Modular Learning: 8 Tips for Effective Online Teaching
Table of contents.
Due to the COVID-19 pandemic, many teachers in affected areas worldwide suddenly faced the task of getting their instructional materials ready to facilitate modular learning as a strategy for the sustained delivery of education to their students. I am one of these teachers, but the possibility of teaching the students exclusively online did not deter me because I have already worked on my instructional modules designed for online delivery.
Since 2012, and during COVID-19 times, I gradually developed a learning model for effective modular learning. I call it the Blended Website Learning Model, an innovative learning system that I immediately put to use at the beginning of the pandemic.
So if you’re someone willing to innovate in your modular learning approach and make the teaching and learning process more efficient and less time-consuming, I dedicate this article to you. You may work on the tips gradually until you become comfortable with them.
Once you can apply these eight tips to your classes, I assure you that you will not be spending endless hours checking your papers and getting frustrated with the inability of your students to keep up. Once in place, you will spend less effort and time to work on your instructional materials for modular learning in the new normal.
Besides, today’s trends follow a digital path as global technological innovations occur at light speed. Teachers have to keep up to be relevant.
Given the experience I gathered through the years, I would like to share eight tips on modular learning. These tips will somehow ease the teachers’ struggle for something they are not mentally and technically ready to face. The pandemic has changed the way teaching is carried out.
I start this discussion by defining modular learning, asynchronous versus asynchronous delivery of lessons, problems encountered, and solutions to those problems.
Earlier, I synthesized the lessons learned and the corresponding fixes in a learning model – the Blended Website Learning Model for more effective achievement of desired learning outcomes or most essential learning competencies (MELCs) for each course. You may refer to this model later on.

What is Modular Learning?
Modular learning, as the word connotes, uses learning modules that facilitate student learning by themselves. Modular learning is a form of distance learning that uses Self-Learning Modules (SLM) based on the most essential learning competencies (MELCS) developed by the teachers with the aid of curriculum developers.
The modules include sections on motivation and assessment that serve as teachers’ and students’ guides to achieve desired competencies. Feedback mechanisms aid teachers in monitoring student achievement and identify those who require follow-up interventions.
Self-paced learning modules can educate learners through carefully written guideposts that direct the learner on what action to take. The contents of the learning module follow a particular learning model that makes instruction effective.
Upon our department chair’s advice, I used the 4H or Experiential Learning Model (ELM) based on the Experiential Learning Theory developed by educators for more than a century. I am not an education graduate. Hence, I have to study ELM carefully.
8 Tips to Achieve the Course Outcomes in Modular Learning
1. write your instructional tips to students online.
Teaching is a repetitive exercise. So what I did is to write articles about the lessons I teach and publish them online. I update those articles once in a while to ensure their relevance.
Although educational articles on almost anything under the sun can be found online, I find some tips lacking credibility and proper documentation. Thus, I embarked on my blogging platform (this website) to house my tips for students on specific topics I teach in the classroom.
I made sure that the tips I gave use the latest information or reliable references online for my students to refer to for further reading. Besides, many of the legitimate and well-referenced material are behind a paywall which my students do not have the means to purchase. Nevertheless, there are free, open-access articles that anyone can access with extra effort.
2. Compress and upload instructional materials on a fast-loading website
I uploaded all of my instructional modules in pdf on a fast-loading website I created at the beginning of the pandemic. I compress each module in the free pdf compressor provided by ilovepdf.com . Compressing the modules makes downloading into students’ smartphones easy. The small files also save them bandwidth, thus reduced data consumption in their internet subscription.
I studied website development for quite a while, anticipating the emphasis on modular learning in the future. I started with Webnode sometime in 2012. Webnode uses drag-and-drop technology, which works for a beginning website developer like me. I even purchased a domain name for my free account on that website.
However, after several years of use, I found the technology lacks the flexibility I need. I want to maintain an independent website without the costly upgrades when the traffic exceeds my subscription. Hence, I shifted to an independently hosted WordPress.org Content Management System (CMS) platform. But not before I practiced in the WordPress.com website.
