Higher levels of organization are more generally stated and each supporting level becomes more specific. The introduction and conclusion will never be lower than the first level of organization.
- Support : Each main idea should have two or more supporting topics. If your research does not have enough information to support the main idea you are presenting, you should, in general, complete additional research or revise the outline.

How To Write A Research Paper
Step-By-Step Tutorial With Examples + FREE Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Expert Reviewer: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | March 2024
For many students, crafting a strong research paper from scratch can feel like a daunting task – and rightly so! In this post, we’ll unpack what a research paper is, what it needs to do , and how to write one – in three easy steps. 🙂
Overview: Writing A Research Paper
What (exactly) is a research paper.
- How to write a research paper
- Stage 1 : Topic & literature search
- Stage 2 : Structure & outline
- Stage 3 : Iterative writing
- Key takeaways
Let’s start by asking the most important question, “ What is a research paper? ”.
Simply put, a research paper is a scholarly written work where the writer (that’s you!) answers a specific question (this is called a research question ) through evidence-based arguments . Evidence-based is the keyword here. In other words, a research paper is different from an essay or other writing assignments that draw from the writer’s personal opinions or experiences. With a research paper, it’s all about building your arguments based on evidence (we’ll talk more about that evidence a little later).
Now, it’s worth noting that there are many different types of research papers , including analytical papers (the type I just described), argumentative papers, and interpretative papers. Here, we’ll focus on analytical papers , as these are some of the most common – but if you’re keen to learn about other types of research papers, be sure to check out the rest of the blog .
With that basic foundation laid, let’s get down to business and look at how to write a research paper .

Overview: The 3-Stage Process
While there are, of course, many potential approaches you can take to write a research paper, there are typically three stages to the writing process. So, in this tutorial, we’ll present a straightforward three-step process that we use when working with students at Grad Coach.
These three steps are:
- Finding a research topic and reviewing the existing literature
- Developing a provisional structure and outline for your paper, and
- Writing up your initial draft and then refining it iteratively
Let’s dig into each of these.
Need a helping hand?
Step 1: Find a topic and review the literature
As we mentioned earlier, in a research paper, you, as the researcher, will try to answer a question . More specifically, that’s called a research question , and it sets the direction of your entire paper. What’s important to understand though is that you’ll need to answer that research question with the help of high-quality sources – for example, journal articles, government reports, case studies, and so on. We’ll circle back to this in a minute.
The first stage of the research process is deciding on what your research question will be and then reviewing the existing literature (in other words, past studies and papers) to see what they say about that specific research question. In some cases, your professor may provide you with a predetermined research question (or set of questions). However, in many cases, you’ll need to find your own research question within a certain topic area.
Finding a strong research question hinges on identifying a meaningful research gap – in other words, an area that’s lacking in existing research. There’s a lot to unpack here, so if you wanna learn more, check out the plain-language explainer video below.
Once you’ve figured out which question (or questions) you’ll attempt to answer in your research paper, you’ll need to do a deep dive into the existing literature – this is called a “ literature search ”. Again, there are many ways to go about this, but your most likely starting point will be Google Scholar .
If you’re new to Google Scholar, think of it as Google for the academic world. You can start by simply entering a few different keywords that are relevant to your research question and it will then present a host of articles for you to review. What you want to pay close attention to here is the number of citations for each paper – the more citations a paper has, the more credible it is (generally speaking – there are some exceptions, of course).

Ideally, what you’re looking for are well-cited papers that are highly relevant to your topic. That said, keep in mind that citations are a cumulative metric , so older papers will often have more citations than newer papers – just because they’ve been around for longer. So, don’t fixate on this metric in isolation – relevance and recency are also very important.
Beyond Google Scholar, you’ll also definitely want to check out academic databases and aggregators such as Science Direct, PubMed, JStor and so on. These will often overlap with the results that you find in Google Scholar, but they can also reveal some hidden gems – so, be sure to check them out.
Once you’ve worked your way through all the literature, you’ll want to catalogue all this information in some sort of spreadsheet so that you can easily recall who said what, when and within what context. If you’d like, we’ve got a free literature spreadsheet that helps you do exactly that.

Step 2: Develop a structure and outline
With your research question pinned down and your literature digested and catalogued, it’s time to move on to planning your actual research paper .
It might sound obvious, but it’s really important to have some sort of rough outline in place before you start writing your paper. So often, we see students eagerly rushing into the writing phase, only to land up with a disjointed research paper that rambles on in multiple
Now, the secret here is to not get caught up in the fine details . Realistically, all you need at this stage is a bullet-point list that describes (in broad strokes) what you’ll discuss and in what order. It’s also useful to remember that you’re not glued to this outline – in all likelihood, you’ll chop and change some sections once you start writing, and that’s perfectly okay. What’s important is that you have some sort of roadmap in place from the start.

At this stage you might be wondering, “ But how should I structure my research paper? ”. Well, there’s no one-size-fits-all solution here, but in general, a research paper will consist of a few relatively standardised components:
- Introduction
- Literature review
- Methodology
Let’s take a look at each of these.
First up is the introduction section . As the name suggests, the purpose of the introduction is to set the scene for your research paper. There are usually (at least) four ingredients that go into this section – these are the background to the topic, the research problem and resultant research question , and the justification or rationale. If you’re interested, the video below unpacks the introduction section in more detail.
The next section of your research paper will typically be your literature review . Remember all that literature you worked through earlier? Well, this is where you’ll present your interpretation of all that content . You’ll do this by writing about recent trends, developments, and arguments within the literature – but more specifically, those that are relevant to your research question . The literature review can oftentimes seem a little daunting, even to seasoned researchers, so be sure to check out our extensive collection of literature review content here .
With the introduction and lit review out of the way, the next section of your paper is the research methodology . In a nutshell, the methodology section should describe to your reader what you did (beyond just reviewing the existing literature) to answer your research question. For example, what data did you collect, how did you collect that data, how did you analyse that data and so on? For each choice, you’ll also need to justify why you chose to do it that way, and what the strengths and weaknesses of your approach were.
Now, it’s worth mentioning that for some research papers, this aspect of the project may be a lot simpler . For example, you may only need to draw on secondary sources (in other words, existing data sets). In some cases, you may just be asked to draw your conclusions from the literature search itself (in other words, there may be no data analysis at all). But, if you are required to collect and analyse data, you’ll need to pay a lot of attention to the methodology section. The video below provides an example of what the methodology section might look like.
By this stage of your paper, you will have explained what your research question is, what the existing literature has to say about that question, and how you analysed additional data to try to answer your question. So, the natural next step is to present your analysis of that data . This section is usually called the “results” or “analysis” section and this is where you’ll showcase your findings.
Depending on your school’s requirements, you may need to present and interpret the data in one section – or you might split the presentation and the interpretation into two sections. In the latter case, your “results” section will just describe the data, and the “discussion” is where you’ll interpret that data and explicitly link your analysis back to your research question. If you’re not sure which approach to take, check in with your professor or take a look at past papers to see what the norms are for your programme.
Alright – once you’ve presented and discussed your results, it’s time to wrap it up . This usually takes the form of the “ conclusion ” section. In the conclusion, you’ll need to highlight the key takeaways from your study and close the loop by explicitly answering your research question. Again, the exact requirements here will vary depending on your programme (and you may not even need a conclusion section at all) – so be sure to check with your professor if you’re unsure.
Step 3: Write and refine
Finally, it’s time to get writing. All too often though, students hit a brick wall right about here… So, how do you avoid this happening to you?
Well, there’s a lot to be said when it comes to writing a research paper (or any sort of academic piece), but we’ll share three practical tips to help you get started.
First and foremost , it’s essential to approach your writing as an iterative process. In other words, you need to start with a really messy first draft and then polish it over multiple rounds of editing. Don’t waste your time trying to write a perfect research paper in one go. Instead, take the pressure off yourself by adopting an iterative approach.
Secondly , it’s important to always lean towards critical writing , rather than descriptive writing. What does this mean? Well, at the simplest level, descriptive writing focuses on the “ what ”, while critical writing digs into the “ so what ” – in other words, the implications. If you’re not familiar with these two types of writing, don’t worry! You can find a plain-language explanation here.
Last but not least, you’ll need to get your referencing right. Specifically, you’ll need to provide credible, correctly formatted citations for the statements you make. We see students making referencing mistakes all the time and it costs them dearly. The good news is that you can easily avoid this by using a simple reference manager . If you don’t have one, check out our video about Mendeley, an easy (and free) reference management tool that you can start using today.
Recap: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered a lot of ground here. To recap, the three steps to writing a high-quality research paper are:
- To choose a research question and review the literature
- To plan your paper structure and draft an outline
- To take an iterative approach to writing, focusing on critical writing and strong referencing
Remember, this is just a b ig-picture overview of the research paper development process and there’s a lot more nuance to unpack. So, be sure to grab a copy of our free research paper template to learn more about how to write a research paper.
You Might Also Like:

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Paper – Structure, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Paper
Definition:
Research Paper is a written document that presents the author’s original research, analysis, and interpretation of a specific topic or issue.
It is typically based on Empirical Evidence, and may involve qualitative or quantitative research methods, or a combination of both. The purpose of a research paper is to contribute new knowledge or insights to a particular field of study, and to demonstrate the author’s understanding of the existing literature and theories related to the topic.
Structure of Research Paper
The structure of a research paper typically follows a standard format, consisting of several sections that convey specific information about the research study. The following is a detailed explanation of the structure of a research paper:
The title page contains the title of the paper, the name(s) of the author(s), and the affiliation(s) of the author(s). It also includes the date of submission and possibly, the name of the journal or conference where the paper is to be published.
The abstract is a brief summary of the research paper, typically ranging from 100 to 250 words. It should include the research question, the methods used, the key findings, and the implications of the results. The abstract should be written in a concise and clear manner to allow readers to quickly grasp the essence of the research.
Introduction
The introduction section of a research paper provides background information about the research problem, the research question, and the research objectives. It also outlines the significance of the research, the research gap that it aims to fill, and the approach taken to address the research question. Finally, the introduction section ends with a clear statement of the research hypothesis or research question.
Literature Review
The literature review section of a research paper provides an overview of the existing literature on the topic of study. It includes a critical analysis and synthesis of the literature, highlighting the key concepts, themes, and debates. The literature review should also demonstrate the research gap and how the current study seeks to address it.
The methods section of a research paper describes the research design, the sample selection, the data collection and analysis procedures, and the statistical methods used to analyze the data. This section should provide sufficient detail for other researchers to replicate the study.
The results section presents the findings of the research, using tables, graphs, and figures to illustrate the data. The findings should be presented in a clear and concise manner, with reference to the research question and hypothesis.
The discussion section of a research paper interprets the findings and discusses their implications for the research question, the literature review, and the field of study. It should also address the limitations of the study and suggest future research directions.
The conclusion section summarizes the main findings of the study, restates the research question and hypothesis, and provides a final reflection on the significance of the research.
The references section provides a list of all the sources cited in the paper, following a specific citation style such as APA, MLA or Chicago.
How to Write Research Paper
You can write Research Paper by the following guide:
- Choose a Topic: The first step is to select a topic that interests you and is relevant to your field of study. Brainstorm ideas and narrow down to a research question that is specific and researchable.
- Conduct a Literature Review: The literature review helps you identify the gap in the existing research and provides a basis for your research question. It also helps you to develop a theoretical framework and research hypothesis.
- Develop a Thesis Statement : The thesis statement is the main argument of your research paper. It should be clear, concise and specific to your research question.
- Plan your Research: Develop a research plan that outlines the methods, data sources, and data analysis procedures. This will help you to collect and analyze data effectively.
- Collect and Analyze Data: Collect data using various methods such as surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments. Analyze data using statistical tools or other qualitative methods.
- Organize your Paper : Organize your paper into sections such as Introduction, Literature Review, Methods, Results, Discussion, and Conclusion. Ensure that each section is coherent and follows a logical flow.
- Write your Paper : Start by writing the introduction, followed by the literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. Ensure that your writing is clear, concise, and follows the required formatting and citation styles.
- Edit and Proofread your Paper: Review your paper for grammar and spelling errors, and ensure that it is well-structured and easy to read. Ask someone else to review your paper to get feedback and suggestions for improvement.
- Cite your Sources: Ensure that you properly cite all sources used in your research paper. This is essential for giving credit to the original authors and avoiding plagiarism.
Research Paper Example
Note : The below example research paper is for illustrative purposes only and is not an actual research paper. Actual research papers may have different structures, contents, and formats depending on the field of study, research question, data collection and analysis methods, and other factors. Students should always consult with their professors or supervisors for specific guidelines and expectations for their research papers.
Research Paper Example sample for Students:
Title: The Impact of Social Media on Mental Health among Young Adults
Abstract: This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults. A literature review was conducted to examine the existing research on the topic. A survey was then administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO (Fear of Missing Out) are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Introduction: Social media has become an integral part of modern life, particularly among young adults. While social media has many benefits, including increased communication and social connectivity, it has also been associated with negative outcomes, such as addiction, cyberbullying, and mental health problems. This study aims to investigate the impact of social media use on the mental health of young adults.
Literature Review: The literature review highlights the existing research on the impact of social media use on mental health. The review shows that social media use is associated with depression, anxiety, stress, and other mental health problems. The review also identifies the factors that contribute to the negative impact of social media, including social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Methods : A survey was administered to 200 university students to collect data on their social media use, mental health status, and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. The survey included questions on social media use, mental health status (measured using the DASS-21), and perceived impact of social media on their mental health. Data were analyzed using descriptive statistics and regression analysis.
Results : The results showed that social media use is positively associated with depression, anxiety, and stress. The study also found that social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO are significant predictors of mental health problems among young adults.
Discussion : The study’s findings suggest that social media use has a negative impact on the mental health of young adults. The study highlights the need for interventions that address the factors contributing to the negative impact of social media, such as social comparison, cyberbullying, and FOMO.
Conclusion : In conclusion, social media use has a significant impact on the mental health of young adults. The study’s findings underscore the need for interventions that promote healthy social media use and address the negative outcomes associated with social media use. Future research can explore the effectiveness of interventions aimed at reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health. Additionally, longitudinal studies can investigate the long-term effects of social media use on mental health.
Limitations : The study has some limitations, including the use of self-report measures and a cross-sectional design. The use of self-report measures may result in biased responses, and a cross-sectional design limits the ability to establish causality.
Implications: The study’s findings have implications for mental health professionals, educators, and policymakers. Mental health professionals can use the findings to develop interventions that address the negative impact of social media use on mental health. Educators can incorporate social media literacy into their curriculum to promote healthy social media use among young adults. Policymakers can use the findings to develop policies that protect young adults from the negative outcomes associated with social media use.
References :
- Twenge, J. M., & Campbell, W. K. (2019). Associations between screen time and lower psychological well-being among children and adolescents: Evidence from a population-based study. Preventive medicine reports, 15, 100918.
- Primack, B. A., Shensa, A., Escobar-Viera, C. G., Barrett, E. L., Sidani, J. E., Colditz, J. B., … & James, A. E. (2017). Use of multiple social media platforms and symptoms of depression and anxiety: A nationally-representative study among US young adults. Computers in Human Behavior, 69, 1-9.
- Van der Meer, T. G., & Verhoeven, J. W. (2017). Social media and its impact on academic performance of students. Journal of Information Technology Education: Research, 16, 383-398.
Appendix : The survey used in this study is provided below.
Social Media and Mental Health Survey
- How often do you use social media per day?
- Less than 30 minutes
- 30 minutes to 1 hour
- 1 to 2 hours
- 2 to 4 hours
- More than 4 hours
- Which social media platforms do you use?
- Others (Please specify)
- How often do you experience the following on social media?
- Social comparison (comparing yourself to others)
- Cyberbullying
- Fear of Missing Out (FOMO)
- Have you ever experienced any of the following mental health problems in the past month?
- Do you think social media use has a positive or negative impact on your mental health?
- Very positive
- Somewhat positive
- Somewhat negative
- Very negative
- In your opinion, which factors contribute to the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Social comparison
- In your opinion, what interventions could be effective in reducing the negative impact of social media on mental health?
- Education on healthy social media use
- Counseling for mental health problems caused by social media
- Social media detox programs
- Regulation of social media use
Thank you for your participation!
Applications of Research Paper
Research papers have several applications in various fields, including:
- Advancing knowledge: Research papers contribute to the advancement of knowledge by generating new insights, theories, and findings that can inform future research and practice. They help to answer important questions, clarify existing knowledge, and identify areas that require further investigation.
- Informing policy: Research papers can inform policy decisions by providing evidence-based recommendations for policymakers. They can help to identify gaps in current policies, evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, and inform the development of new policies and regulations.
- Improving practice: Research papers can improve practice by providing evidence-based guidance for professionals in various fields, including medicine, education, business, and psychology. They can inform the development of best practices, guidelines, and standards of care that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- Educating students : Research papers are often used as teaching tools in universities and colleges to educate students about research methods, data analysis, and academic writing. They help students to develop critical thinking skills, research skills, and communication skills that are essential for success in many careers.
- Fostering collaboration: Research papers can foster collaboration among researchers, practitioners, and policymakers by providing a platform for sharing knowledge and ideas. They can facilitate interdisciplinary collaborations and partnerships that can lead to innovative solutions to complex problems.
When to Write Research Paper
Research papers are typically written when a person has completed a research project or when they have conducted a study and have obtained data or findings that they want to share with the academic or professional community. Research papers are usually written in academic settings, such as universities, but they can also be written in professional settings, such as research organizations, government agencies, or private companies.
Here are some common situations where a person might need to write a research paper:
- For academic purposes: Students in universities and colleges are often required to write research papers as part of their coursework, particularly in the social sciences, natural sciences, and humanities. Writing research papers helps students to develop research skills, critical thinking skills, and academic writing skills.
- For publication: Researchers often write research papers to publish their findings in academic journals or to present their work at academic conferences. Publishing research papers is an important way to disseminate research findings to the academic community and to establish oneself as an expert in a particular field.
- To inform policy or practice : Researchers may write research papers to inform policy decisions or to improve practice in various fields. Research findings can be used to inform the development of policies, guidelines, and best practices that can improve outcomes for individuals and organizations.
- To share new insights or ideas: Researchers may write research papers to share new insights or ideas with the academic or professional community. They may present new theories, propose new research methods, or challenge existing paradigms in their field.
Purpose of Research Paper
The purpose of a research paper is to present the results of a study or investigation in a clear, concise, and structured manner. Research papers are written to communicate new knowledge, ideas, or findings to a specific audience, such as researchers, scholars, practitioners, or policymakers. The primary purposes of a research paper are:
- To contribute to the body of knowledge : Research papers aim to add new knowledge or insights to a particular field or discipline. They do this by reporting the results of empirical studies, reviewing and synthesizing existing literature, proposing new theories, or providing new perspectives on a topic.
- To inform or persuade: Research papers are written to inform or persuade the reader about a particular issue, topic, or phenomenon. They present evidence and arguments to support their claims and seek to persuade the reader of the validity of their findings or recommendations.
- To advance the field: Research papers seek to advance the field or discipline by identifying gaps in knowledge, proposing new research questions or approaches, or challenging existing assumptions or paradigms. They aim to contribute to ongoing debates and discussions within a field and to stimulate further research and inquiry.
- To demonstrate research skills: Research papers demonstrate the author’s research skills, including their ability to design and conduct a study, collect and analyze data, and interpret and communicate findings. They also demonstrate the author’s ability to critically evaluate existing literature, synthesize information from multiple sources, and write in a clear and structured manner.
Characteristics of Research Paper
Research papers have several characteristics that distinguish them from other forms of academic or professional writing. Here are some common characteristics of research papers:
- Evidence-based: Research papers are based on empirical evidence, which is collected through rigorous research methods such as experiments, surveys, observations, or interviews. They rely on objective data and facts to support their claims and conclusions.
- Structured and organized: Research papers have a clear and logical structure, with sections such as introduction, literature review, methods, results, discussion, and conclusion. They are organized in a way that helps the reader to follow the argument and understand the findings.
- Formal and objective: Research papers are written in a formal and objective tone, with an emphasis on clarity, precision, and accuracy. They avoid subjective language or personal opinions and instead rely on objective data and analysis to support their arguments.
- Citations and references: Research papers include citations and references to acknowledge the sources of information and ideas used in the paper. They use a specific citation style, such as APA, MLA, or Chicago, to ensure consistency and accuracy.
- Peer-reviewed: Research papers are often peer-reviewed, which means they are evaluated by other experts in the field before they are published. Peer-review ensures that the research is of high quality, meets ethical standards, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge in the field.
- Objective and unbiased: Research papers strive to be objective and unbiased in their presentation of the findings. They avoid personal biases or preconceptions and instead rely on the data and analysis to draw conclusions.
Advantages of Research Paper
Research papers have many advantages, both for the individual researcher and for the broader academic and professional community. Here are some advantages of research papers:
- Contribution to knowledge: Research papers contribute to the body of knowledge in a particular field or discipline. They add new information, insights, and perspectives to existing literature and help advance the understanding of a particular phenomenon or issue.
- Opportunity for intellectual growth: Research papers provide an opportunity for intellectual growth for the researcher. They require critical thinking, problem-solving, and creativity, which can help develop the researcher’s skills and knowledge.
- Career advancement: Research papers can help advance the researcher’s career by demonstrating their expertise and contributions to the field. They can also lead to new research opportunities, collaborations, and funding.
- Academic recognition: Research papers can lead to academic recognition in the form of awards, grants, or invitations to speak at conferences or events. They can also contribute to the researcher’s reputation and standing in the field.
- Impact on policy and practice: Research papers can have a significant impact on policy and practice. They can inform policy decisions, guide practice, and lead to changes in laws, regulations, or procedures.
- Advancement of society: Research papers can contribute to the advancement of society by addressing important issues, identifying solutions to problems, and promoting social justice and equality.
Limitations of Research Paper
Research papers also have some limitations that should be considered when interpreting their findings or implications. Here are some common limitations of research papers:
- Limited generalizability: Research findings may not be generalizable to other populations, settings, or contexts. Studies often use specific samples or conditions that may not reflect the broader population or real-world situations.
- Potential for bias : Research papers may be biased due to factors such as sample selection, measurement errors, or researcher biases. It is important to evaluate the quality of the research design and methods used to ensure that the findings are valid and reliable.
- Ethical concerns: Research papers may raise ethical concerns, such as the use of vulnerable populations or invasive procedures. Researchers must adhere to ethical guidelines and obtain informed consent from participants to ensure that the research is conducted in a responsible and respectful manner.
- Limitations of methodology: Research papers may be limited by the methodology used to collect and analyze data. For example, certain research methods may not capture the complexity or nuance of a particular phenomenon, or may not be appropriate for certain research questions.
- Publication bias: Research papers may be subject to publication bias, where positive or significant findings are more likely to be published than negative or non-significant findings. This can skew the overall findings of a particular area of research.
- Time and resource constraints: Research papers may be limited by time and resource constraints, which can affect the quality and scope of the research. Researchers may not have access to certain data or resources, or may be unable to conduct long-term studies due to practical limitations.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

How to Cite Research Paper – All Formats and...

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Paper Format – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples
Marketing91
Research brief: Meaning, Components, Importance & Ways to Prepare
June 12, 2023 | By Hitesh Bhasin | Filed Under: Marketing
Have you ever faced a situation where a researcher has not exactly given the results that you require? Have you ever discussed research as what you want precisely and been disappointed to find that there is a disparity in your expectation and the outcomes? This is because of a failure in communication , that is particular an insufficient brief.
This is where we exactly wish to discuss research brief.
A research brief is a statement that comes from the sponsor, who sets the objectives and background. This is to enable the researcher to plan the research and conduct an appropriate study on it. Research Brief can be as good as a market research study and is very important to a researcher.
It provides good insight and influences on the choice of methodology to be adopted in the research. It also provides an objective to which the project links itself.
It is a short and non-technical summary of a discussion paper that is purely intended for decision-makers with a concentration on the paper’s policy-relevant findings.
Table of Contents
Components of a Research Brief
Some sponsors deliver the brief orally by developing many detail points at the time of initial discussion with the researcher. On the other hand, the brief can also be completely thought through and committed to a paper.
This is very important when many research agencies need to submit proposals. Whether the research brief is oral or written, it should pay attention to the following points:
- Problem Background – This is a short record of the events which has actually led to the study. This provides an insight into the researcher a better viewpoint and understanding of the objective of the project.
- Problem Description – The researcher requires details in depth to perform the research. When the scope of the research is described properly, the research process gets easier. It becomes helpful for the sponsor to monitor the progress of the research.
- Market Analysis – The researcher needs to know the geographical areas of the research. Hence this should be part of the research brief.
- Objective Statement – The object of the researcher should be put statement. The researcher should gather the details from the sponsor and then provide a view of what has to be achieved.
- Time and Budget – The research brief should mention the time and budget constraints of the research.
Importance of Research Brief

Now, why is research brief important? It is like the way you set a foundation for a building; research brief provides a strong foundation for the research process.
Writing a research brief is important to the success of any market research project. However, it can be difficult to craft the perfect brief that meets the necessity of both the client and the researcher but eventually leads to the desired outcomes.
It helps a researcher to identify a problem to be researched, the exact background of the problem, the required details to address the problem, time and budget constraints within which the research is supposed to be designed.
Example of Research Brief
Keeping the above points in mind, let us take a small example of the way to write a market research brief.
To write a market research brief, it clarifies the research requirement and also makes sure that the ideas are well articulated. It helps to write a better research proposal , conduct user research, and achieve the desired outcome.
Background:
Describe the problem that is required to solve. Include applicable background and the challenge during the research.
Business and Project Objectives:
Explain the business objectives. For example: to increase sales /profit. Try to be specific as you can.
Also, describe the purpose of research and the expected outcomes. What is the decision that you require to make?
Market Objectives:
Market research objective typically follows from the above two objectives. Hence you will need to summarise the aim and information of the research. This will help to mention the questions required for answering.
Stakeholders:
Here, you will need to consider the participant who will sign-off and act on the research outcomes listed.
Research Methods, scope, sample, and guidelines:
Here, you will explain what is required. This will help you to focus on what is important and also have a piece of knowledge of the research investment. Here, more focus is given on the scope of the work and type of research . The inputs and the sample are also analyzed.
Research outcomes:
Here, you will require to define the delivery part of the research.
Ways to prepare Research Brief

Having discussed the basic of research brief, the following points will give you a brief idea of the ways to prepare yourself to write an effective research brief.
- Start with a summary of the current situation. Also, define in clear words as what you are already aware of. It would be more useful if you could include more details on your thought about the responsibility for the project on you and the research agency.
- After a summary, set up the business and research objectives . For business objectives, you need to mention the overall strategy and what is the importance of the current research. For research objectives, list the issues and topics that are likely to discover. List the problems to solve. Based on the research agency design, define clearly the business and research objectives. Having a clear objective will help you to assess the quality and also focus on the research agency’s report.
- Next, you may suggest about the ways about data collection . You can decide on a suitable research methodology that you think will be best fit the project.
- List what the outcomes of the project and the deliverables are. Like for example, you might just want to advise on survey design . For this, statistically robust data would be ideal. Or sometimes, you might write a full report with data, interpretation, recommendations, etc. Whatever it is, be clear as what is required. Suggest a timetable and mention the deadline to receive proposals and other deliverables.

