Common Characteristics of Developing Countries | Economics
Following are some of the basic and important characteristics which are common to all developing economies:
An idea of the characteristics of a developing economy must have been gathered from the above analysis of the definitions of an underdeveloped economy. Various developing countries differ a good deal from each other. Some countries such as countries of Africa do not face problem of rapid population growth, others have to cope with the consequences of rapid population growth. Some developing countries are largely dependent on exports of primary products, others do not show such dependence, and others do not show such dependence.
Some developing countries have weak institutional structure such as lack of property rights, absence of the rule of law and political instability which affect incentives to invest. Besides, there are lot of differences with regard to levels of education, health, food production and availability of natural resources. However, despite this great diversity there are many common features of the developing economies. It is because of common characteristics that their developmental problems are studied within a common analytical framework of development economics.

Characteristic # 1. Low Per Capita Income :
ADVERTISEMENTS:
The first important feature of the developing countries is their low per capita income. According to the World Bank estimates for the year 1995, average per capita income of the low income countries is $ 430 as compared to $ 24,930 of the high-income countries including U.S.A., U.K., France and Japan. According to these estimates for the year 1995, per capita income was $340 in India, $ 620 in China, $240 in Bangladesh, $ 700 in Sri Lanka. As against these, for the year 1995 per capita income was $ 26,980 in USA, $ 23,750 in Sweden, $ 39,640 in Japan and 40,630 in Switzerland.
It may however be noted that the extent of poverty prevailing in the developing countries is not fully reflected in the per capita income which is only an average income and also includes the incomes of the rich also. Large inequalities in income distribution prevailing in these economies have made the lives of the people more miserable. A large bulk of population of these countries lives below the poverty line.
For example, the recent estimates reveal that about 28 per cent of India’s population (i.e. about 260 million people) lives below the poverty line, that is, they are unable to get even sufficient calories of food needed for minimum subsistence, not to speak of minimum clothing and housing facilities. The situation in other developing countries is no better.
The low levels of per capita income and poverty in developing countries is due to low levels of productivity in various fields of production. The low levels of productivity in the developing economies has been caused by dominance of low-productivity agriculture and informal sectors in their economies, low levels of capital formation – both physical and human (education, health), lack of technological progress, rapid population growth which are in fact the very characteristics of the underdeveloped nature of the developing economies. By utilising their natural resources accelerating rate of capital formation and making progress in technology they can increase their levels of productivity and income and break the vicious circle of poverty operating in them.
It may however be noted that after the Second World War and with getting political freedom from colonial rule, in a good number of the underdeveloped countries the process of growth has been started and their gross domestic product (GDP) and per capita income are increasing.
Characteristic # 2. Excessive Dependence on Agriculture :
A developing country is generally predominantly agricultural. About 60 to 75 per cent of its population depends on agriculture and its allied activities for its livelihood. Further, about 30 to 50 per cent of national income of these countries is obtained from agriculture alone. This excessive dependence on agriculture is the result of low productivity and backwardness of their agriculture and lack of modern industrial growth.
In the present-day developed countries, the modern industrial growth brought about structural transformation with the proportion of working population engaged in agriculture falling drastically and that employed in the modern industrial and services sectors rising enormously. This occurred due to the rapid growth of the modern sector on the one hand and tremendous rise in productivity in agriculture on the other.
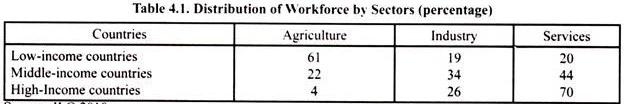
The dominance of agriculture in developing countries can be known from the distribution of their workforce by sectors. According to estimates made by ILO given in Table 4.1 on an average 61 per cent of workforce of low-income developing countries was employed in agriculture whereas only 19 per cent in industry and 20 per cent in services. On the contrary, in high income, that is, developed countries only 4 per cent of their workforce is employed in agriculture, while 26 per cent of their workforce is employed in industry and 70 per cent in services.
IvyPanda . (2023) '119 Developing Countries Essay Topic Ideas & Examples'. 26 September.
IvyPanda . 2023. "119 Developing Countries Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." September 26, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/developing-countries-essay-topics/.
1. IvyPanda . "119 Developing Countries Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." September 26, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/developing-countries-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
IvyPanda . "119 Developing Countries Essay Topic Ideas & Examples." September 26, 2023. https://ivypanda.com/essays/topic/developing-countries-essay-topics/.
- Agriculture Essay Ideas
- Capitalism Paper Topics
- Deforestation Research Ideas
- Child Labour Research Topics
- Equality Topics
- Famine Essay Titles
- Gender Discrimination Research Topics
- Macroeconomics Topics
The countries in which the process of development has started but is not completed, have a developing phase of different economic aspects or dimensions like per capita income or GDP per capita, human development index (HDI), living standards, fulfillment of basic needs, and so on. The UN identifies developing countries as a country with a relatively low standard of living, underdeveloped industrial bases, and moderate to low human development index. Therefore, developing nations are those nations of the world, which have lower per capita income as compared to developed nations like the USA, Germany, China, Japan, etc. Here we will discuss the different characteristics of developing countries of the world.
Developing countries have been suffering from common attributes like mass poverty, high population growth, lower living standards, illiteracy, unemployment and underemployment, underutilization of resources, socio-political variability, lack of good governance, uncertainty, and vulnerability, low access to finance, and so on.
Developing countries are sometimes also known as underdeveloped countries or poor countries or third-world countries or less developed countries or backward countries. These countries are in a hurry for economic development by utilizing their resources. However, they are lagging in the race of development and instability. The degree of uncertainty and vulnerability in these countries may differ from one to another but all are facing some degree of susceptibility and struggle to develop.