WordPress as a Tool in Modular Learning
I used WordPress to develop the simple but fast-loading website that students can easily load on their cellphones. It scores an almost perfect speed of 99% in both mobile and desktop (Figure 1).
I used Neve, a WordPress theme with no frills nor bloat software, to delay loading. All instructional modules are instantly available to students after entering the password I gave them.
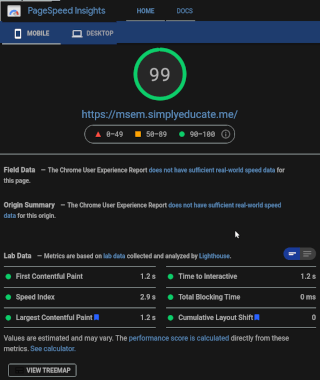
The instructional material website simply works. No frills, no fuss.
Anyone can easily create a WordPress website in minutes. Just have your email and password ready to create an account in WordPress.com for free. You can create your website later, like what I did when I first started. As you practice using the free WordPress website, you will get to be familiar with how websites work.
You may listen to the simple instruction in the video I give below. Knowing how to create your website will give you more opportunities to become digitally savvy. Modular learning will be much more easily as you gain experience and expertise.
3. Use a Learning Management System to assess student performance
I had a limited two-day training on the use of Moodle before the COVID-19 pandemic began. By a stroke of luck, I could use the LMS as a modular learning tool in the middle of the semester when the government declared a nationwide Enhanced Community Quarantine (ECQ) to stem the brewing spread of the dreaded virus.
Using a Learning Management System (LMS) such as the free, open-source Modular Object-Oriented Dynamic Learning Environment (MOODLE) can help a lot in designing quizzes and periodic examinations. The once time-consuming task of checking the students’ quizzes and periodic examinations is done real time.
Using a Learning Management System (LMS) such as the free, open-source Modular Object-Oriented Dynamic Learning Environment (Moodle™) can help a lot in designing quizzes and periodic examinations. The once time-consuming task of checking the students’ quizzes and periodic examinations is done real time .
Students get their quiz or exam results in a matter of seconds. Once they submit their quiz, long exam, or midterm or final exam, they get the results right away.
I give students two chances of taking the quiz or major examination, mindful of the glitch that students experience while taking the assessment. Last semester, the internet connection of some students break while taking the quiz. Hence, it is good practice to give them another chance. Further, giving the students another chance to take the quiz provides them an opportunity to correct their answers and establish mastery of the subject matter.
I pushed my knowledge of Moodle further, not by just being a user, but by studying the process of its installation, mainly as part of my hobby and partly as a challenge to create a website to house the LMS myself. Having my own Moodle site gives me the independence and freedom to innovate.
I realized I can create an independent Moodle site on my GoDaddy server. In short, I figured that the only thing I need to put Moodle to work was to register a unique domain name. I hosted Moodle in the same platform where my blogging site, Simplyeducate.me, is being hosted. The LMS had virtually a free ride as a sub-domain.
I don’t mind spending a little more for my convenience. It’s an investment to save time and effort. In addition, I learn and enjoy the new functionality as I implement the system.
Moodle takes time to load; it’s slow
Although Moodle was designed to house complete learning modules for learners, my students have trouble accessing it. I had the impression that Moodle, being an open source project, had too many functionalities that made it heavy to load. Also, many of my students use cellphones in accessing the lessons online.
After spending considerable time looking for answers online and tweaking the Moodle website, I gave up, even though I successfully enhanced the speed of the LMS. I cannot make the Moodle site load faster without adding more investment in Random Access Memory (RAM) capacities and having it work on a Solid State Drive (SSD). I have a limited budget for this expense.