Research Brief Template

Given below the template for research brief:
Research Brief: Project Name
#1 background.
In this area, give the background of the research brief.
#2 Business objectives
In this area, define the business objectives. Ideally, for a better understanding and readability, it would be good if the points are bulleted.
#3 Marketing objectives
In this area, type your marketing objectives. In case you have any other kind of objectives apart from marketing, you could change the section title.
In this area, define the research target here. Here, name all the target groups that will be a part of the research and the reason for it. Capture any other applicable details of the target group .
In this area, mention the Budget information. Mentioning a range of budget is fine. Also, indicate an upper limit in case you have any.
In this area, mention the timeline of the research. The approximate time as when this work would be over. Also, when can you provide the final analysis?
#6 Deliverables
In this area, mention the report requirements. For example, whether a detail report is required or just a presentation.
#7 Contact information
In this area, mention the contact information for questions or clarification. It could be Client company name or Individual name, title, e-mail id, phone number, and mailing address.
Liked this post? Check out the complete series on Market research
Related posts:
- What is Brand Brief? Components of Brand Brief and Examples
- Causal Research – Meaning, Explanation, Examples, Components
- What is a Design Brief and How to Write it in 9 Easy Steps?
- Qualitative Research: Meaning, and Features of Qualitative Research
- Advertising Message – Definition, Meaning, Importance and Components
- Research Ethics – Importance and Principles of Ethics in Research
- Market Space – Definition, Meaning, Characteristics, Components
- Sales Agreement – Meaning, Components and Samples
- How to Write Research Proposal? Research Proposal Format
- 7 Key Differences between Research Method and Research Methodology
About Hitesh Bhasin
Hitesh Bhasin is the CEO of Marketing91 and has over a decade of experience in the marketing field. He is an accomplished author of thousands of insightful articles, including in-depth analyses of brands and companies. Holding an MBA in Marketing, Hitesh manages several offline ventures, where he applies all the concepts of Marketing that he writes about.
All Knowledge Banks (Hub Pages)
- Marketing Hub
- Management Hub
- Marketing Strategy
- Advertising Hub
- Branding Hub
- Market Research
- Small Business Marketing
- Sales and Selling
- Marketing Careers
- Internet Marketing
- Business Model of Brands
- Marketing Mix of Brands
- Brand Competitors
- Strategy of Brands
- SWOT of Brands
- Customer Management
- Top 10 Lists
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- About Marketing91
- Marketing91 Team
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Terms of Use
- Editorial Policy
WE WRITE ON
- Digital Marketing
- Human Resources
- Operations Management
- Marketing News
- Marketing mix's
- Competitors
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game New
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Official Writing
How to Write a Briefing Paper
Last Updated: December 30, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Michael R. Lewis . Michael R. Lewis is a retired corporate executive, entrepreneur, and investment advisor in Texas. He has over 40 years of experience in business and finance, including as a Vice President for Blue Cross Blue Shield of Texas. He has a BBA in Industrial Management from the University of Texas at Austin. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 580,481 times.
A briefing paper outlines a particular issue and its background, usually for a government official or other policy maker. These decision-makers have to make hard choices about many different topics every day, and they do not have time to research each one in-depth. A briefing paper helps bring a single issue to someone's attention and fills in key details he or she needs to know. It then proposes solutions and recommends improvements. Knowing how to write a briefing paper is a useful skill for students, business professionals, politicians and community activists. A persuasive briefing paper is concise, well-organized and covers the most important and relevant facts and solutions.
Mapping Out and Setting Up Your Paper

- Determining the scope of the briefing paper is important because it will allow the reader to know exactly what information is covered and what is not.

- Who will read this paper? Government officials? Business executives? Journalists? Some combination of these?
- How much does the audience already know about this issue? Do they know anything at all? What does the audience need to know?
- What authority does the audience have over the issue? What changes are they capable of making?

- Because a briefing paper is typically only a page or two long, it needs to be condensed. Policy makers are very busy, and yours is not the only issue on their plates. There's no room for unnecessary information or long-winded explanations. Decide on your key points in advance to craft a concise briefing paper.

- A template can help you organize your thoughts and more quickly craft a briefing paper.

- The name corresponds to the person to whom the briefing paper is addressed.
- The date corresponds to the date on which the paper was submitted.
- The subject line should describe in a few words the main topic of the briefing paper, such as "The Prevalence of Bullying in the North County School District." This lets the reader know, without even skimming the document, the issue that will be addressed.

- For a very busy reader, the summary offers the key points in advance, thus allowing skimming over of the rest of the document.
- A well-crafted briefing paper is often concise enough that this section is unnecessary. However, for issues that require immediate action, this can be a way to highlight the urgency of the paper by clearly indicating the deadline within the summary.
- The summary should be no more than three to four bullet points.
Describing the Issue

- For example, you might write something like: "Violent incidents related to bullying are on the rise in schools within the North County School District. Current disciplinary policies may not be adequate for addressing this issue."

- This section should include the information necessary for the reader to make a decision about this issue. Information not necessary for this purpose, however interesting it may be, should be excluded.
- If you haven't already, do some research before writing this section. You want the information in section to be as accurate, specific, and up to date as possible. [6] X Research source
- When necessary, translate the information for your audience to make this section clear and simple. Avoid jargon, technical language, or information that isn't of central concern to the audience.
- Use statistics and data as appropriate, but explain things in terms that your audience will be able to quickly and easily understand.

- You may, however, choose to discuss the pros and cons of various proposed or current actions, highlighting the strengths and weaknesses of each. [7] X Research source
Offering Conclusions and Recommendations

- Try to link the issue directly to the reader's self-interest to make your paper more persuasive.
- For example, you might say something like: "Bullying related incidents are leading parents to consider private school options. They are linked to lower test scores and graduation rates, making our schools appear less effective in the eyes of the community. They reduce our district's opportunities to supplement funding with federal and private grants."

- Some briefing papers will outline the proposed solution(s) in a section labeled "recommendations," but some writers prefer "next steps," believing this has a softer feel that is less presumptuous or aggressive. [9] X Research source Remember that the reader will be the one who makes the final decision on this issue, not you.
- This section need not be "balanced" as the background/considerations section was. This can be a place for you to express your view as to what should be done.
- It should be noted, however, that you do not have to endorse a particular solution. You can also just lay out some options with their pros and cons, and simply urge the reader to consider these choices and take action of some kind to address the issue. You don't necessarily specify which action would be most appropriate.

- Make sure any solution you propose is clear and directly related to the issue as you have outlined it. For example, imagine you have highlighted the lack of bullying prevention programs in your previous section. Here, it will make sense to suggest such a program, and perhaps point to their effectiveness at other schools. If prevention programs haven't already come up, a solution like this may feel like it came out of nowhere.
Editing the Paper

- Look for information that is off topic or less important and remove that material, especially if it doesn't relate to the solution(s) you offer.
- By the same token, make sure there aren't key pieces of information missing that are necessary to make your argument clear and convincing. You may need to swap out one piece of information for another.
- Try to put yourself in the shoes of a politician or bureaucrat as you edit. Think about how many pieces of information these individuals receive every day. Don't contribute to the problem. Be part of the solution by providing the information necessary to make a decision--no more, no less.

- Especially if you are an expert on a topic you are writing about, it's easy to forget, at least momentarily, that language that is every day for you may be difficult for others to understand.
- Keep in mind that it is likewise not always immediately obvious why something is important to people who aren't already familiar with a topic. Policy makers usually can't be experts on every topic they have to make decisions about.

- A paper with spelling, style, or grammatical errors may be taken less seriously by your reader. You may be doing more harm than good by submitting such a paper, as it may discredit your perspective.
Sample Briefing Papers

Expert Q&A
- Keep in mind that while your paper may be addressed to a certain person, others may read it also--staffers, colleagues, and even the media. This is a good reason to keep your writing as accessible as possible, even if your intended reader has some knowledge of the topic. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0
- Review briefing papers written by prominent leaders and accomplished professors to learn from their persuasive approaches. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 0

You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://www.writingforresults.net/classic.pdf
- ↑ http://www.edu.gov.mb.ca/k12/cur/socstud/frame_found_sr2/tns/tn-21.pdf
- ↑ https://mason.gmu.edu/~pnorton/hypermedia/briefing.htm
- ↑ http://grammar.yourdictionary.com/grammar-rules-and-tips/tips-for-writing-a-briefing-document.html
About This Article

To write a briefing paper, start with an opening section entitled "Purpose" that summarizes the issue. Next, create a section called "Background" and outline the key facts about the issue, focusing on recent developments and the current state of the situation. Wrap up the paper with a "Conclusion" section that makes it clear why the issue is important. Try to link the issue directly to the reader's self-interest to make the paper more persuasive! For helpful tips on editing briefing papers, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Francis Lelngei
Dec 31, 2018
Did this article help you?
Kealoha Soriano
Feb 3, 2017
Beth Villarreal
May 22, 2017
Mar 15, 2017
Alexandru Ilia
Dec 27, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
wikiHow Tech Help Pro:
Level up your tech skills and stay ahead of the curve
Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature
How to Write a Research Paper Introduction (with Examples)

The research paper introduction section, along with the Title and Abstract, can be considered the face of any research paper. The following article is intended to guide you in organizing and writing the research paper introduction for a quality academic article or dissertation.
The research paper introduction aims to present the topic to the reader. A study will only be accepted for publishing if you can ascertain that the available literature cannot answer your research question. So it is important to ensure that you have read important studies on that particular topic, especially those within the last five to ten years, and that they are properly referenced in this section. 1 What should be included in the research paper introduction is decided by what you want to tell readers about the reason behind the research and how you plan to fill the knowledge gap. The best research paper introduction provides a systemic review of existing work and demonstrates additional work that needs to be done. It needs to be brief, captivating, and well-referenced; a well-drafted research paper introduction will help the researcher win half the battle.
The introduction for a research paper is where you set up your topic and approach for the reader. It has several key goals:
- Present your research topic
- Capture reader interest
- Summarize existing research
- Position your own approach
- Define your specific research problem and problem statement
- Highlight the novelty and contributions of the study
- Give an overview of the paper’s structure
The research paper introduction can vary in size and structure depending on whether your paper presents the results of original empirical research or is a review paper. Some research paper introduction examples are only half a page while others are a few pages long. In many cases, the introduction will be shorter than all of the other sections of your paper; its length depends on the size of your paper as a whole.
- Break through writer’s block. Write your research paper introduction with Paperpal Copilot
Table of Contents
What is the introduction for a research paper, why is the introduction important in a research paper, craft a compelling introduction section with paperpal. try now, 1. introduce the research topic:, 2. determine a research niche:, 3. place your research within the research niche:, craft accurate research paper introductions with paperpal. start writing now, frequently asked questions on research paper introduction, key points to remember.
The introduction in a research paper is placed at the beginning to guide the reader from a broad subject area to the specific topic that your research addresses. They present the following information to the reader
- Scope: The topic covered in the research paper
- Context: Background of your topic
- Importance: Why your research matters in that particular area of research and the industry problem that can be targeted
The research paper introduction conveys a lot of information and can be considered an essential roadmap for the rest of your paper. A good introduction for a research paper is important for the following reasons:
- It stimulates your reader’s interest: A good introduction section can make your readers want to read your paper by capturing their interest. It informs the reader what they are going to learn and helps determine if the topic is of interest to them.
- It helps the reader understand the research background: Without a clear introduction, your readers may feel confused and even struggle when reading your paper. A good research paper introduction will prepare them for the in-depth research to come. It provides you the opportunity to engage with the readers and demonstrate your knowledge and authority on the specific topic.
- It explains why your research paper is worth reading: Your introduction can convey a lot of information to your readers. It introduces the topic, why the topic is important, and how you plan to proceed with your research.
- It helps guide the reader through the rest of the paper: The research paper introduction gives the reader a sense of the nature of the information that will support your arguments and the general organization of the paragraphs that will follow. It offers an overview of what to expect when reading the main body of your paper.
What are the parts of introduction in the research?
A good research paper introduction section should comprise three main elements: 2
- What is known: This sets the stage for your research. It informs the readers of what is known on the subject.
- What is lacking: This is aimed at justifying the reason for carrying out your research. This could involve investigating a new concept or method or building upon previous research.
- What you aim to do: This part briefly states the objectives of your research and its major contributions. Your detailed hypothesis will also form a part of this section.
How to write a research paper introduction?
The first step in writing the research paper introduction is to inform the reader what your topic is and why it’s interesting or important. This is generally accomplished with a strong opening statement. The second step involves establishing the kinds of research that have been done and ending with limitations or gaps in the research that you intend to address. Finally, the research paper introduction clarifies how your own research fits in and what problem it addresses. If your research involved testing hypotheses, these should be stated along with your research question. The hypothesis should be presented in the past tense since it will have been tested by the time you are writing the research paper introduction.
The following key points, with examples, can guide you when writing the research paper introduction section:
- Highlight the importance of the research field or topic
- Describe the background of the topic
- Present an overview of current research on the topic
Example: The inclusion of experiential and competency-based learning has benefitted electronics engineering education. Industry partnerships provide an excellent alternative for students wanting to engage in solving real-world challenges. Industry-academia participation has grown in recent years due to the need for skilled engineers with practical training and specialized expertise. However, from the educational perspective, many activities are needed to incorporate sustainable development goals into the university curricula and consolidate learning innovation in universities.
- Reveal a gap in existing research or oppose an existing assumption
- Formulate the research question
Example: There have been plausible efforts to integrate educational activities in higher education electronics engineering programs. However, very few studies have considered using educational research methods for performance evaluation of competency-based higher engineering education, with a focus on technical and or transversal skills. To remedy the current need for evaluating competencies in STEM fields and providing sustainable development goals in engineering education, in this study, a comparison was drawn between study groups without and with industry partners.
- State the purpose of your study
- Highlight the key characteristics of your study
- Describe important results
- Highlight the novelty of the study.
- Offer a brief overview of the structure of the paper.
Example: The study evaluates the main competency needed in the applied electronics course, which is a fundamental core subject for many electronics engineering undergraduate programs. We compared two groups, without and with an industrial partner, that offered real-world projects to solve during the semester. This comparison can help determine significant differences in both groups in terms of developing subject competency and achieving sustainable development goals.
Write a Research Paper Introduction in Minutes with Paperpal
Paperpal Copilot is a generative AI-powered academic writing assistant. It’s trained on millions of published scholarly articles and over 20 years of STM experience. Paperpal Copilot helps authors write better and faster with:
- Real-time writing suggestions
- In-depth checks for language and grammar correction
- Paraphrasing to add variety, ensure academic tone, and trim text to meet journal limits
With Paperpal Copilot, create a research paper introduction effortlessly. In this step-by-step guide, we’ll walk you through how Paperpal transforms your initial ideas into a polished and publication-ready introduction.