The common characteristics of developing nations are briefly explained below.
Major Characteristics of Developing Countries
Low Per Capita Real Income
The real per capita income of developing countries is very low as compared to developed countries. This means the average income or per person income of developing nations is little and it is not sufficient to invest or save. Therefore, low per capita income in developing countries results in low savings, and low investment and ultimately creates a vicious cycle of poverty. This is one of the most serious problems faced by underdeveloped countries.
Mass Poverty
Most individuals in developing nations have been suffering from the problem of poverty. They are not able to fulfill even their basic needs. The low per capita in developing nations also reflects the problem of poverty. So, poverty in underdeveloped countries is seen in terms of lack of fulfillment of basic needs, illiteracy, unemployment, and lack of other socio-economic participation and access apart from low per capita income.
Rapid Population Growth
Developing countries have either a high population growth rate or a larger size of population. There are different factors behind higher population growth in developing countries. The higher child and infant mortality rates in such countries compel people to feel insured and give birth to more children. Lack of family planning education and options, lack of sex education, and belief that additional kids mean additional labor force and additional labor force means additional income and wealth, etc. also stimulate people in developing countries to give birth to more children. This is also supported by the thought of conservatism existed in such nations.
The Problem of Unemployment and Underemployment
Unemployment and underemployment are other major problems and common features of developing or underdeveloped nations. The problem of unemployment and underemployment in developing countries is emerged due to excessive dependency on agriculture, low industrial development, lack of proper utilization of natural resources, lack of workforce planning, and so on. In developing nations, the problem of underemployment is more serious than unemployment. People are compelled to engage themselves in inferior jobs due to the non-availability of alternative sources of jobs. The underemployment problem in high extent is found especially in rural and back warded areas of such countries.
Excessive Dependence on Agriculture
The majority of the population in developing nations is engaged in the agriculture sector, especially in rural areas. Agriculture is the only sole source of income and employment in such nations. This sector has also a higher share of the gross domestic product in poor countries. In the case of the South Asian economies, more than 70 percent population is, directly and indirectly, engaged in the agriculture sector.
Technological Backwardness
The development of a nation is a positive and increasing function of innovative technology. Technological use in developing countries is very low and used technology is also outdated. This causes a high cost of production and a high capital-output ratio in underdeveloped nations. Because of the high capital-output ratio, high labor-output ratio, and low wage rates, the input productivity is low and that reduces the gross domestic product of the nations. Illiteracy, lack of proper education, lack of skill development programs, and deficiency of capital to install innovative techniques are some of the major causes of technological backwardness in developing nations.
Dualistic Economy
Duality or dualism means the existence of two sectors as the modern sector or advanced sector and the traditional or back warded sector within an economy that operates side by side. Most developing countries are characterized by the existence of dualism. Urban sectors are highly advanced and rural parts are having the problems like a lack of social and economic facilities. People in rural areas are majorly engaged in the agriculture sector and in urban areas they are in the service and industrial sectors of the economy.
Lack of Infrastructures
Infrastructural development like the development of transportation, communication, irrigation, power, financial institutions, social overheads, etc. is not well developed in developing nations. Moreover, developed infrastructure is also unmanaged, and not distributed efficiently and equitably. This has created a threat to development in such nations.
Lower Productivity
In developing nations, the productivity of factors is also low. This is due to a lack of capital and managerial skills for getting innovative technologies, and policies and managing them efficiently. Malnutrition, insufficient health care, a healthy support system, living in an unhygienic environment, poor health and work-life of workers, etc. are factors that are attributed to lower productivity in developing nations.
High Consumption and Low Saving
In developing countries, income is low and this causes a high propensity to consume, a low propensity to save and capital formation is also low. People living in such nations have been facing the problems of poverty and they are being unable to fulfill most of their needs. This will compel them to expend more portion of their income on consumption. The higher portion of consumption out of earned income results in a lower saving rate and consequently lower capital formation. Ultimately these countries will depend on foreign aid, loans, and remittance earnings that have limited utility to expand the economy.
The above-explained points show the state and characteristics of developing countries. Apart from explained points, excessive dependency on developed nations, having inadequate provisions of social services like education facilities, health facilities, safe drinking water distribution, sanitation, etc., and dependence on primary exports due to lack of development and expansion of secondary and tertiary sectors of the economy, etc. are also major characteristics of developing countries of the world. These countries are affected more severely by the economic crisis derived from the coronavirus of 2020. So, challenges to development for developing nations have been added furthermore. In a summary, the major characteristics of developing countries are presented in the following table.
Ahuja, H.L (2016). Advanced Economic Theory . New Delhi: S Chand and Company Limited.
Todaro, M.P. & Smith, S.C. (2009). Economic Development . New York: Pearson Education.
6 thoughts on “Characteristics of Developing Countries”
Pingback: Is Thailand a Developing Country? – Thailand Trip Expert
thanks for the reality points they have fully drawn a picture of poverty. my question is how can dualistic economy be handled as away of reducing poverty?
I really enjoyed reading this So true
The lesson is so nice I understand and I enjoy the lesson
The lesson is good and points are easy to understand and master Thank you for the good services
These are indicators of poverty as proposed by the Global North’s perception of poverty in Global South. Why not ask the Global South to give their voice to what define poverty in their right.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Privacy Overview
Insert/edit link.
Enter the destination URL
Or link to existing content

Characteristics of Developing Economies

Even though developing nations have very different backgrounds in terms of resources, history, demography, religion and politics, they still share a few common characteristics. Today, we will go over six common characteristics of developing economies.