But Moodle is a good performance assessment site that enhances modular learning
I found the assessment function of Moodle very useful, so I kept it as an assessment site that students will log on once they are ready. Another advantage is that the LMS enables me to prepare my quizzes easily and checks the quizzes and periodic exams automatically. I just record the points my students get in Excel to give the corresponding percentages on the different assessment criteria.
That functionality surely saved me time in checking the students’ performance. It’s even better than administering questions in a face-to-face learning session. It worked well for me serving as an assessment site. I just set the period wherein the quiz will be available to students.
Also, the system can shuffle the questions and the answers in the exam. Each student has a different set of questions and answers, ensuring a unique performance record.
4. Conduct regular short synchronous meetings to remind and update the students
I conduct regular, synchronous meetings with my students to give them a feel of classroom ambiance; it simulates a face-to-face interaction. While most of my students can attend the meeting via Zoom, a video teleconferencing software program, several of them could not connect to the internet for valid reasons.
Among the valid reasons I have learned from my students for their inability to connect during synchronous meetings are the following:
- poor internet connection,
- exhausted data allocation,
- attending to emergencies, and
Recording of synchronous meetings
Recognizing these student difficulties, I always record the proceedings of the synchronous meetings. I upload the zoom video in MP4 format in mediafire.com , the cloud service I have been using for easy access. Then I provide a link to the fast website I created for the instructional materials.
Once the students have the opportunity to go online after resolving their issues during synchronous meetings, they are able to access the proceedings of the meeting. The poor internet connection can be remedied by going online during non-peak hours. Midnight until the early hours of the morning appears to have fewer users online.
The recorded videos do not last more than an hour. Making them short saves bandwidth as well as limits file size to a manageable size that students can download with ease.
5. Follow-up students through Messenger
Almost everyone has an account on Facebook together with Messenger nowadays. I tell my students to communicate with me through Messenger if there are concerns that they need me to know.
During Zoom sessions, some students could not easily express their burdens while others listen. Hence, they can send private messages to prevent getting embarrassed for their queries.
Since most of my work is done online, I can readily see the notifications that I have messages from my students. I consider the communication part of my consultation time. It also presents an opportunity to empathize with the students on their unique concerns.
So far, Messenger has become an effective tool to connect with students and give them support, especially in crucial times. Also, it is easy to find them online if I need to issue additional instructions related to the subjects I teach.
6. Use an Ishikawa diagram to contextualize the Most Essential Learning Outcomes
Given the considerable time that students have to devote to keeping up with their subjects, I design my modules as briefly as I can muster without sacrificing the essential outcomes of the modules. I present these outcomes in an Ishikawa or fishbone diagram at the beginning of the semester.
Figure 2 presents an Ishikawa diagram showing the learning outcomes I prepared for my students. The diagram visualizes the expected competencies that students could gain during the semester. Guided by the outline, they will see their pace in context while performing the tasks at hand. Seeing the goal serves as motivation for them to go on.
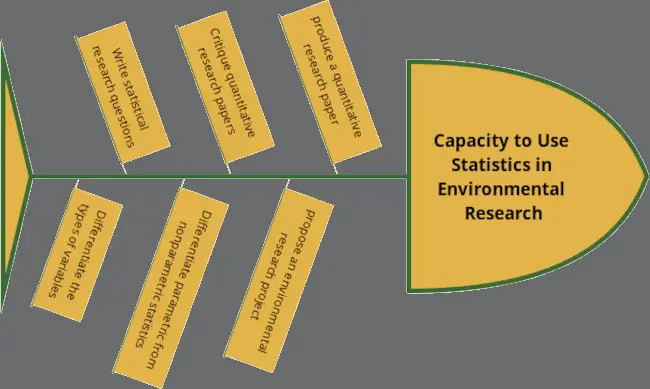
The fishbone diagram motivates the students concerning the overall outcome of the things that they do each learning session. One learning activity progresses to another one that leads towards the goal of learning.
Hence, the process of modular learning becomes meaningful to students. Incremental, modular learning transpires.