How to use Paperpal to write the Introduction section
Step 1: Sign up on Paperpal and click on the Copilot feature, under this choose Outlines > Research Article > Introduction
Step 2: Add your unstructured notes or initial draft, whether in English or another language, to Paperpal, which is to be used as the base for your content.
Step 3: Fill in the specifics, such as your field of study, brief description or details you want to include, which will help the AI generate the outline for your Introduction.
Step 4: Use this outline and sentence suggestions to develop your content, adding citations where needed and modifying it to align with your specific research focus.
Step 5: Turn to Paperpal’s granular language checks to refine your content, tailor it to reflect your personal writing style, and ensure it effectively conveys your message.
You can use the same process to develop each section of your article, and finally your research paper in half the time and without any of the stress.
The purpose of the research paper introduction is to introduce the reader to the problem definition, justify the need for the study, and describe the main theme of the study. The aim is to gain the reader’s attention by providing them with necessary background information and establishing the main purpose and direction of the research.
The length of the research paper introduction can vary across journals and disciplines. While there are no strict word limits for writing the research paper introduction, an ideal length would be one page, with a maximum of 400 words over 1-4 paragraphs. Generally, it is one of the shorter sections of the paper as the reader is assumed to have at least a reasonable knowledge about the topic. 2 For example, for a study evaluating the role of building design in ensuring fire safety, there is no need to discuss definitions and nature of fire in the introduction; you could start by commenting upon the existing practices for fire safety and how your study will add to the existing knowledge and practice.
When deciding what to include in the research paper introduction, the rest of the paper should also be considered. The aim is to introduce the reader smoothly to the topic and facilitate an easy read without much dependency on external sources. 3 Below is a list of elements you can include to prepare a research paper introduction outline and follow it when you are writing the research paper introduction. Topic introduction: This can include key definitions and a brief history of the topic. Research context and background: Offer the readers some general information and then narrow it down to specific aspects. Details of the research you conducted: A brief literature review can be included to support your arguments or line of thought. Rationale for the study: This establishes the relevance of your study and establishes its importance. Importance of your research: The main contributions are highlighted to help establish the novelty of your study Research hypothesis: Introduce your research question and propose an expected outcome. Organization of the paper: Include a short paragraph of 3-4 sentences that highlights your plan for the entire paper
Cite only works that are most relevant to your topic; as a general rule, you can include one to three. Note that readers want to see evidence of original thinking. So it is better to avoid using too many references as it does not leave much room for your personal standpoint to shine through. Citations in your research paper introduction support the key points, and the number of citations depend on the subject matter and the point discussed. If the research paper introduction is too long or overflowing with citations, it is better to cite a few review articles rather than the individual articles summarized in the review. A good point to remember when citing research papers in the introduction section is to include at least one-third of the references in the introduction.
The literature review plays a significant role in the research paper introduction section. A good literature review accomplishes the following: Introduces the topic – Establishes the study’s significance – Provides an overview of the relevant literature – Provides context for the study using literature – Identifies knowledge gaps However, remember to avoid making the following mistakes when writing a research paper introduction: Do not use studies from the literature review to aggressively support your research Avoid direct quoting Do not allow literature review to be the focus of this section. Instead, the literature review should only aid in setting a foundation for the manuscript.
Remember the following key points for writing a good research paper introduction: 4
- Avoid stuffing too much general information: Avoid including what an average reader would know and include only that information related to the problem being addressed in the research paper introduction. For example, when describing a comparative study of non-traditional methods for mechanical design optimization, information related to the traditional methods and differences between traditional and non-traditional methods would not be relevant. In this case, the introduction for the research paper should begin with the state-of-the-art non-traditional methods and methods to evaluate the efficiency of newly developed algorithms.
- Avoid packing too many references: Cite only the required works in your research paper introduction. The other works can be included in the discussion section to strengthen your findings.
- Avoid extensive criticism of previous studies: Avoid being overly critical of earlier studies while setting the rationale for your study. A better place for this would be the Discussion section, where you can highlight the advantages of your method.
- Avoid describing conclusions of the study: When writing a research paper introduction remember not to include the findings of your study. The aim is to let the readers know what question is being answered. The actual answer should only be given in the Results and Discussion section.
To summarize, the research paper introduction section should be brief yet informative. It should convince the reader the need to conduct the study and motivate him to read further. If you’re feeling stuck or unsure, choose trusted AI academic writing assistants like Paperpal to effortlessly craft your research paper introduction and other sections of your research article.
1. Jawaid, S. A., & Jawaid, M. (2019). How to write introduction and discussion. Saudi Journal of Anaesthesia, 13(Suppl 1), S18.
2. Dewan, P., & Gupta, P. (2016). Writing the title, abstract and introduction: Looks matter!. Indian pediatrics, 53, 235-241.
3. Cetin, S., & Hackam, D. J. (2005). An approach to the writing of a scientific Manuscript1. Journal of Surgical Research, 128(2), 165-167.
4. Bavdekar, S. B. (2015). Writing introduction: Laying the foundations of a research paper. Journal of the Association of Physicians of India, 63(7), 44-6.
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Scientific Writing Style Guides Explained
- 5 Reasons for Rejection After Peer Review
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
- 8 Most Effective Ways to Increase Motivation for Thesis Writing
Practice vs. Practise: Learn the Difference
Academic paraphrasing: why paperpal’s rewrite should be your first choice , you may also like, phd qualifying exam: tips for success , ai in education: it’s time to change the..., is it ethical to use ai-generated abstracts without..., what are journal guidelines on using generative ai..., quillbot review: features, pricing, and free alternatives, what is an academic paper types and elements , should you use ai tools like chatgpt for..., publish research papers: 9 steps for successful publications , what are the different types of research papers, how to make translating academic papers less challenging.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
APA Sample Paper

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Note: This page reflects the latest version of the APA Publication Manual (i.e., APA 7), which released in October 2019. The equivalent resource for the older APA 6 style can be found here .
Media Files: APA Sample Student Paper , APA Sample Professional Paper
This resource is enhanced by Acrobat PDF files. Download the free Acrobat Reader
Note: The APA Publication Manual, 7 th Edition specifies different formatting conventions for student and professional papers (i.e., papers written for credit in a course and papers intended for scholarly publication). These differences mostly extend to the title page and running head. Crucially, citation practices do not differ between the two styles of paper.
However, for your convenience, we have provided two versions of our APA 7 sample paper below: one in student style and one in professional style.
Note: For accessibility purposes, we have used "Track Changes" to make comments along the margins of these samples. Those authored by [AF] denote explanations of formatting and [AWC] denote directions for writing and citing in APA 7.
APA 7 Student Paper:
Apa 7 professional paper:.
Research Paper Guide
Research Paper Example
Research Paper Examples - Free Sample Papers for Different Formats!

People also read
Research Paper Writing - A Step by Step Guide
Guide to Creating Effective Research Paper Outline
Interesting Research Paper Topics for 2024
Research Proposal Writing - A Step-by-Step Guide
How to Start a Research Paper - 7 Easy Steps
How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper - A Step by Step Guide
Writing a Literature Review For a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
Qualitative Research - Methods, Types, and Examples
8 Types of Qualitative Research - Overview & Examples
Qualitative vs Quantitative Research - Learning the Basics
200+ Engaging Psychology Research Paper Topics for Students in 2024
Learn How to Write a Hypothesis in a Research Paper: Examples and Tips!
20+ Types of Research With Examples - A Detailed Guide
Understanding Quantitative Research - Types & Data Collection Techniques
230+ Sociology Research Topics & Ideas for Students
How to Cite a Research Paper - A Complete Guide
Excellent History Research Paper Topics- 300+ Ideas
A Guide on Writing the Method Section of a Research Paper - Examples & Tips
How To Write an Introduction Paragraph For a Research Paper: Learn with Examples
Crafting a Winning Research Paper Title: A Complete Guide
Writing a Research Paper Conclusion - Step-by-Step Guide
Writing a Thesis For a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
How To Write A Discussion For A Research Paper | Examples & Tips
How To Write The Results Section of A Research Paper | Steps & Examples
Writing a Problem Statement for a Research Paper - A Comprehensive Guide
Finding Sources For a Research Paper: A Complete Guide
A Guide on How to Edit a Research Paper
200+ Ethical Research Paper Topics to Begin With (2024)
300+ Controversial Research Paper Topics & Ideas - 2024 Edition
150+ Argumentative Research Paper Topics For You - 2024
How to Write a Research Methodology for a Research Paper
Crafting a comprehensive research paper can be daunting. Understanding diverse citation styles and various subject areas presents a challenge for many.
Without clear examples, students often feel lost and overwhelmed, unsure of how to start or which style fits their subject.
Explore our collection of expertly written research paper examples. We’ve covered various citation styles and a diverse range of subjects.
So, read on!
- 1. Research Paper Example for Different Formats
- 2. Examples for Different Research Paper Parts
- 3. Research Paper Examples for Different Fields
- 4. Research Paper Example Outline
Research Paper Example for Different Formats
Following a specific formatting style is essential while writing a research paper . Knowing the conventions and guidelines for each format can help you in creating a perfect paper. Here we have gathered examples of research paper for most commonly applied citation styles :
Social Media and Social Media Marketing: A Literature Review
APA Research Paper Example
APA (American Psychological Association) style is commonly used in social sciences, psychology, and education. This format is recognized for its clear and concise writing, emphasis on proper citations, and orderly presentation of ideas.
Here are some research paper examples in APA style:
Research Paper Example APA 7th Edition
Research Paper Example MLA
MLA (Modern Language Association) style is frequently employed in humanities disciplines, including literature, languages, and cultural studies. An MLA research paper might explore literature analysis, linguistic studies, or historical research within the humanities.
Here is an example:
Found Voices: Carl Sagan
Research Paper Example Chicago
Chicago style is utilized in various fields like history, arts, and social sciences. Research papers in Chicago style could delve into historical events, artistic analyses, or social science inquiries.
Here is a research paper formatted in Chicago style:
Chicago Research Paper Sample
Research Paper Example Harvard
Harvard style is widely used in business, management, and some social sciences. Research papers in Harvard style might address business strategies, case studies, or social policies.
View this sample Harvard style paper here:
Harvard Research Paper Sample
Examples for Different Research Paper Parts
A research paper has different parts. Each part is important for the overall success of the paper. Chapters in a research paper must be written correctly, using a certain format and structure.
The following are examples of how different sections of the research paper can be written.
Research Proposal
The research proposal acts as a detailed plan or roadmap for your study, outlining the focus of your research and its significance. It's essential as it not only guides your research but also persuades others about the value of your study.
Example of Research Proposal
An abstract serves as a concise overview of your entire research paper. It provides a quick insight into the main elements of your study. It summarizes your research's purpose, methods, findings, and conclusions in a brief format.
Research Paper Example Abstract
Literature Review
A literature review summarizes the existing research on your study's topic, showcasing what has already been explored. This section adds credibility to your own research by analyzing and summarizing prior studies related to your topic.
Literature Review Research Paper Example
Methodology
The methodology section functions as a detailed explanation of how you conducted your research. This part covers the tools, techniques, and steps used to collect and analyze data for your study.
Methods Section of Research Paper Example
How to Write the Methods Section of a Research Paper
The conclusion summarizes your findings, their significance and the impact of your research. This section outlines the key takeaways and the broader implications of your study's results.
Research Paper Conclusion Example
Research Paper Examples for Different Fields
Research papers can be about any subject that needs a detailed study. The following examples show research papers for different subjects.
History Research Paper Sample
Preparing a history research paper involves investigating and presenting information about past events. This may include exploring perspectives, analyzing sources, and constructing a narrative that explains the significance of historical events.
View this history research paper sample:
Many Faces of Generalissimo Fransisco Franco
Sociology Research Paper Sample
In sociology research, statistics and data are harnessed to explore societal issues within a particular region or group. These findings are thoroughly analyzed to gain an understanding of the structure and dynamics present within these communities.
Here is a sample:
A Descriptive Statistical Analysis within the State of Virginia
Science Fair Research Paper Sample
A science research paper involves explaining a scientific experiment or project. It includes outlining the purpose, procedures, observations, and results of the experiment in a clear, logical manner.
Here are some examples:
Science Fair Paper Format
What Do I Need To Do For The Science Fair?
Psychology Research Paper Sample
Writing a psychology research paper involves studying human behavior and mental processes. This process includes conducting experiments, gathering data, and analyzing results to understand the human mind, emotions, and behavior.
Here is an example psychology paper:
The Effects of Food Deprivation on Concentration and Perseverance
Art History Research Paper Sample
Studying art history includes examining artworks, understanding their historical context, and learning about the artists. This helps analyze and interpret how art has evolved over various periods and regions.
Check out this sample paper analyzing European art and impacts:
European Art History: A Primer
Research Paper Example Outline
Before you plan on writing a well-researched paper, make a rough draft. An outline can be a great help when it comes to organizing vast amounts of research material for your paper.
Here is an outline of a research paper example:
Here is a downloadable sample of a standard research paper outline:
Research Paper Outline
Want to create the perfect outline for your paper? Check out this in-depth guide on creating a research paper outline for a structured paper!
Good Research Paper Examples for Students
Here are some more samples of research paper for students to learn from:
Fiscal Research Center - Action Plan
Qualitative Research Paper Example
Research Paper Example Introduction
How to Write a Research Paper Example
Research Paper Example for High School
Now that you have explored the research paper examples, you can start working on your research project. Hopefully, these examples will help you understand the writing process for a research paper.
If you're facing challenges with your writing requirements, you can hire our essay writing service .
Our team is experienced in delivering perfectly formatted, 100% original research papers. So, whether you need help with a part of research or an entire paper, our experts are here to deliver.
So, why miss out? Place your ‘ write my research paper ’ request today and get a top-quality research paper!