Common Characteristics of Developing Economies
1. Low Per Capita Real Income
Low per capita real income is one of the most defining characteristics of developing economies. They suffer from low per capita real income level, which results in low savings and low investments.
It means the average person doesn’t earn enough money to invest or save money. They spend whatever they make. Thus, it creates a cycle of poverty that most of the population struggles to escape. The percentage of people in absolute poverty (the minimum income level) is high in developing countries.
2. High Population Growth Rate
Another common characteristic of developing countries is that they either have high population growth rates or large populations. Often, this is because of a lack of family planning options and the belief that more children could result in a higher labor force for the family to earn income. This increase in recent decades could be because of higher birth rates and reduced death rates through improved health care.
3. High Rates of Unemployment
In rural areas, unemployment suffers from large seasonal variations. However, unemployment is a more complex problem requiring policies beyond traditional fixes.
4. Dependence on Primary Sector
Almost 75% of the population of low-income countries is rurally based. As income levels rise, the structure of demand changes, which leads to a rise in the manufacturing sector and then the services sector.
5. Dependence on Exports of Primary Commodities
Since a significant portion of output originates from the primary sector, a large portion of exports is also from the primary sector. For example, copper accounts for two-thirds of Zambia’s exports.
Similar Posts:
- Cyclical Unemployment
- Frictional Unemployment
- Structural Unemployment
- Economies of Scale
- The Demographic Transition Model
2 thoughts on “Characteristics of Developing Economies”
Thank you intelligenteconomist.com i love you all! This helped me pass my test and I THINK I want to live again. ps. very sad whats happening in the world.. ;(
To what extent would it be argued that all developing countries share same set of characteristics
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Characteristics of Developing Countries

Related Papers
Mohammad Younus
Mehrab Khan
The purpose of this study is to analyze the relationship between growth in agricultural sector and poverty in Pakistan. It explores that how much the poor people have gained from growth in agricultural sector of Pakistan by considering growth magnitude and benefits obtained by the poor people resulting from growth for the period of 1985 to 2005 through applying OLS Regression Technique. The results indicate that the variable of growth in agricultural sector is significantly and negatively associated with the variable of poverty, i.e., the growth in agricultural sector of Pakistan will result in reducing the level of poverty in Pakistan.
Muhammad Ali
Tahir Hasnain
muhammad hammad
Anwar Chishti
muhammad darban
Lahore Journal of Economics
Turab Hussain
Lahore University of Management Sciences Opp. Sector 'U', DHA, Lahore Cantt. 54792, Lahore, Pakistan Tel.: 92-42-5722670-79, x4222, 4201 Fax: 92-42-5722591 Website: www.lums.edu.pk/cmer ... This paper addresses two topics which essentially compliment ...
Fiaz Khattak
RELATED PAPERS
Cristina Boicu
Lahore Garrison University Journal of Life Sciences
Shanza Siddique
Journal of Economic Research
The Journal of Economic Research
08777 010 4008 JUAL ALMOND BANDAR LAMPUNG HARGA KACANG ALMOND DI TANAH ABANG harga kacang almond di tanah abang
European Heart Journal
Maurizio Parato
Canadian Journal of Civil Engineering
Nadir Touileb
Joao Victor Ribeiro
Journal of Cystic Fibrosis
Valerie Urbach
UHD Journal of Science and Technology
Rawand Raouf Abdalla H
Muniram Budhu
Isaque Siqueira
Danang Anggoro
Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society of London. Series A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences
Computer Vision – ECCV 2020 Workshops
Takamichi Miyata
Abderrahmane Zaatri
Tishreen University Journal- Arts and Humanities Sciences Series
Nagham Kikhia
Helmut Brand
Jozef Waanders , Karsten Meijer
J. Mater. Chem. B
Alessandro Donati
Histopathology
Pieter E Postmus
Proceedings of the 5th World Congress on New Technologies
caeser tapiwa
Microbial Cell Factories
paula nousiainen
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

Provide details on what you need help with along with a budget and time limit. Questions are posted anonymously and can be made 100% private.

Studypool matches you to the best tutor to help you with your question. Our tutors are highly qualified and vetted.

Your matched tutor provides personalized help according to your question details. Payment is made only after you have completed your 1-on-1 session and are satisfied with your session.

- Homework Q&A
- Become a Tutor
All Subjects
Mathematics
Programming
Health & Medical
Engineering
Computer Science
Foreign Languages
Access over 20 million homework & study documents
Characteristics of developing countries essay.
Sign up to view the full document!

24/7 Homework Help
Stuck on a homework question? Our verified tutors can answer all questions, from basic math to advanced rocket science !

Similar Documents
working on a homework question?
Studypool is powered by Microtutoring TM
Copyright © 2024. Studypool Inc.
Studypool is not sponsored or endorsed by any college or university.
Ongoing Conversations

Access over 20 million homework documents through the notebank
Get on-demand Q&A homework help from verified tutors
Read 1000s of rich book guides covering popular titles

Sign up with Google
Sign up with Facebook
Already have an account? Login
Login with Google
Login with Facebook
Don't have an account? Sign Up
- Open access
- Published: 11 May 2024
Insight into the research history and trends of total anomalous pulmonary venous connection: a bibliometric analysis
- Chen Wen 1 ,
- Geng Shen 2 ,
- Chenhao Fang 3 &
- Lan Tian 4
Journal of Cardiothoracic Surgery volume 19 , Article number: 285 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
Metrics details
Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection (TAPVC) is a rare congenital heart disease characterized by the inability of all pulmonary veins to connect to the left atrium. Our previous bibliometric article summarized the characteristics of only the 100 most cited papers in TAPVC research. The purpose of this study was to use comprehensive bibliometric analysis to examine the development history, current status, and future trends in the field of TAPVC.