7. Give generous time for achievement of MELCs
I give a generous time of at least two weeks for students to achieve the expected learning outcomes. Giving them leeway to perform and reflect on their assigned tasks facilitates retention and helps them perform at their very best.
Writing many tasks without enough time to ponder or reflect on their work leads to a half-baked performance. Thus, less than stellar work dampens the motivation to do things in the best way they can.
Seeing some prescribed MELCs as part of modular learning online, I get the impression that they’re more applicable to face-to-face interactions. Chances are, the students become overstressed with tasks to do without the focused guidance of their teachers, making online learning a mechanical activity fixated on compliance.
8. Use a Feedback table
To keep track of student performance and encourage them to perform within the time frame, I prepared a feedback table to show what stage they were already in. Whenever I meet the students during synchronous meetings, I present the feedback table to the class and ask them if I have recorded their submissions correctly.
Some of my students would tell me they have submitted, but I could not verify their submissions. Perhaps failing to upload is due to a poor internet connection. Given the real-time feedback I get via Messenger, they try again until they have successfully uploaded. I confirm that I have received their outputs. Thus, the student’s anxiety because of failure to upload the required submissions is eliminated or minimized.
The feedback table finds support in Dr. Tali Sharot’s book on changing people’s behavior. It emphasizes the importance of feedback to change people’s behavior.
I invite you to listen to the highly motivating speech of Dr. Sharot in TED Talk that can change not only your student’s behavior towards the assigned tasks but also your ingrained habits. The lecture emphasizes the importance of feedback.
The feedback table instantly tells me potential problems and takes corrective measures before they get worse. Students exert more effort to keep up with their classmates once they notice that some of their classmates have already accomplished the modules. Modular learning becomes more effective with a monitoring system like this.
Figure 3 provides an example of a feedback table where you can quickly troubleshoot submission problems and ensure that no student is left behind.
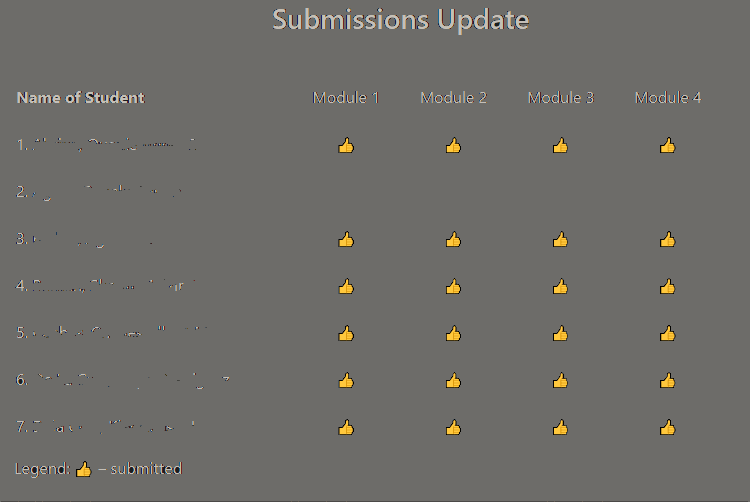

Modular Learning is here to Stay
Whether the pandemic will last for quite a time, online modular learning will become the norm rather than an exception. The educational system has already shifted to Education 4, in tune with Industry 4.0 , where interconnectivity through the Internet of Things (IoT), lies at its core.
Despite the setbacks experienced by teachers on the effects of modular learning , we must be progressive in our thinking. The challenges are not without answers as technology progresses. Most students can access a laptop, or virtually everyone can access a cell phone, to download educational materials like the ones I make available on my IM website.
Although some of my students are hundreds of miles away, or even on an island, they can still access my instructional modules using their cell phones. I make online learning easy for them by applying the tips I previously gave—make the website load faster by compressing images and videos and make my instructional modules simpler to follow. I focus on a few but crucial and most essential learning outcomes.
Stop being bookish. This time it’s online learning, not face-to-face classes where you cram in everything you want to the detriment of your students.