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading
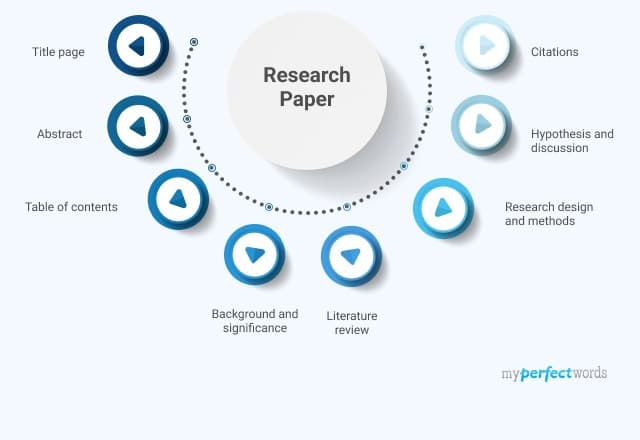
Wound: a Brief Analysis of Kandi Culture
This essay about kandi explores its significance within the rave and electronic dance music (EDM) cultures. Kandi, consisting of colorful beaded bracelets and other jewelry, is more than a fashion accessory; it symbolizes identity, community, and the core values of rave culture, encapsulated in the acronym PLUR (Peace, Love, Unity, Respect). The essay discusses the origins of kandi in the early 1990s American rave scene and its connections to 1960s and 70s countercultures. It emphasizes the ritualistic exchange of kandi through the PLUR handshake, a practice that reinforces communal values and strengthens social bonds among ravers. Each piece of kandi is often personalized, serving as a memento of musical events and personal connections. Ultimately, kandi is portrayed as a vibrant and integral part of rave culture, embodying its history, values, and ethos of inclusivity.
How it works
In the vibrant world of rave culture and electronic dance music (EDM), few symbols are as iconic or carry as much meaning as “kandi.” These colorful beaded bracelets serve as more than mere fashion accessories; they embody a rich tradition of identity, community, and values within the EDM community. Kandi consists of handmade bracelets, necklaces, and other jewelry items, crafted from pony beads and often exchanged among ravers through a specific ritual known as the “PLUR handshake.” This essay explores the significance of kandi, its roots in rave culture, and the values it represents.
Kandi first became popular in the early 1990s when rave culture began to flourish in the United States. Originating from underground scenes in urban centers like Los Angeles and San Francisco, kandi was inspired by a mix of DIY fashion, the vibrant aesthetics of the 1960s and 70s countercultures, and a desire to create visible tokens of rave community and its inclusive ethos. The colorful beads were not only a way to stand out in the often dimly lit rave settings but also served as a means of communication and connection among attendees.
The act of exchanging kandi is central to its meaning. This exchange is governed by the acronym PLUR, which stands for Peace, Love, Unity, and Respect. These principles form the philosophical backbone of rave culture, promoting harmonious social interaction, empathy, and community. The PLUR handshake, which involves a series of hand gestures ending with the transfer of a bracelet from one person’s wrist to another’s, is a ritual that reinforces these values. It transforms the simple act of giving away a bracelet into a meaningful exchange of goodwill and acceptance, creating and deepening bonds within the community.
Moreover, kandi is often personalized with specific patterns, colors, or charms that can signify anything from a favorite music DJ or band to a personal mantra or memory. This customization makes each piece of kandi a unique, personal artifact, imbued with the maker’s energy and story. For many in the rave community, kandi bracelets act as mementos that chronicle their experiences and relationships formed at raves and festivals. The bracelets are worn as badges of honor, each one representing a moment of connection and the shared experience of music and dance.
Kandi’s significance extends beyond its immediate visual appeal and function as a social tool. It also serves as an emblem of identity and a marker of belonging within the rave culture. For those outside this community, the bright, playful appearance of kandi may simply represent an eccentric fashion statement. However, for those within the community, wearing kandi signifies a deeper alignment with the values of PLUR, an ongoing commitment to the ethos of rave culture, and a continuous celebration of its inclusive spirit.
In conclusion, kandi is much more than decorative jewelry; it is a complex symbol laden with cultural significance within the rave and EDM communities. Through its creation, exchange, and display, kandi promotes values of peace, love, unity, and respect, fostering a sense of community and identity among its participants. As rave culture continues to evolve and spread globally, the tradition of kandi remains a vibrant and integral part of this dynamic cultural movement, encapsulating its history, values, and communal spirit.
Cite this page
Wound: A Brief Analysis Of Kandi Culture. (2024, Apr 22). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/wound-a-brief-analysis-of-kandi-culture/
"Wound: A Brief Analysis Of Kandi Culture." PapersOwl.com , 22 Apr 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/wound-a-brief-analysis-of-kandi-culture/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Wound: A Brief Analysis Of Kandi Culture . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/wound-a-brief-analysis-of-kandi-culture/ [Accessed: 22 Apr. 2024]
"Wound: A Brief Analysis Of Kandi Culture." PapersOwl.com, Apr 22, 2024. Accessed April 22, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/wound-a-brief-analysis-of-kandi-culture/
"Wound: A Brief Analysis Of Kandi Culture," PapersOwl.com , 22-Apr-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/wound-a-brief-analysis-of-kandi-culture/. [Accessed: 22-Apr-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). Wound: A Brief Analysis Of Kandi Culture . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/wound-a-brief-analysis-of-kandi-culture/ [Accessed: 22-Apr-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers
AI Index: State of AI in 13 Charts
In the new report, foundation models dominate, benchmarks fall, prices skyrocket, and on the global stage, the U.S. overshadows.