All publications on TAPVC published between 2000 and 2023 were collected from the Web of Science Core Collection. The publication and citation data were quantitatively analyzed by publication year, country, institution, author, and journal. Co-authorship and co-occurrence analyses were performed using VOSviewer, and keyword and reference bursts were identified using CiteSpace. Pearson’s test was used to examine the correlations between two continuous variables.
As of July 20, 2023, we identified 368 publications with 3320 citations. These publications were published in 132 journals and authored by 1835 researchers from 457 institutions in 47 countries. For the number of publications, the top country, top institution, top author, and top journals were the United States ( n = 82), Shanghai Jiao Tong University ( n = 13), Huiwen Chen ( n = 9), and Annals of Thoracic Surgery and Pediatric Cardiology ( n = 29 each), respectively. For the number of citations, the top country, top affiliation, top author, and top journal were the United States ( n = 1348), University of Toronto ( n = 250), Christopher A. Caldarone ( n = 315), and Annals of Thoracic Surgery ( n = 746), respectively. The number of national publications significantly correlated with GDP ( R = 0.887, P < 0.001), research & development (R&D) expenditure ( R = 0.375, P = 0.013), population ( R = 0.694, P < 0.001), and journals ( R = 0.751, P < 0.001). The number of national citations significantly correlated with GDP ( R = 0.881, P < 0.001), R&D expenditure ( R = 0.446, P = 0.003), population ( R = 0.305, P = 0.037), and journals ( R = 0.917, P < 0.001). International collaboration in the field of TAPVC was not well developed. The most commonly cited publication discussed era changes in mortality and reoperation rate in TAPVC patients. The most common keywords were “total anomalous pulmonary venous connection” and “congenital heart disease”. The keyword “case report” appeared most recently, with an average occurrence year of 2021.8. The co-occurrence analysis grouped 26 keywords into six themes: surgical repair of TAPVC, postoperative pulmonary vein stenosis, surgical repair of TAPVC patients with heterotaxy, application of echocardiography in diagnosing TAPVC, application of echocardiography in the prenatal diagnosis of TAPVC, and application of the sutureless technique in the surgical repair of TAPVC patients with right atrial isomerism or a single ventricle. Citation burst detection identified 32 references with citation bursts, seven of which had ongoing citation bursts until 2023.
Conclusions
This study conducted a bibliometric analysis to provide a comprehensive overview of TAPVC research. We hope to offer new ideas for promoting development in the field of TAPVC.
Peer Review reports
Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection (TAPVC) is a rare congenital anomaly that accounts for approximately 1–3% of congenital heart disease and is characterized by the inability of all pulmonary veins to connect to the left atrium [ 1 ]. The clinical presentation depends on the severity of pulmonary venous obstruction and the size of the right-to-left shunt. Patients usually present with symptoms in early childhood and are diagnosed within one year. When preoperative pulmonary venous obstruction is absent, pulmonary blood flow returns freely to the right atrium through the anomalous pulmonary connection. Subsequently, it crosses the foramen ovale, and the patient is usually born with mild symptoms. The pulmonary vascular resistance decreases after birth, excessive pulmonary circulation occurs, and elevated volume and pressure loads are transmitted to the right heart. Patients exhibit shortness of breath, tachycardia, and feeding difficulties and suffer from severe stunted growth, with most dying within the first year of life. If preoperative pulmonary venous obstruction is present, pulmonary venous hypertension and edema progress with increased pulmonary blood flow after birth. Hypoxemia and acidosis progress as a result of reflexive pulmonary artery vasoconstriction and poor gas exchange caused by pulmonary edema, and patients even develop symptoms similar to those of respiratory distress syndrome [ 2 ]. If left untreated, the mortality rate can reach 80% in the first year of life [ 3 ]. Surgery is the only effective treatment for TAPVC, and the underlying physiology of TAPVC determines the timing of surgery and the necessity of temporary measures. Elective surgical repair of TAPVC without preoperative pulmonary venous obstruction can be performed in neonates or postponed until 3–6 months of age. TAPVC with preoperative pulmonary venous obstruction is usually repaired by emergency surgery, which can be temporarily relieved through catheterization [ 4 ]. Although progress in diagnostic techniques, surgical interventions, and perioperative management has significantly improved the perioperative survival rate, postoperative pulmonary vein stenosis (PVS) remains a great challenge and leads to a disappointing prognosis [ 5 ]. Consequently, research on TAPVC is highly important. In recent years, TAPVC has received much attention, and there is an increasing body of publications on this topic. It is essential to understand the development history, current status, and future trends in the field of TAPVC.
In recent years, bibliometric analysis has become a common tool for analyzing the characteristics of a publication, such as publication year, countries, institutions, authors, journals, citations, and keywords. This analysis method allows researchers to determine the knowledge structure, development history, and future trends in a particular field [ 6 ]. With the increase in the number of scientific publications and the importance of research influence, bibliometric analysis plays an important role in evaluating research. Although bibliometric analysis has been widely used in the medical field, to our knowledge, only one bibliometric article on TAPVC research that we published earlier is available [ 7 ]. Our previous article only summarized the characteristics of the 100 most cited papers in the field of TAPVC. At present, there is no systematic or comprehensive bibliometric study on TAPVC. This new analysis explored the following specific aspects of TAPVC research. First, the number of publications and citations was examined by year, country, institution, author, journal, and keyword. Second, the correlations between a country’s number of publications and citations and its gross domestic product (GDP), percentage of GDP spent on research, population size, and number of journals were examined. Finally, keyword co-occurrence analysis was performed to understand the research themes. In general, a comprehensive analysis of the development history, research hotspots, and future trends in the field of TAPVC was performed using bibliometric tools. This study is expected to provide a reference and new ideas for promoting the development of TAPVC.