A 30-minute or less synchronous meeting is more than enough to brief your students about the module, the expected learning outcomes, and ask a few questions to get their feedback on the modules and constraints on their performance.
Advanced countries are already eyeing the many uses of machine learning , and interest is growing in getting a degree in this field. Are our students ready to become part of this technological development?
In the information age, teachers are no longer what they used to be. We are now facilitators and innovators of learning through online modular learning as the information age changed the way people gain information.
We must undo the belief that we are the authorities of knowledge. Digital technology has shaped how we live, learn, and navigate this increasingly automated world.
Kudos to all teachers! Let’s rock the world of online modular learning.
© P. A. Regoniel 22 June 2021
Related Posts

Choosing the Right Topic: How to Find Inspiration for Your Research Paper

MA in Curriculum and Instruction: 5 Key Benefits

A Study on the Vision and Mission of the Palawan State University and the Goals and Program Objectives of its Graduate School
About the author, patrick regoniel.
Dr. Regoniel, a faculty member of the graduate school, served as consultant to various environmental research and development projects covering issues and concerns on climate change, coral reef resources and management, economic valuation of environmental and natural resources, mining, and waste management and pollution. He has extensive experience on applied statistics, systems modelling and analysis, an avid practitioner of LaTeX, and a multidisciplinary web developer. He leverages pioneering AI-powered content creation tools to produce unique and comprehensive articles in this website.
Thank you for your comment. Teaching in the new normal requires constant innovation and a change in mindset.
Thank you so much for sharing this! The different modes of learning in this new normal are somehow confusing, but this really helped. I also appreciate the tips you gave on how to teach effectively in modular learning!
SimplyEducate.Me Privacy Policy

Creating Manageable and Flexible Learning Pathways With Modularization
What are modules.
A module is a cohesive and stand-alone unit of learning that has specific start and end points.
Most educators already take a modular approach to teaching. For example, breaking a course down into purposeful “units” or “sessions” helps learners, especially novices, focus attention so they can remember what they are learning better and build their knowledge over time. This process is sometimes referred to as “chunking” (Mayer & Moreno, 2003). Modules include both content and activities designed to help the learners apply and integrate their learning. This diagram provides a visualization of a potential structure for a module of learning.
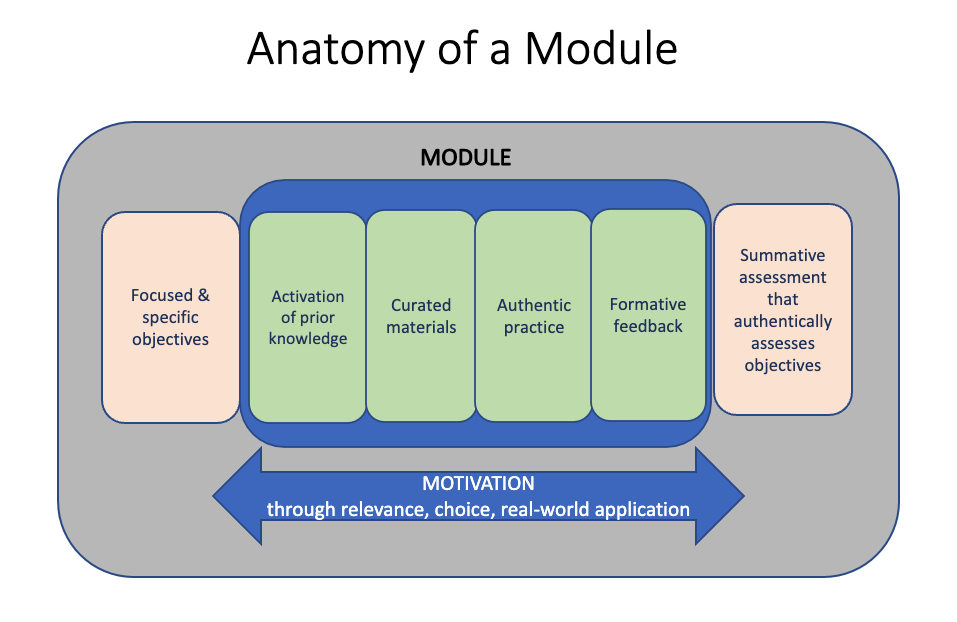
Students are more likely to get the most out of a module if all the materials and activities are bundled together in an easily accessible space, such as a Canvas course. This makes it possible for them to revisit the materials and activities as often as needed and check their understanding.