This year’s AI Index — a 500-page report tracking 2023’s worldwide trends in AI — is out.
The index is an independent initiative at the Stanford Institute for Human-Centered Artificial Intelligence (HAI), led by the AI Index Steering Committee, an interdisciplinary group of experts from across academia and industry. This year’s report covers the rise of multimodal foundation models, major cash investments into generative AI, new performance benchmarks, shifting global opinions, and new major regulations.
Don’t have an afternoon to pore through the findings? Check out the high level here.
A Move Toward Open-Sourced
This past year, organizations released 149 foundation models, more than double the number released in 2022. Of these newly released models, 65.7% were open-source (meaning they can be freely used and modified by anyone), compared with only 44.4% in 2022 and 33.3% in 2021.
But At a Cost of Performance?
Closed-source models still outperform their open-sourced counterparts. On 10 selected benchmarks, closed models achieved a median performance advantage of 24.2%, with differences ranging from as little as 4.0% on mathematical tasks like GSM8K to as much as 317.7% on agentic tasks like AgentBench.
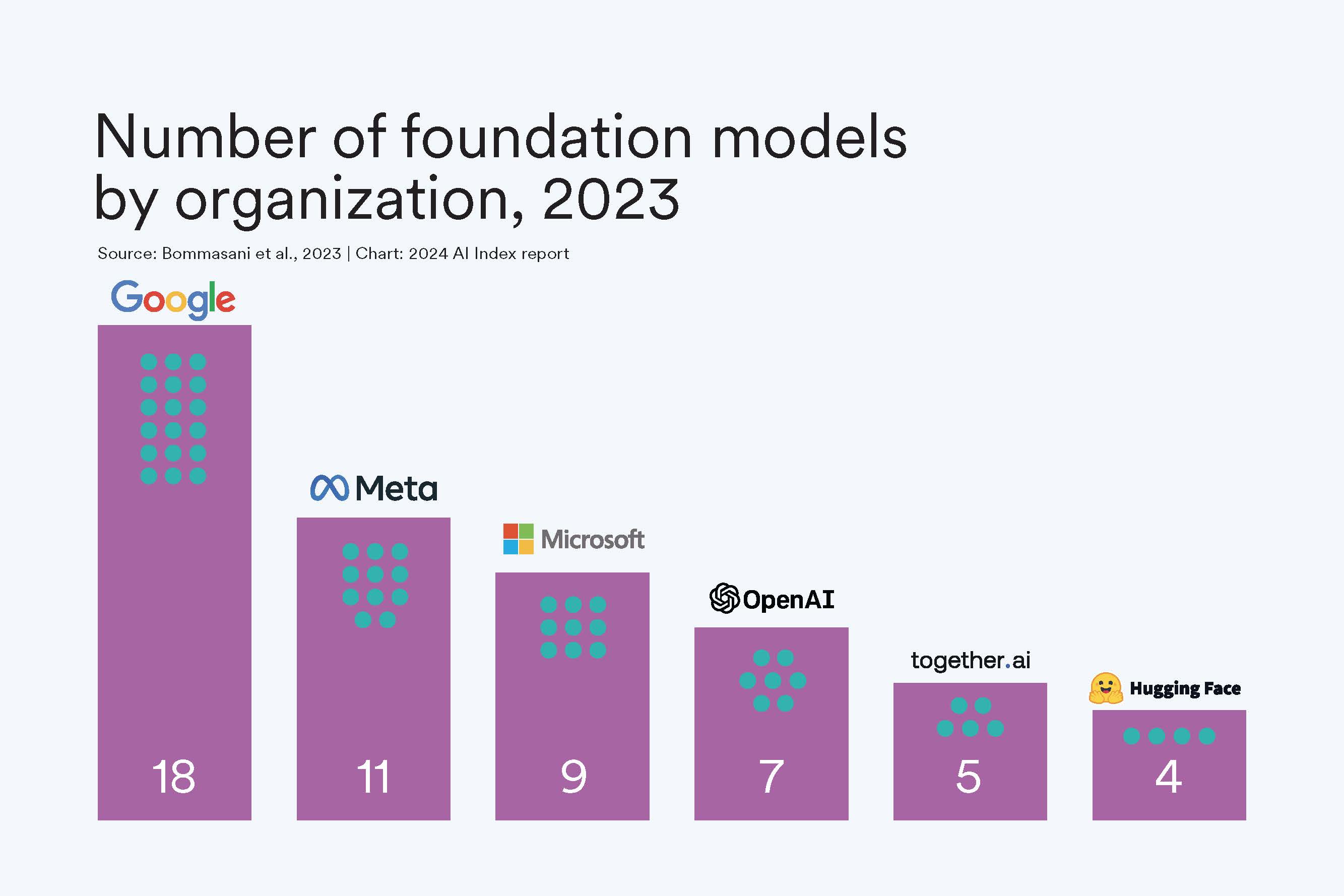
Biggest Players
Industry dominates AI, especially in building and releasing foundation models. This past year Google edged out other industry players in releasing the most models, including Gemini and RT-2. In fact, since 2019, Google has led in releasing the most foundation models, with a total of 40, followed by OpenAI with 20. Academia trails industry: This past year, UC Berkeley released three models and Stanford two.
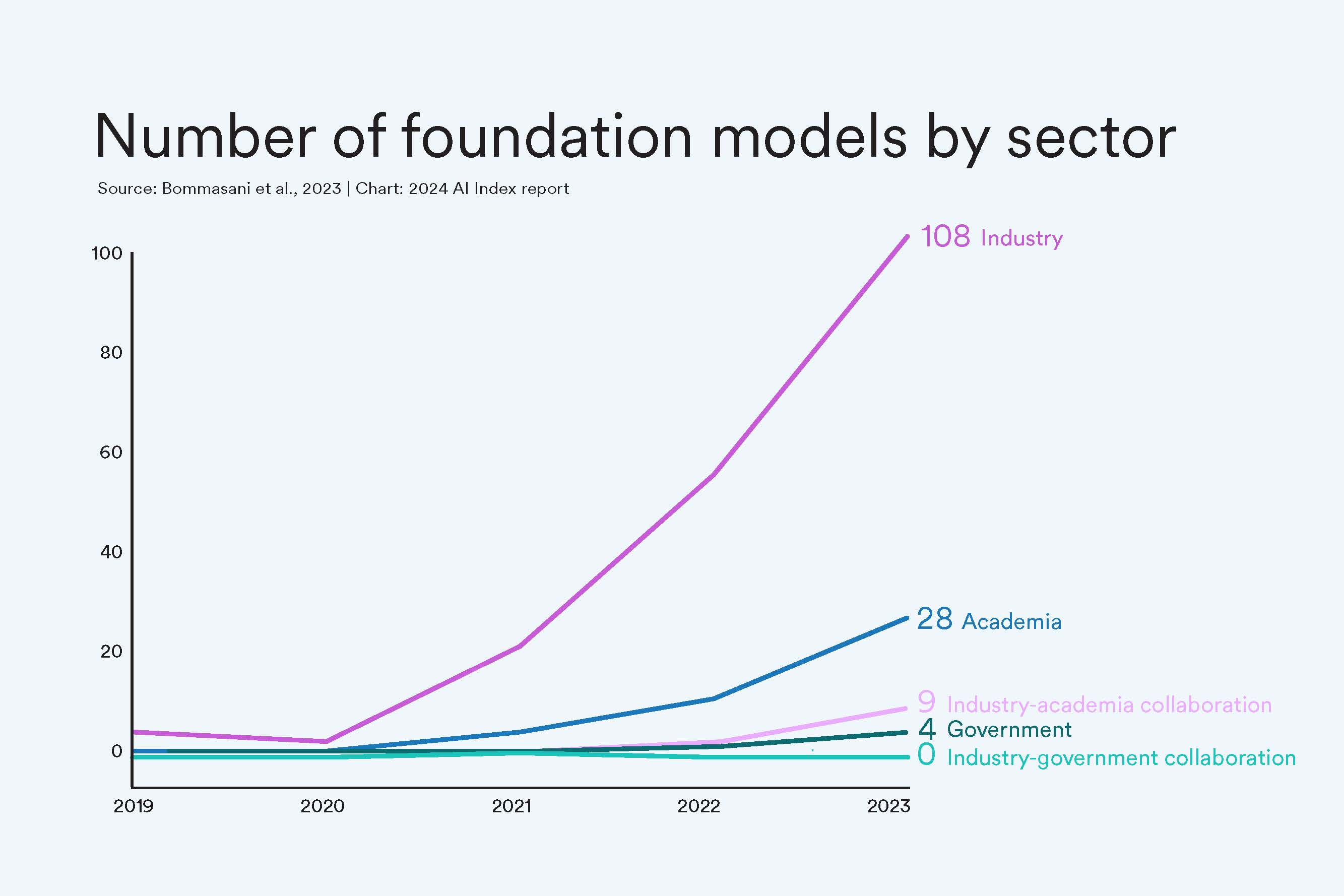
Industry Dwarfs All
If you needed more striking evidence that corporate AI is the only player in the room right now, this should do it. In 2023, industry accounted for 72% of all new foundation models.
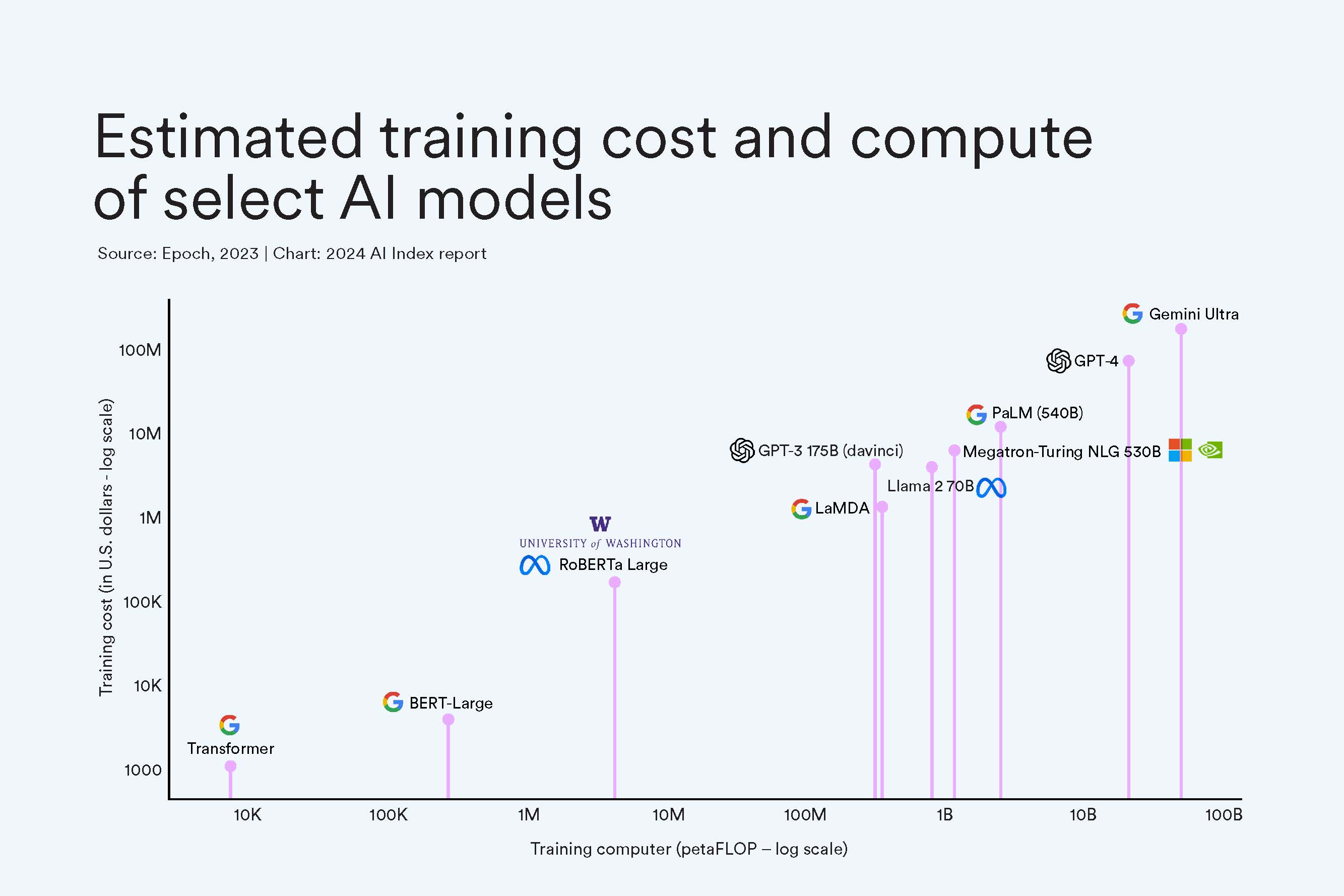
Prices Skyrocket
One of the reasons academia and government have been edged out of the AI race: the exponential increase in cost of training these giant models. Google’s Gemini Ultra cost an estimated $191 million worth of compute to train, while OpenAI’s GPT-4 cost an estimated $78 million. In comparison, in 2017, the original Transformer model, which introduced the architecture that underpins virtually every modern LLM, cost around $900.
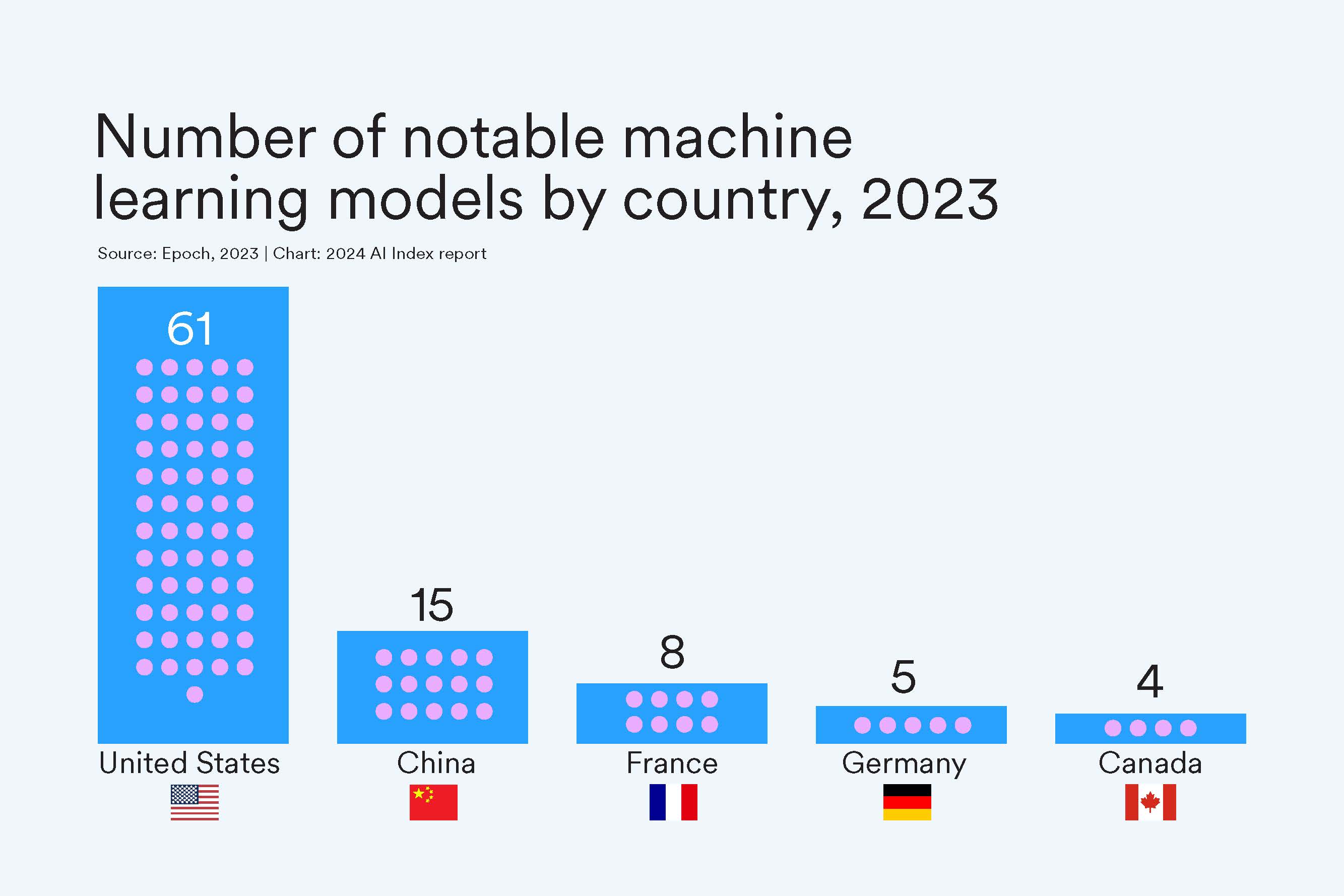
What AI Race?
At least in terms of notable machine learning models, the United States vastly outpaced other countries in 2023, developing a total of 61 models in 2023. Since 2019, the U.S. has consistently led in originating the majority of notable models, followed by China and the UK.
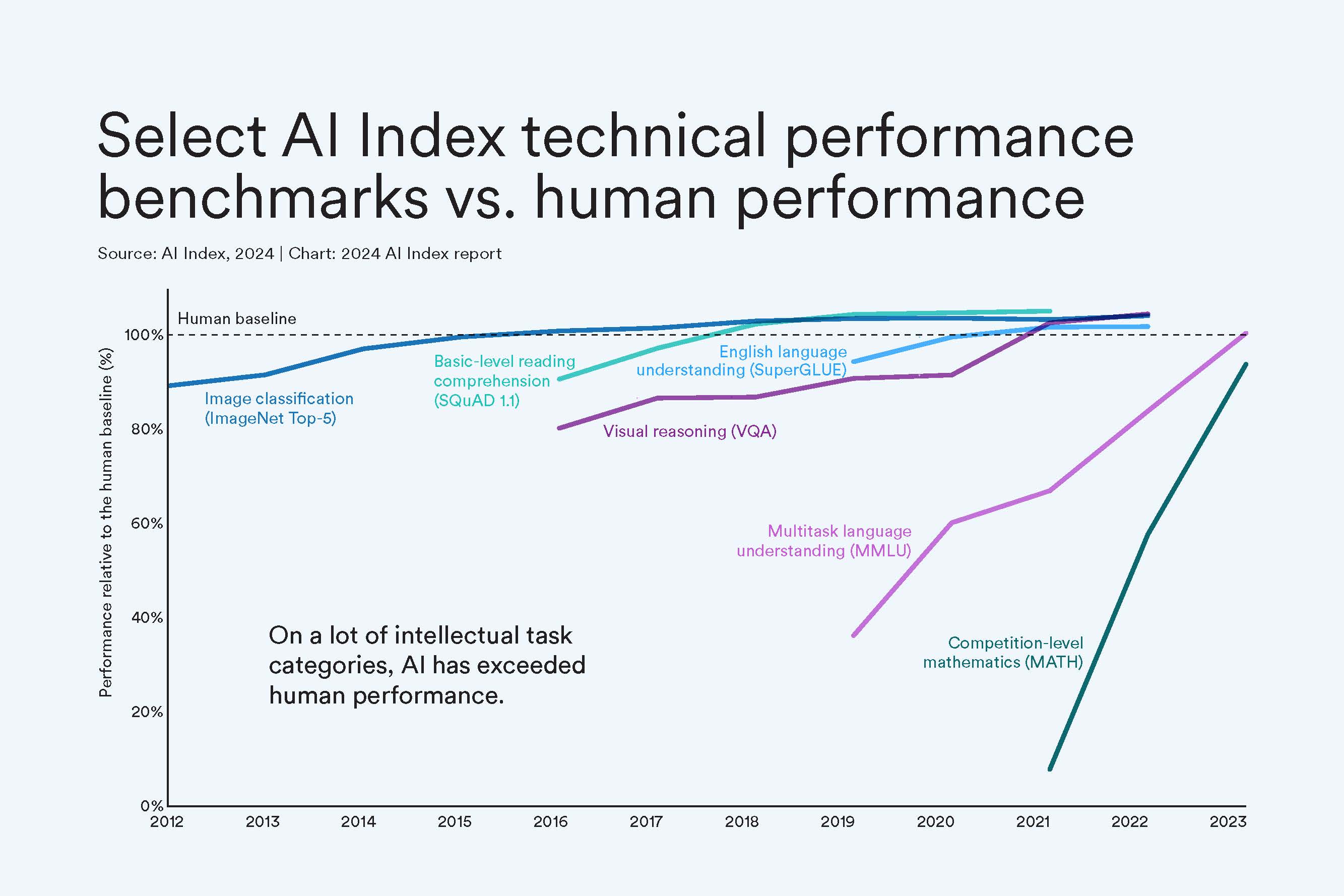
Move Over, Human
As of 2023, AI has hit human-level performance on many significant AI benchmarks, from those testing reading comprehension to visual reasoning. Still, it falls just short on some benchmarks like competition-level math. Because AI has been blasting past so many standard benchmarks, AI scholars have had to create new and more difficult challenges. This year’s index also tracked several of these new benchmarks, including those for tasks in coding, advanced reasoning, and agentic behavior.
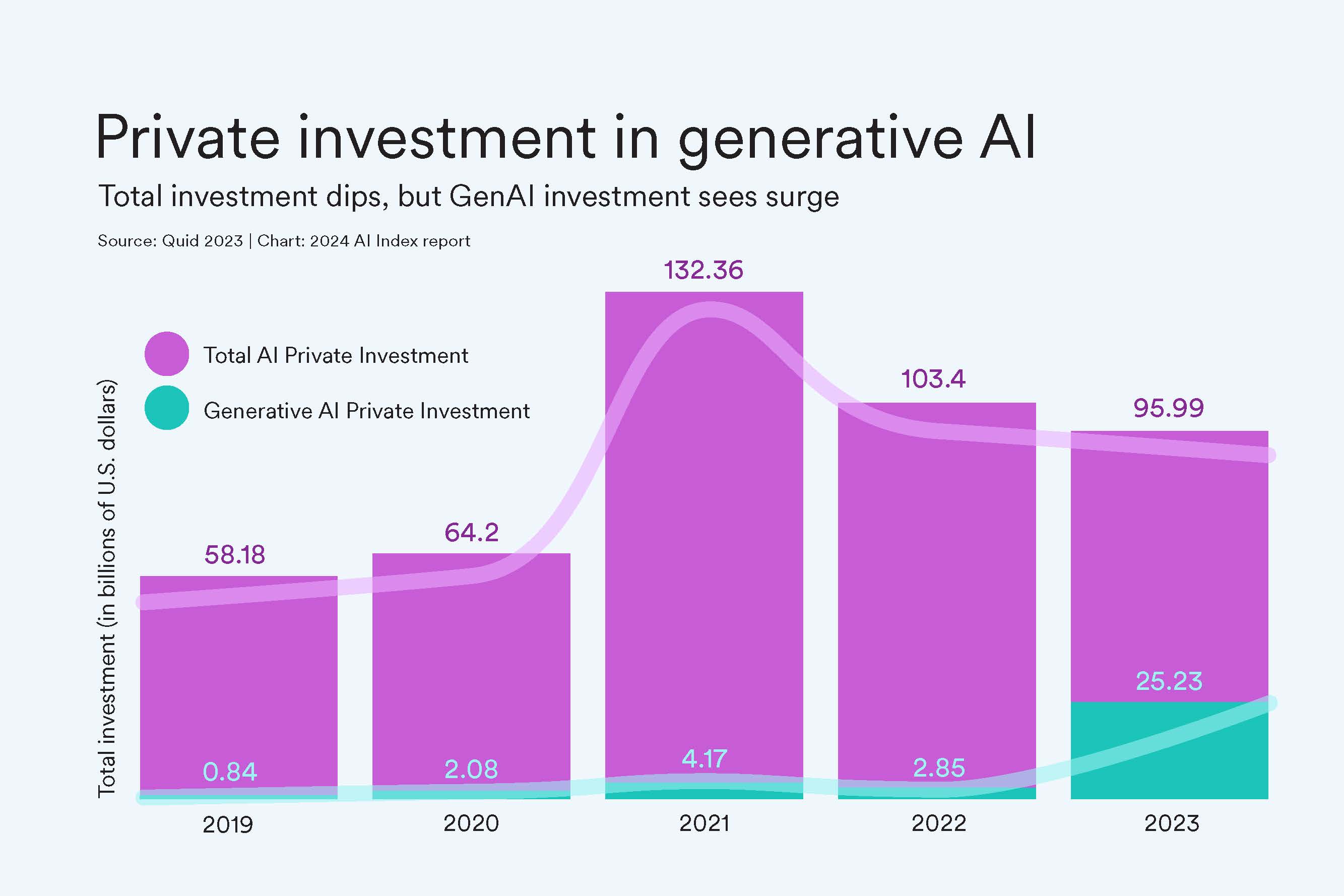