Data source
Compared with other databases such as Scopus, PubMed, and Medline, the Web of Science is more accurate and comprehensive and can serve as an important data source for medical researchers to perform bibliometric analysis [ 8 ]. All the relevant publications on TAPVC were retrieved using the advanced searching functionality of the Web of Science core collection (WoSCC) on July 20, 2023. The author developed the following search strategy after consulting with publication search specialists. The words “total anomalous pulmonary venous connection,” “total anomalous pulmonary venous drainage,” “total anomalous pulmonary venous return,” “TAPVC,” “TAPVD,” or “TAPVR” were used as search terms in the title. The publication year was limited to 2000–2023. Only publications written in English were included to promote analysis of the content. Because publication types such as meeting abstracts and editorials do not have the same frequency of citations and peer-review process, only publication types of articles or reviews were included in the analysis. After filtering, a full record with citations was downloaded from the database in plain text format. The impact factor (IF) of journals was obtained by manual retrieval through the Journal Citation Report (JCR) 2022 (Clarivate Analytics) [ 9 ]. The latest gross national product (GDP), research & development (R&D) expenditure, and population data for different countries are obtained from the World Bank.
Bibliometric analysis
VOSviewer [ 10 ] and Citespace [ 11 ] are the main bibliometric analysis software. The number of accumulated publications was fitted with the publication year using SPSS software. The numbers of publications, citations, and keywords were analyzed using VOSviewer. Countries, institutions, authors, and journals were ranked by the number of publications or citations. A co-authorship relationship occurs when two authors participate in the same publication. Co-authorship analysis was used to reveal country, institution, and author collaborations. Collaborations between countries were visualized using an online bibliometric website ( https://bibliometric.com ). The frequency of collaboration between countries was calculated using the bibliometrix package in R [ 12 ]. The keywords represent the theme of the publication. Keyword co-occurrence refers to the existence of two different keywords in the same publication, and the keyword co-occurrence network can reveal research hotspots [ 13 ]. The emergence of keywords in different periods reflects the changing trend of research hotspots. A citation burst refers to a significant increase in the number of citations a publication receives, which lasts at least two years [ 11 ]. References and keywords that were associated with citation bursts were identified using CiteSpace. Pearson’s test was used to examine the correlations between the number of publications or citations and the GDP, R&D expenditure, population, and journals of different countries. The correlations between the number of publications or citations and the IFs of different journals were also investigated. A two-sided P value < 0.05 was considered to indicate statistical significance.
Annual publication growth
A total of 558 publications were retrieved, including 356 articles, 12 reviews, and 190 publications of other types. Articles and reviews ( n = 368) were included in further analysis. The growth of publications with respect to publication year is shown in Fig. 1 A. The number of publications on TAPVC showed an overall increasing trend, suggesting increasing interest in the research field of TAPVC. Before 2016, the number of publications fluctuated with the publication year. In subsequent years, the number of publications grew rapidly (the significant reduction in 2023 is attributed to incomplete data). An S curve function was utilized to explore the relationship between the cumulative number of publications and the publication year, which fit the trend well (R 2 = 0.940) (Fig. 1 B). This strong correlation suggests that the field of TAPVC is still in a period of rapid growth and development.
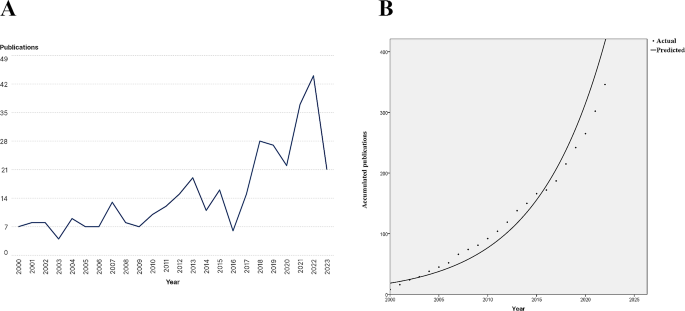
Number of publications per year (A) and the cumulative number of publications (B)
National production of publications
To study each country’s contribution to the TAPVC field, the number of publications for each country was examined. A total of 47 countries/regions worldwide have conducted research on TAPVC (Fig. 2 A). The top 20 countries/regions with the most publications are displayed in Supplementary Fig. 1, Additional File 1 . There was no doubt that the United States was the main impetus in the field of TAPVC, with 82 publications, followed by China ( n = 72), Japan ( n = 50), and India ( n = 48). Each of the remaining countries/regions has fewer 30 publications. Pearson’s analysis revealed that there was a significant correlation between the number of publications and the GDP ( R = 0.887, P < 0.001) (Fig. 2 B), R&D expenditure ( R = 0.375, P = 0.013) (Fig. 2 C) and population ( R = 0.694, P < 0.001) (Fig. 2 D) of different countries.