Modularization is a process that extends the idea of modules to offer learners flexible pathways while also continuing to engage them in a purposeful learning experience. These pathways may take place within a semester-long course, or they may be offered as a one-credit or non-credit badged experience.
For example:
- In a course, all students complete a sequence of foundational modules and then have the option of selecting from a library of topical modules to pursue a personal interest in more depth. This increases learners’ engagement and creates opportunities for them to share the specialized knowledge they have gained with the rest of the class. Providing students with choice can increase student motivation, and offering multiple ways to demonstrate knowledge creates a more inclusive learning experience (Ambrose et al., 2010; Addy et al., 2021).
- Some skills and concepts are important to many fields (e.g., lab safety, ethical research). Offering one module, or a sequence of shared modules, assures that the orientation and assessment of student learning in a specific area is consistent across multiple contexts.
- Students on co-op may not have the time to take a semester-long course, but they may benefit from a short and timely burst of learning that will be helpful to their work (e.g., learning an in-demand skill or process). What they learn will also be perceived as more relevant because they can see that the skill or process is valued and often used in their place of work.
- Examine the syllabi for all the courses you teach. If possible, do this with several colleagues in your department or discipline. Do any concepts or skills span multiple courses? If so, consider how you might collaborate to create one or more modules that could be shared. Note that modules created in Canvas can be easily imported across courses.
- If you develop a module that you think might be valuable to others, consider uploading it to the Canvas Commons so that other Northeastern instructors can benefit from your work.
- Set aside class time to talk with learners about modular resources that would be valuable to them. Perhaps you could partner with them to create one or more modules, or perhaps they could even take responsibility for creating a module for others in the class or even beyond the class.
References:
Addy, T. Dube, D., Mitchell, K. A., & SoRelle, M. E. (2021). What inclusive instructors do: Principles and practices for excellence in college teaching (First edition.). Stylus Publishing, LLC.
Ambrose, S., Bridges, M., DiPietro, M., Lovett, M., & Norman, M. (2010). How learning works: Seven research-based principles for smart teaching (1st ed.). Jossey-Bass.
Mayer, R & Moreno, R. (2003). Nine ways to reduce cognitive load in multimedia learning, Educational Psychologist . 38 (1) 43-52. DOI: 10.1207/S15326985EP3801_6
Understanding Modular Learning
Learn about Modular Learning in this educational glossary entry.
Modular learning is a teaching and learning approach that breaks down a course or curriculum into smaller, self-contained units known as modules. Each module focuses on a specific topic or skill, allowing learners to study and master one concept at a time before moving on to the next. This modular structure provides flexibility and customization, enabling students to progress at their own pace and revisit specific modules as needed.
Key Features of Modular Learning
Modular learning is characterized by several key features that distinguish it from traditional classroom-based education:
- Self-contained Units: Modules are self-contained learning units that cover a specific topic or skill. This compartmentalization allows for focused study and clear learning objectives.
- Flexibility: Learners have the flexibility to choose the sequence in which they study modules, enabling personalized learning paths based on individual needs and preferences.
- Adaptive Learning: Modular learning can be adaptive, with learners progressing to more advanced modules based on their mastery of prerequisite concepts.
- Reusability: Modules can be reused across different courses or programs, making it easier to update and customize learning materials.
- Assessment: Assessments are often integrated into each module to evaluate learner understanding and mastery of the content.
- Interactivity: Modular learning can incorporate various interactive elements such as quizzes, simulations, and multimedia resources to enhance engagement and retention.