Private Investment Drops (But We See You, GenAI)
While AI private investment has steadily dropped since 2021, generative AI is gaining steam. In 2023, the sector attracted $25.2 billion, nearly ninefold the investment of 2022 and about 30 times the amount from 2019 (call it the ChatGPT effect). Generative AI accounted for over a quarter of all AI-related private investments in 2023.
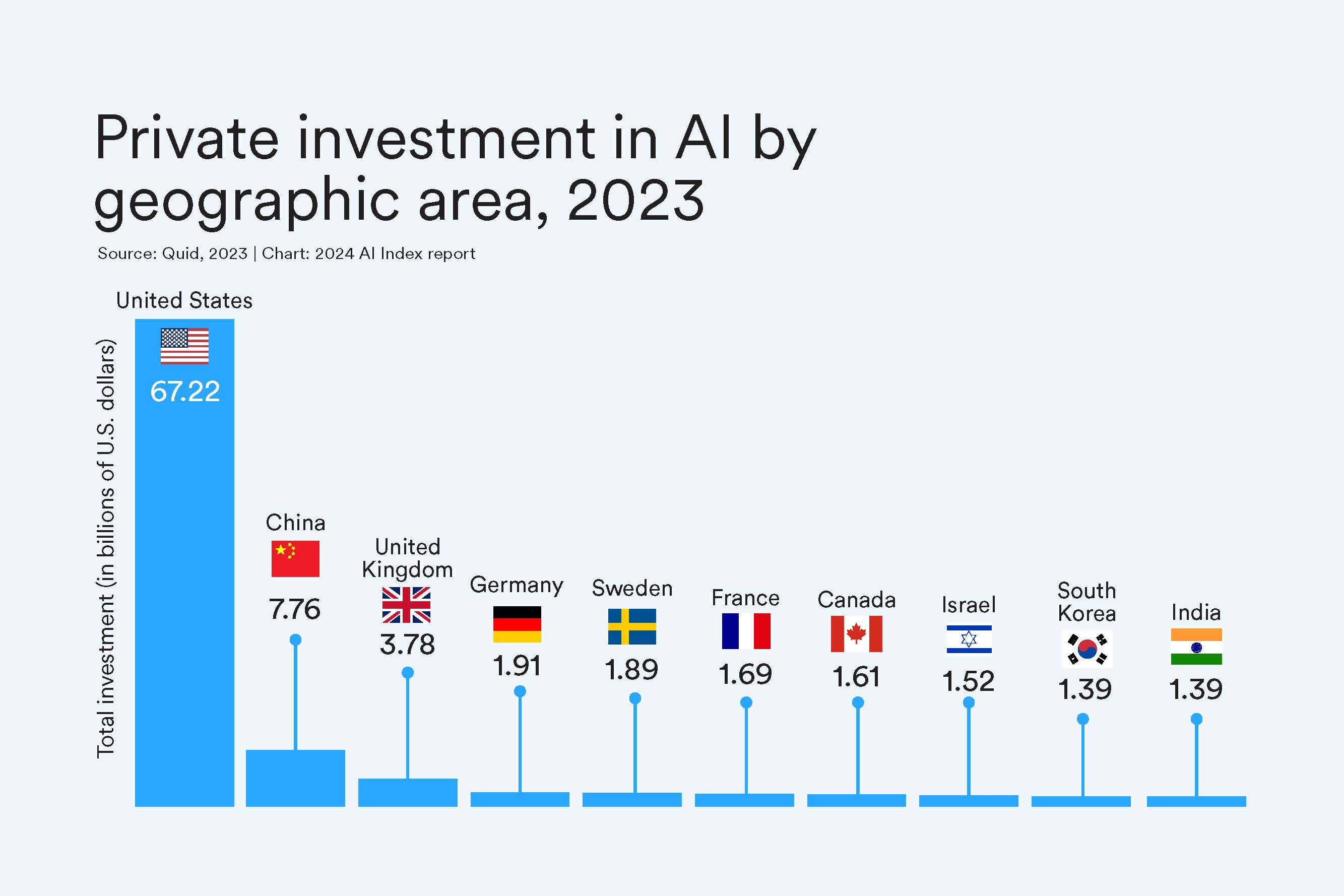
U.S. Wins $$ Race
And again, in 2023 the United States dominates in AI private investment. In 2023, the $67.2 billion invested in the U.S. was roughly 8.7 times greater than the amount invested in the next highest country, China, and 17.8 times the amount invested in the United Kingdom. That lineup looks the same when zooming out: Cumulatively since 2013, the United States leads investments at $335.2 billion, followed by China with $103.7 billion, and the United Kingdom at $22.3 billion.
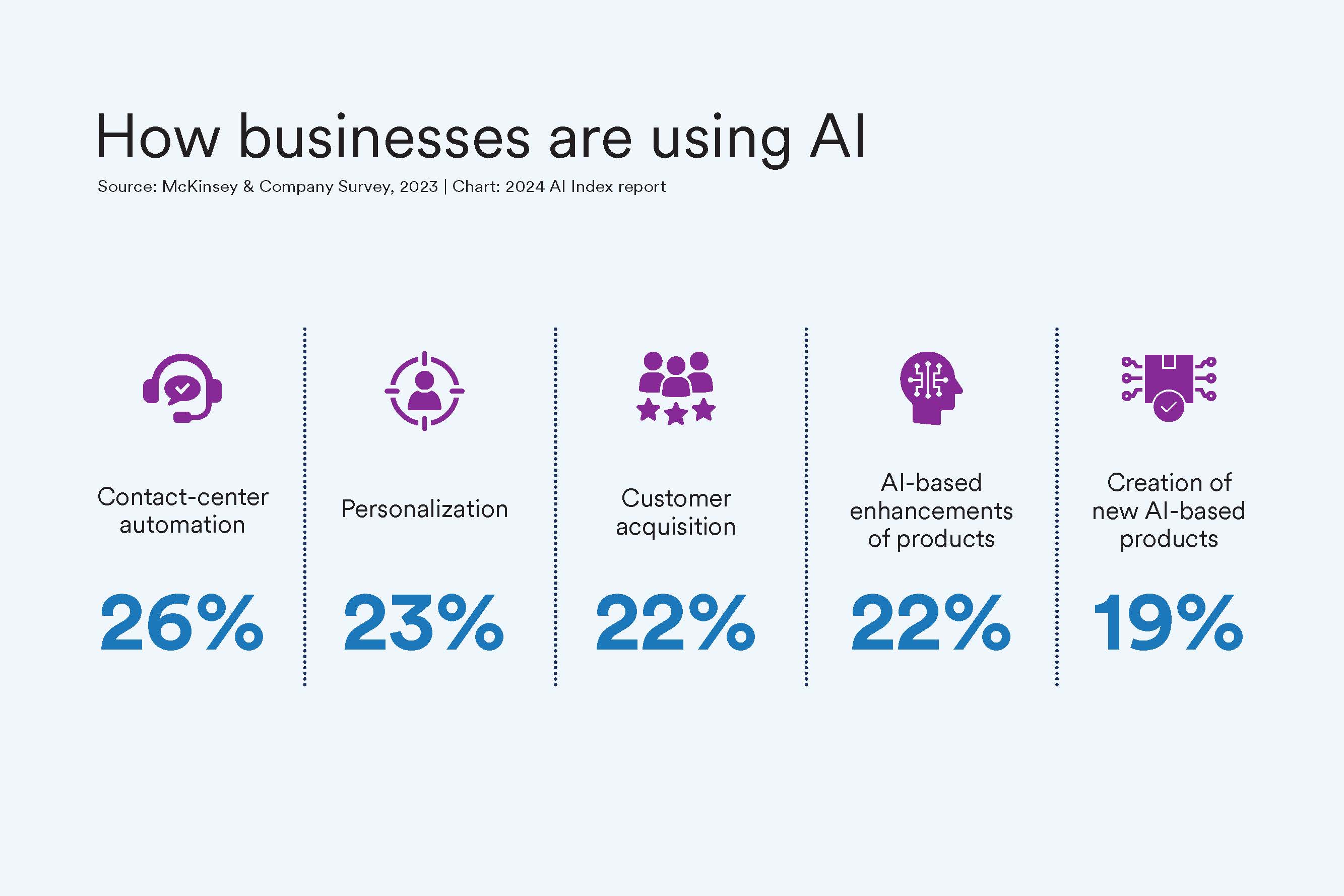
Where is Corporate Adoption?
More companies are implementing AI in some part of their business: In surveys, 55% of organizations said they were using AI in 2023, up from 50% in 2022 and 20% in 2017. Businesses report using AI to automate contact centers, personalize content, and acquire new customers.
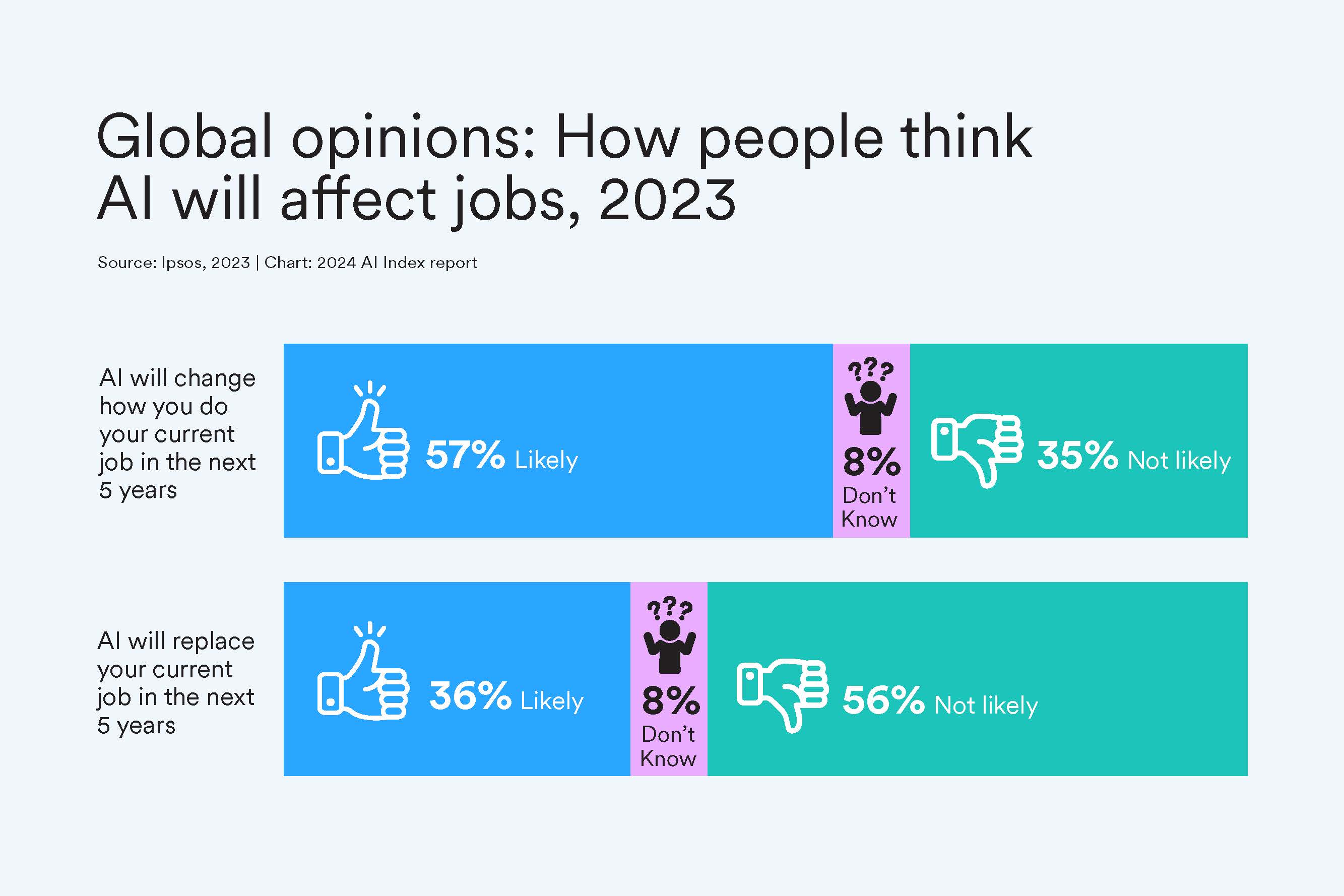
Younger and Wealthier People Worry About Jobs
Globally, most people expect AI to change their jobs, and more than a third expect AI to replace them. Younger generations — Gen Z and millennials — anticipate more substantial effects from AI compared with older generations like Gen X and baby boomers. Specifically, 66% of Gen Z compared with 46% of boomer respondents believe AI will significantly affect their current jobs. Meanwhile, individuals with higher incomes, more education, and decision-making roles foresee AI having a great impact on their employment.
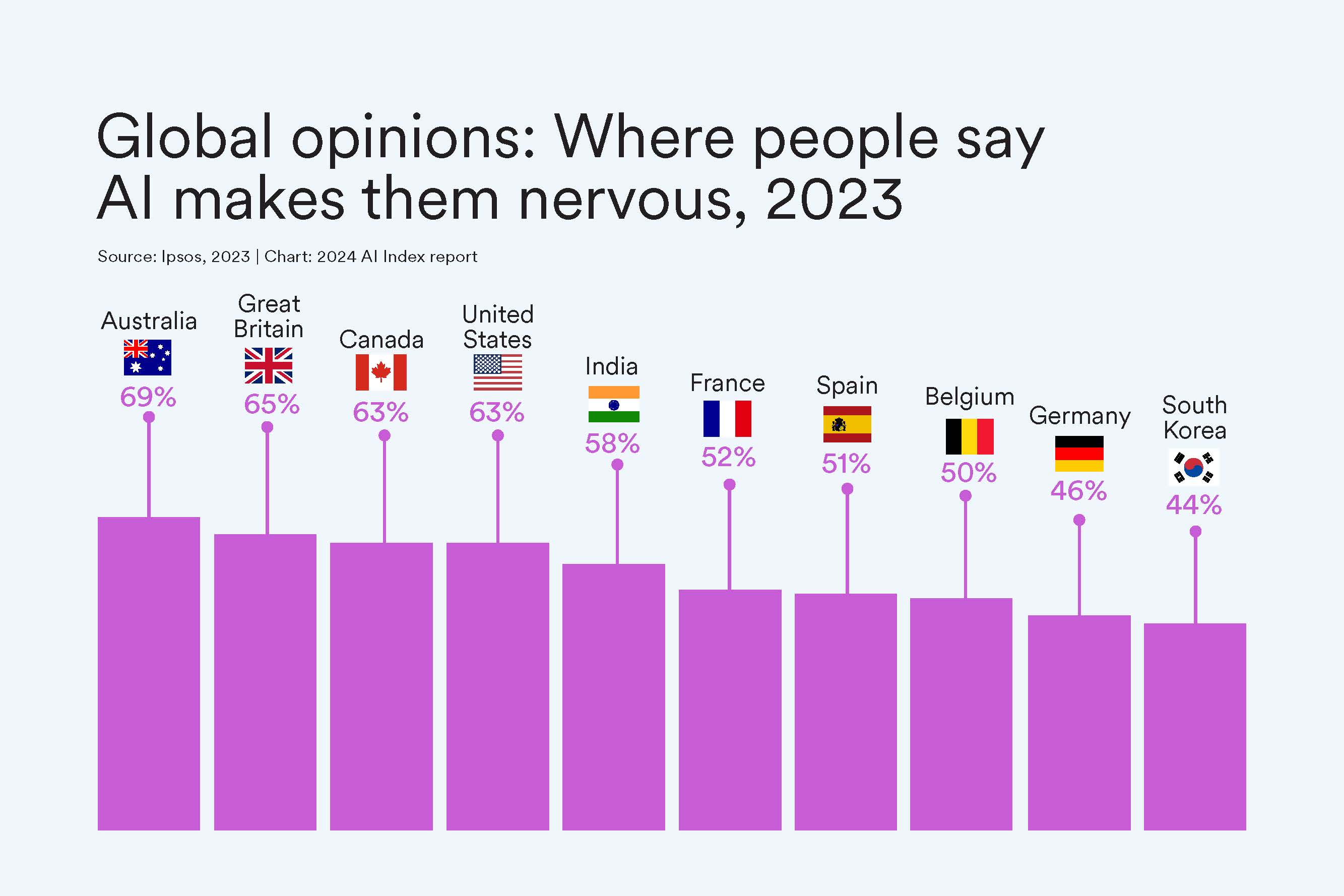
While the Commonwealth Worries About AI Products
When asked in a survey about whether AI products and services make you nervous, 69% of Aussies and 65% of Brits said yes. Japan is the least worried about their AI products at 23%.
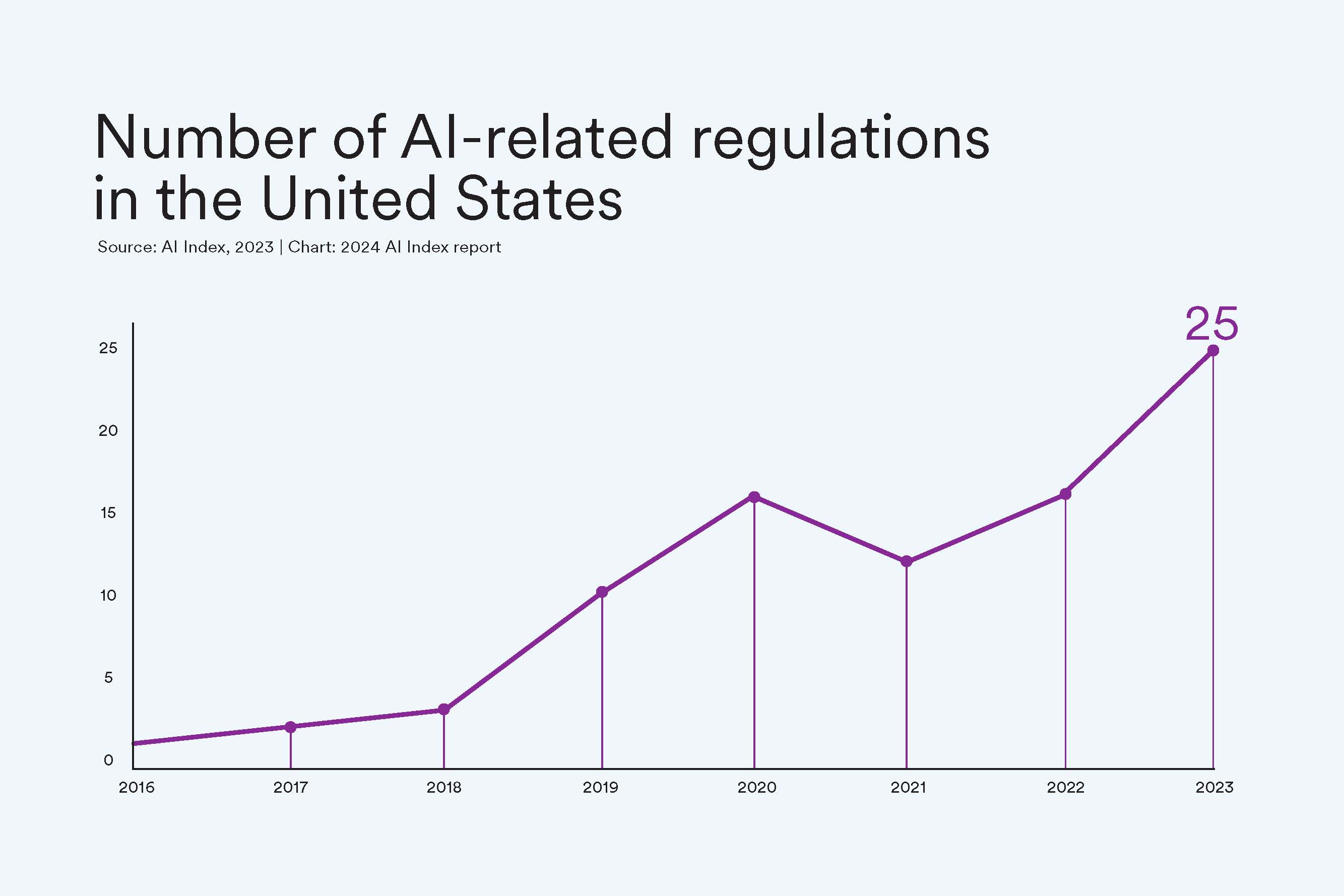
Regulation Rallies
More American regulatory agencies are passing regulations to protect citizens and govern the use of AI tools and data. For example, the Copyright Office and the Library of Congress passed copyright registration guidance concerning works that contained material generated by AI, while the Securities and Exchange Commission developed a cybersecurity risk management strategy, governance, and incident disclosure plan. The agencies to pass the most regulation were the Executive Office of the President and the Commerce Department.
The AI Index was first created to track AI development. The index collaborates with such organizations as LinkedIn, Quid, McKinsey, Studyportals, the Schwartz Reisman Institute, and the International Federation of Robotics to gather the most current research and feature important insights on the AI ecosystem.
More News Topics
VASA-1: Lifelike Audio-Driven Talking Faces Generated in Real Time
- Follow on Twitter
- Like on Facebook
- Follow on LinkedIn
- Subscribe on Youtube
- Follow on Instagram
- Subscribe to our RSS feed
Share this page:
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Reddit