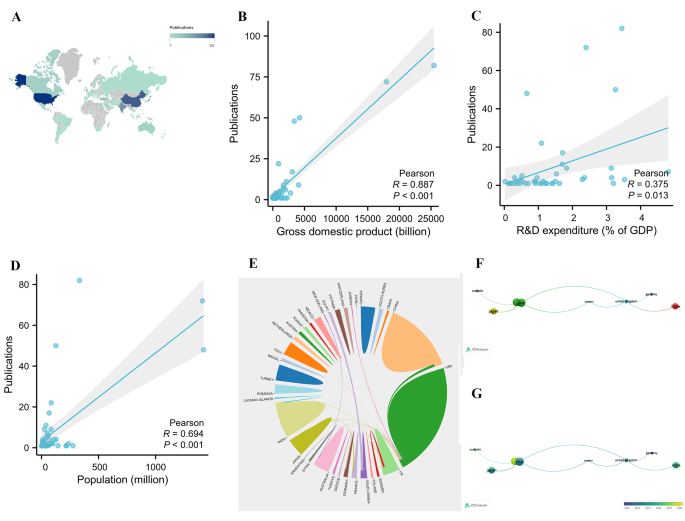
(A) Each country’s contribution to the field of total anomalous pulmonary venous connection; Pearson’s analysis revealed a significant correlation between the number of publications and gross domestic product (B) , research and development (R&D) expenditure (C) and population (D) of different countries. (E) Collaborations between countries; (F) Network clustering of country co-authorship analysis; (G) Time-overlapping network of country co-authorship analysis
The collaborations between countries are displayed in Fig. 2 E. The United States was the leader in international collaborations in the field of TAPVC. The most frequent collaborations were between the United States and the United Kingdom, the United States and China, the United States and Sweden, the United Kingdom and Sweden, the United Kingdom and India, and Egypt and Saudi Arabia, with a frequency of three each. To study the collaborations between countries, a co-authorship analysis of publications from these countries was performed (Fig. 2 F). The circle size represents the number of publications, and the color represents the cluster. These 47 countries formed eight clusters, with the red and green clusters being the largest, each comprising four countries. The color of the circle in the time-overlapping network indicates the average year of publication for each country (Fig. 2 G). Overall, there were very few connections between different clusters, indicating that international collaboration in the field of TAPVC needs to be better developed.
Institutional production of publications
To study each institution’s contribution to the TAPVC field, the number of publications for each institution was examined. A total of 457 institutions worldwide were involved in the research field of TAPVC. The top 20 institutions with the most publications are shown in Supplementary Fig. 2, Additional File 1 . Seven of the top 20 institutions were from China, followed by the United States and Australia, with 6 and 3 institutions, respectively. In terms of the specific institution, Shanghai Jiao Tong University topped the list with 13 publications, followed by All India Institute of Medical Sciences, Capital Medical University, and Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia with 9, 8, and 8 publications, respectively.
To study the collaborations between institutions, a co-authorship analysis of publications from these institutions was performed (Fig. 3 A). The circle size represents the number of publications, and the color represents the cluster. These 457 institutions formed five clusters, with the red cluster being the largest, which comprised 11 institutions, mainly from the United States. The time-overlapping network showed the average year of publication for each institution (Fig. 3 B). Overall, there were very few connections between different clusters, indicating that institutional collaboration in the field of TAPVC was not well developed.
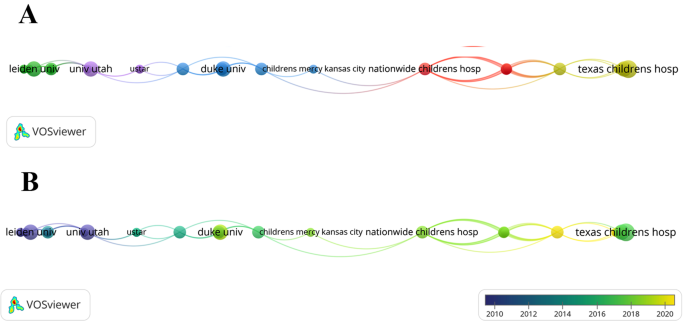
(A) Network clustering of institutional co-authorship analysis; (B) Time-overlapping network of institutional co-authorship analysis
Author production of publications
To study each author’s contribution to the TAPVC field, the number of publications for each institution was examined. A total of 1 835 authors have been committed to the field of TAPVC, and most (88.1%) have published only one publication. Each core author (2.8%) has published at least three publications, and these authors collaborated as research teams. The top 20 authors with the most publications are displayed in Supplementary Fig. 3, Additional File 1 . Huiwen Chen was the greatest contributor, with 9 publications, followed by Guocheng Shi, with 8 publications. Christopher A. Caldarone, Yves d’Udekem, Igor E. Konstantinov, and Zhongqun Zhu each had 7 publications.
To study the collaboration between authors, a co-authorship analysis was performed, and the results are displayed in Fig. 4 A. The circle size represents the number of publications, and the color represents the cluster. These authors formed 9 clusters, with the red cluster being the largest, comprising 17 authors, mainly from Shanghai Jiao Tong University. The time-overlapping network showed the average year of publication for each author (Fig. 4 B). Researchers from China have formed research networks in the field of TAPVC.
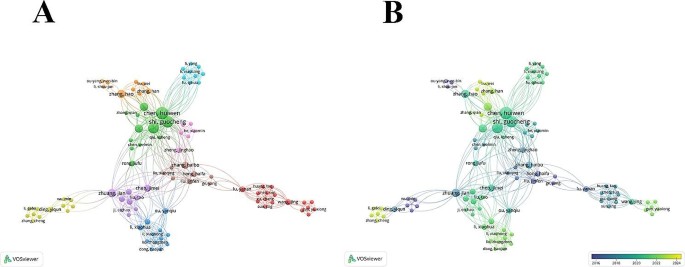
(A) Network clustering of the results of the researcher co-authorship analysis; (B) Time-overlapping network of the researcher co-authorship analysis
Disciplinary distribution of publications
To study the disciplinary distribution in the field of TAPVC, the number of publications for each WOS category was examined. The four disciplines with the most publications were cardiac & cardiovascular systems ( n = 244), surgery ( n = 120), pediatrics ( n = 81), and respiratory system ( n = 72). Other disciplines included radiology, nuclear medicine & medical imaging ( n = 28), medicine, general & internal ( n = 24), obstetrics & gynecology ( n = 15), acoustics ( n = 15), genetics & heredity ( n = 11), and peripheral vascular disease ( n = 9). This indicated that the research performed in this field was broad and diverse and could attract the attention of researchers from different fields.