Benefits of Modular Learning
Modular learning offers several benefits for both educators and learners:
- Customization: Learners can tailor their learning experience by selecting modules that align with their interests, goals, and learning styles.
- Self-paced Learning: Modular learning allows learners to progress at their own pace, providing opportunities for remediation and extension as needed.
- Enhanced Retention: Breaking down complex topics into smaller modules can improve retention and understanding by focusing on one concept at a time.
- Accessibility: Modular learning can be delivered online, making education more accessible to learners who may not have access to traditional classroom settings.
- Scalability: Institutions can scale their educational offerings more effectively by modularizing courses and programs, making it easier to update content and adapt to changing needs.
- Engagement: Interactive elements in modular learning can enhance learner engagement and motivation, leading to a more immersive learning experience.
Implementation of Modular Learning
Implementing modular learning effectively requires careful planning and design to ensure a seamless learning experience for students. Here are some key considerations for implementing modular learning:
- Curriculum Design: Designing modular courses involves breaking down the curriculum into logical units that align with learning objectives and outcomes.
- Sequencing: Determine the sequence in which modules should be studied to ensure a cohesive learning progression and build on prior knowledge.
- Assessment: Develop assessments that align with module objectives and provide feedback to learners on their progress and understanding.
- Resources: Ensure that each module has the necessary resources, including readings, videos, and interactive tools, to support learning objectives.
- Technology: Utilize learning management systems and online platforms to deliver modular content and track learner progress efficiently.
- Support: Provide support mechanisms such as discussion forums, tutoring services, and office hours to assist learners as they engage with modular content.
Examples of Modular Learning
Modular learning is widely used across various educational settings and disciplines. Here are some examples of how modular learning is implemented:
- Language Learning: Language learning apps often use modular lessons to teach vocabulary, grammar, and conversation skills in a structured and sequential manner.
- Professional Development: Online courses for professional development often feature modular content that allows learners to focus on specific skills or topics relevant to their careers.
- STEM Education: Science, technology, engineering, and mathematics (STEM) programs frequently use modular learning to teach complex concepts in a step-by-step approach.
- Corporate Training: Many organizations use modular training programs to deliver employee training on topics such as compliance, safety, and leadership development.
- Higher Education: Universities and colleges are increasingly adopting modular learning approaches to offer flexible and personalized learning experiences for students.
Modular learning is a versatile and effective approach to teaching and learning that offers numerous benefits for educators and learners alike. By breaking down courses into self-contained modules, modular learning provides flexibility, customization, and enhanced engagement, leading to a more personalized and impactful learning experience. As technology continues to advance, modular learning is likely to play an increasingly prominent role in education, offering new opportunities for innovation and improvement in teaching and learning practices.
Help Learning Corner Get Better
Got suggestions or feedback? Let us know through this form or drop us a comment on Facebook .
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
Modular Distance Learning
- Most Cited Papers
- Most Downloaded Papers
- Newest Papers
- Save to Library
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- Academia.edu Publishing
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

COMMENTS
ABSTRACT. Education in the new normal is a challenging task in the Philippines in an attempt to push through education amidst. the deadly pandemic caused by covid-19. The Department of Education ...
The purpose of this descriptive paper was to explore and synthesize literature related to understanding modular learning and how it can be implemented effectively so faculty members embrace its use. An in-depth review of literature addressed topics including, Educational Theories supporting modular learning, the development of modular learning,
8 Tips to Achieve the Course Outcomes in Modular Learning. 1. Write your instructional tips to students online. 2. Compress and upload instructional materials on a fast-loading website. WordPress as a Tool in Modular Learning. 3. Use a Learning Management System to assess student performance.
Modular distance learning has been found to enhance family ties, promote independent learning, and be cost-effective for ensuring continuous learning continuity (Dargo et al., 2021). ...