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Using this experience, we've put together a 'how to' guide on writing an effective research brief, to help you ensure success on your next project. 1. Preparation is key. As with any project, before you start it's crucial you think through what you want and need to deliver. Here are some things you should consider:
in policy relevant research as it progresses. You can write a briefing at any stage in a project; in fact you may want to plan a number of briefings throughout a project. Ask yourself how you can generate conversation around your Research Briefing(s). Speaking with research users during a project allows you to hear
Introduction (about 50 to 100 words) Write a one-paragraph introduction (50 to 100 words) summarizing the policy problem, the research question, and the key findings. Use the introduction and conclusion to the discussion paper as sources for the introduction (and conclusion) of the brief. This is your homework!
Research briefs are the cornerstone of successful projects. They set the tone, define objectives, and guide researchers toward meaningful outcomes. A well-structured brief not only saves time but also ensures the collected data aligns with the project goals. How to Write a Research Brief: Understanding Your Objective. Defining Clear Research Goals
This guide contains: nA step-by-step guide to writing a research brief, from idea conception through to brief. nSuggestions on the sections you should include and the information to supply in each. nTop tips to ensure research agencies or other bidders understand your needs and can ivers on time and on budget. www.iffresearch.com.
Tips for writing a research paper outline. Tip: The key to creating a useful outline is to be consistent in your headings, organization, and levels of specificity. Be Consistent: ensure every heading has a similar tone. State the topic or write short sentences for each heading but avoid doing both.
Step 2: Develop a structure and outline. With your research question pinned down and your literature digested and catalogued, it's time to move on to planning your actual research paper. It might sound obvious, but it's really important to have some sort of rough outline in place before you start writing your paper.
A decimal outline is similar in format to the alphanumeric outline, but with a different numbering system: 1, 1.1, 1.2, etc. Text is written as short notes rather than full sentences. Example: 1 Body paragraph one. 1.1 First point. 1.1.1 Sub-point of first point. 1.1.2 Sub-point of first point.
Create a research paper outline. Write a first draft of the research paper. Write the introduction. Write a compelling body of text. Write the conclusion. The second draft. The revision process. Research paper checklist. Free lecture slides.
Here's what your qualitative research brief should include: Background. Provide a summary of the primary business the client is in, and clearly explain why the business exists, what its mission ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
What is a research briefing? A research briefing is a summary of a single piece of proper research or a series of research studies on a similar topic. A briefing is a concise and understandable consolidation of just the main points of longer, more complex, academic and often impenetrable research.
The abstract is a brief summary of the research paper, typically ranging from 100 to 250 words. It should include the research question, the methods used, the key findings, and the implications of the results. ... Research Paper Example. Note: The below example research paper is for illustrative purposes only and is not an actual research paper ...
A research brief is a statement that comes from the sponsor, who sets the objectives and background. This is to enable the researcher to plan the research and conduct an appropriate study on it. Research Brief can be as good as a market research study and is very important to a researcher. It provides good insight and influences on the choice ...
1. Craft an opening that summarizes the issue. The next part of the paper must describe the issue or problem in some detail. Start with a brief opening, usually labeled "issue" or "purpose" that describes in a sentence or two the main issue the paper focuses on and/or why you are submitting this paper. [4]
Define your specific research problem and problem statement. Highlight the novelty and contributions of the study. Give an overview of the paper's structure. The research paper introduction can vary in size and structure depending on whether your paper presents the results of original empirical research or is a review paper.
Participant characteristics - Summarize your sample's relevant demographic characteristic(s) (e.g., sex, ethnicity, ... • Only the articles cited in the Research Brief paper should appear on your reference page. • Reference page entries must have been cited in the Research Brief's narrative. If a reference is not mentioned in your
Media Files: APA Sample Student Paper , APA Sample Professional Paper This resource is enhanced by Acrobat PDF files. Download the free Acrobat Reader. Note: The APA Publication Manual, 7 th Edition specifies different formatting conventions for student and professional papers (i.e., papers written for credit in a course and papers intended for scholarly publication).
Table of contents. Step 1: Introduce your topic. Step 2: Describe the background. Step 3: Establish your research problem. Step 4: Specify your objective (s) Step 5: Map out your paper. Research paper introduction examples. Frequently asked questions about the research paper introduction.
Research Paper Example Outline. Before you plan on writing a well-researched paper, make a rough draft. An outline can be a great help when it comes to organizing vast amounts of research material for your paper. Here is an outline of a research paper example: I. Title Page. A. Title of the Research Paper.
Policy Briefs 101: A Guide for Translating Research Findings into Policy Impact. This guide was developed to accompany a training the California Policy Lab conducted with the Community Engagement and Research Program at UCLA in March 2023. It is meant to provide an introduction to policy brief writing with additional resources linked throughout.
Essay Example: The realm of scientific research is a testament to human curiosity and our relentless pursuit of knowledge. Yet, within this quest for understanding, there lies a shadow side — unethical research practices. These are not just minor infractions or benign oversights; they ... Research Paper: Words: 391: Date added: 2024/04/22:
Kandi first became popular in the early 1990s when rave culture began to flourish in the United States. Originating from underground scenes in urban centers like Los Angeles and San Francisco, kandi was inspired by a mix of DIY fashion, the vibrant aesthetics of the 1960s and 70s countercultures, and a desire to create visible tokens of rave ...
While AI private investment has steadily dropped since 2021, generative AI is gaining steam. In 2023, the sector attracted $25.2 billion, nearly ninefold the investment of 2022 and about 30 times the amount from 2019 (call it the ChatGPT effect). Generative AI accounted for over a quarter of all AI-related private investments in 2023.
Research proposal examples. Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management".
We introduce VASA, a framework for generating lifelike talking faces of virtual characters with appealing visual affective skills (VAS), given a single static image and a speech audio clip. Our premiere model, VASA-1, is capable of not only producing lip movements that are exquisitely synchronized with the audio, but also capturing a large ...
BR-ePaper | Apr 23, 2024 | Page Brief Recordings Page 11. اردو. EpaperBrecorder. Apr 23, 2024اردو PRINT EDITION BR MARKETS Dollar to PKR . Home Latest BR Research Markets Business World Editorials Opinion Perspectives Technology Life & Style Sports Pakistan Supplements Print.
The first question asks for a ready-made solution, and is not focused or researchable. The second question is a clearer comparative question, but note that it may not be practically feasible. For a smaller research project or thesis, it could be narrowed down further to focus on the effectiveness of drunk driving laws in just one or two countries.