Journal production of publications
These 368 publications were published in 132 journals. The top 20 journals with the most publications are displayed in Supplementary Table 1, Additional File 1 . Annals of Thoracic Surgery and Pediatric Cardiology topped the list with 29 publications each, followed by Journal of Cardiac Surgery with 24 publications. Each of the remaining journals had fewer than 20 publications. There were 48 journals from the United States, followed by the United Kingdom with 19 journals. China, Japan, and Switzerland each had eight journals. Pearson’s analysis revealed a significant correlation between the number of publications and the number of journals ( R = 0.751, P < 0.001) in different countries (Fig. 5 A). Bradford’s law showed that six core journals published 128 publications (Fig. 5 B). These findings can aid researchers in selecting the most appropriate journals to publish their manuscripts.
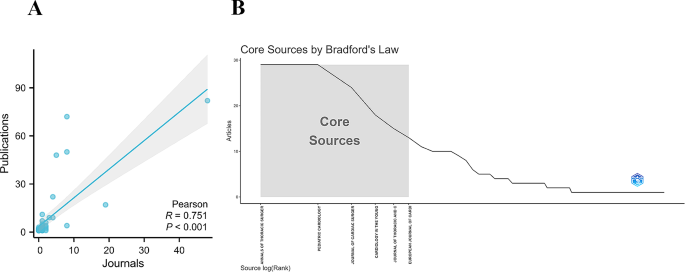
(A) Pearson’s analysis revealed a significant correlation between the number of publications and the number of journals in different countries; (B) Bradford’s law showed that six core journals published 128 publications
Most cited publications
Citation count is one of the indices used to judge the academic influence of a publication. Highly cited publications usually represent important research topics in a specific field. To study the influence of publications in the field of TAPVC, the number of citations each publication received was examined. The 20 most cited publications are displayed in Supplementary Table 2, Additional File 1 , and all of them have been cited more than 40 times. Notably, nineteen of the 20 most-cited publications were published in JCR Q1 journals, and the remaining one was in JCR Q2 journal, indicating that these publications were published in high-level journals. Of these 20 publications, 15 focused on surgical treatment, two examined the application of echocardiography in prenatal diagnosis, two investigated the pathogenic mechanism of TAPVC, and the remaining one examined late neurodevelopmental problems after surgical repair of TAPVC. A publication published in Circulation in 2007 has received the most citations: “Factors associated with mortality and reoperation in 377 children with total anomalous pulmonary venous connection” [ 14 ]. This study involved a large single-institution cohort of patients whose mortality after surgical repair of TAPVC decreased but remained high in young patients and those with cardiac TAPVC or preoperative PVS. Despite improvements in perioperative care, unfavorable anatomic characteristics remain important risk factors for postoperative mortality. The second most cited publication was also published in Circulation: “Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection: morphology and outcome from an international population-based study” [ 15 ]. This international population-based study investigated the morphological characteristics of TAPVC and explored risk factors for postoperative mortality and PVS. The third most cited publication was published in Annals of Thoracic Surgery in 2005: “Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection: An analysis of current management strategies in a single institution” [ 16 ]. This study explored the impact of management strategies on postoperative mortality and PVS and revealed that the prognosis of patients with a single ventricle was still worse than that of patients with two ventricles.
National citations
To study the influence of each country in the field of TAPVC, the number of citations each country received was examined (Fig. 6 A). The top 20 countries/regions with the most citations are displayed in Supplementary Fig. 4, Additional File 1 . The United States ranked first ( n = 1348), followed by Canada ( n = 402). China ( n = 384), Japan ( n = 364), and the United Kingdom ( n = 341). Each of the remaining countries had fewer than 300 citations. Pearson’s analysis revealed that there was a significant correlation between the number of citations and the GDP ( R = 0.881, P < 0.001) (Fig. 6 B), R&D expenditure ( R = 0.446, P = 0.003) (Fig. 6 C), and population ( R = 0.305, P = 0.037) (Fig. 6 D) of different countries.