The coronavirus pandemic (COVID-19) is a global health crisis that has affected educational systems worldwide. North Eastern Mindanao State University (NEMSU), a typical countryside academic institution in the Southern Philippines, did not escape this dilemma. The advent of remote learning to continue the students' learning process has caused difficulties for both the students and the ...
What are modules? A module is a cohesive and stand-alone unit of learning that has specific start and end points.. Most educators already take a modular approach to teaching. For example, breaking a course down into purposeful "units" or "sessions" helps learners, especially novices, focus attention so they can remember what they are learning better and build their knowledge over time.
Modular learning is a teaching and learning approach that breaks down a course or curriculum into smaller, self-contained units known as modules. Each module focuses on a specific topic or skill, allowing learners to study and master one concept at a time before moving on to the next. This modular structure provides flexibility and ...
This study aimed to determine the effectiveness of the modular learning approach to students' academic performance. The study was conducted in Sta. Cruz District in the province of Zambales, Philippines. A Descriptive Research Design was employed. A total of one hundred fifty-four (154) teacher-respondents were randomly selected.
Step 1. Familiarize yourself a little bit with modular learning. Listening to a podcast or a great book about modular learning is a helpful way to understand concretely how it works, how it fits into developmental psychology and learning theories and get you clear on what you want to get out of this experience.
Abstract. The pandemic of COVID-19 has become a global health issue and has had a significant influence on education. The study employed a survey design. The degree to which social media was used for learning was the independent variable. The study used a researcher-made questionnaire to gather the data on the experiences of college students to ...
Additionally, because modular learning allows students to learn at their own pace, it can help reduce feelings of frustration and boredom that can occur when students cannot keep up with the pace of a traditional classroom. 2. Builds Confidence. Another significant impact of modular learning on students is that it builds their confidence.
View Modular Distance Learning Research Papers on Academia.edu for free. ... Modular learning is the most popular type of Distance Learning in the new-normal era. In the Philippines, this learning modality is currently used by all public schools. ... the questions and learning activity sheets were made by the researcher to determine the ...
Table 1A presents the extent of implementation of delivery of instruction on modular learning modality. It was revealed on the table that the extent of implementation of delivery of instruction on modular learning modality has an overall mean of 4.2 with standard deviation of 0.26 which is interpreted as high.
Parents play a vital role as home facilitators. Their primary role in modular learning is to establish a connection and guide the child. (FlipScience, 2020). According to the Department of Education (DepEd), parents and guardians' perform the various roles in Modular Learning such as Module-ator, Bundy-clock, and as Home Innovator. As a
Here are five sentences that are true and relevant about modular learning: 1. Modular learning is an educational approach that breaks down the curriculum into smaller, self-contained units or modules. 2. Each module focuses on a specific topic or skill, allowing students to learn and master one concept at a time before progressing to the next ...
Both modular learning and online learning can be effective in language and science subjects, but their effectiveness depends on various factors. In language subjects such as English, French, German, and Spanish, online learning can be more effective as it offers interactive language exercises, online language labs, and opportunities for real ...
To consider the learners in rural areas where the internet is inaccessible for online l earning, the Modular. Learning modality is currently used by all public schools in the Philippines. Modular ...
Brainly is the knowledge-sharing community where hundreds of millions of students and experts put their heads together to crack their toughest homework questions. Brainly - Learning, Your Way. - Homework Help, AI Tutor & Test Prep
A I. Modular learning gives varied experiences for both students and parents. A. Modular learning has its positive impact. ... what is the set of questions used to gather information in a survey she asked me to leave the room quetly. 1. She quickly agreed to go to the store for milk. ... Get the Brainly App Download iOS App
Abstract. This study was conducted to determine the effectiveness of the modular instruction modality of Central Philippines State University in the lens of students. This study employed a ...
Example of quantitative research tittle related modular learning . See answer. Advertisement. whymeeeeee. Answer: Impact of Modular Learning System in Teachers and Students of ( the place that you do the survey) as part of the new normal. thank you. yes. bawal ba?