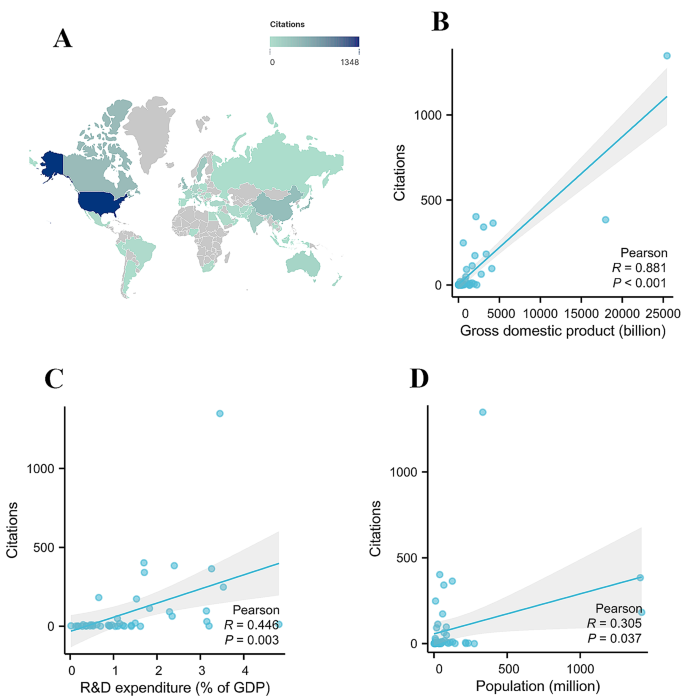
(A) The number of citations each country received in the field of total anomalous pulmonary venous connection; Pearson’s analysis revealed that there was a significant correlation between the number of citations and gross domestic product (B) , research and development (R&D) expenditure (C) , and population (D) of different countries
Institutional citations
To study the influence of each institution in the field of TAPVC, the number of citations each institution received was examined. The top 20 institutions with the most citations are shown in Supplementary Fig. 5, Additional File 1 . Six of the top 20 institutions were from the United States, followed by the United Kingdom, which has four institutions. In terms of the specific institution, the University of Toronto topped the list with 250 citations, followed by Queen Silvia Children’s Hospital, University of London Imperial College of Science, Technology and Medicine, and Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia with 248, 248 and 233 citations, respectively. Each of the remaining institutions had fewer than 200 citations.
Author citations
To study the influence of each author in the field of TAPVC, the number of citations each author received was examined. The top 20 authors with the most citations are displayed in Supplementary Fig. 6, Additional File 1 . Christopher A. Caldarone topped the list with 315 citations, followed by John G. Coles and Glen S. Van Arsdell with 271 citations each. Each of the remaining authors had fewer than 200 citations.
Journal citations
To study the influence of each journal in the field of TAPVC, the number of citations each journal received was examined. The top 20 journals with the most publications are displayed in Supplementary Table 3, Additional File 1 . Annals of Thoracic Surgery topped the list with 746 citations, followed by Circulation and Journal of Thoracic and Cardiovascular Surgery with 402 and 401 citations, respectively. Each of the remaining journals had fewer than 300 citations. Pearson’s analysis revealed a significant correlation between the number of citations and the number of journals ( R = 0.917, P < 0.001) in different countries (Fig. 7 A). There was also a significant correlation between the number of citations and the IF of different journals ( R = 0.398, P < 0.001) (Fig. 7 B).
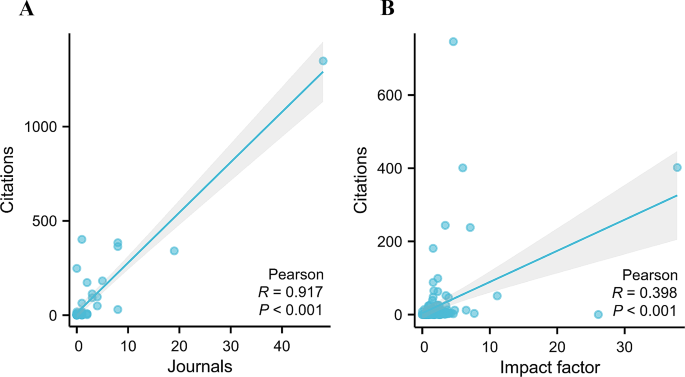
(A) Pearson’s analysis revealed a significant correlation between the number of citations and the number of journals of different countries; (B) There was a significant correlation between the number of citations and the impact factor of different journals
Citation bursts of references
Citation burst detection was performed to capture the rapid increase in the popularity of references over a specific period. A total of 32 references with citation bursts from 2000 to 2023 were identified (Fig. 8 ). The blue line represents the time interval from 2000 to 2023, and the red line represents the period of citation bursts. The publication “Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Connection: The Current Management Strategies in a Pediatric Cohort of 768 Patients”, published in Circulation, had the highest citation burst value of 8.04 [ 5 ]. This multicenter study employed a large cohort of patients (768 individuals) to investigate the influence of current therapeutic regimens on the results of TAPVC. This study revealed that surgical treatment in patients with TAPVC could yield an acceptable outcome and investigated risk factors associated with mortality and postoperative PVS. This study explored the effects of the sutureless technique and revealed that this technique decreased the incidence of postoperative PVS in patients with preoperative PVS but not in patients without preoperative PVS. The publication “Repair of Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Connection: Risk Factors for Postoperative Obstruction” published in Annals of Thoracic Surgery, had the second highest citation burst value of 7.99 [ 17 ]. Because the definition of preoperative PVS has widely varied in prior studies, this research graded the severity of preoperative PVS to precisely examine the risk factors for postoperative PVS. This study may help in the risk stratification of patients with TAPVC. The publication “Surgical results of total anomalous pulmonary venous connection repair in 256 patients”, published in Interactive Cardiovascular and Thoracic Surgery, had the third highest citation burst value of 6.96 [ 18 ]. This study revealed that the long-term outcomes of surgical repair for TAPVC patients were satisfactory, and predictors of mortality and postoperative PVS were investigated. Postoperative PVS was strongly related to mortality, and close follow-up was needed, particularly within six months after surgery. The most recent burst occurred in 2021 and has lasted for three years. Seven references with ongoing citation bursts until 2023 deserve our further attention. Of these publications, six focused on the surgical treatment of TAPVC, and the remaining study focused on the classification of pulmonary venous malformations. One meta-analysis published by Wu et al. is worth noting [ 19 ]. This meta-analysis included 26 studies involving a total of 2702 patients and compared outcomes between the sutureless technique and conventional repair and revealed that the sutureless technique could reduce the incidence of postoperative PVS and re-operations, but could not reduce postoperative early, late, or overall mortality. The popularity of these research topics is likely to continue, and they could thus become potential frontiers in the future.
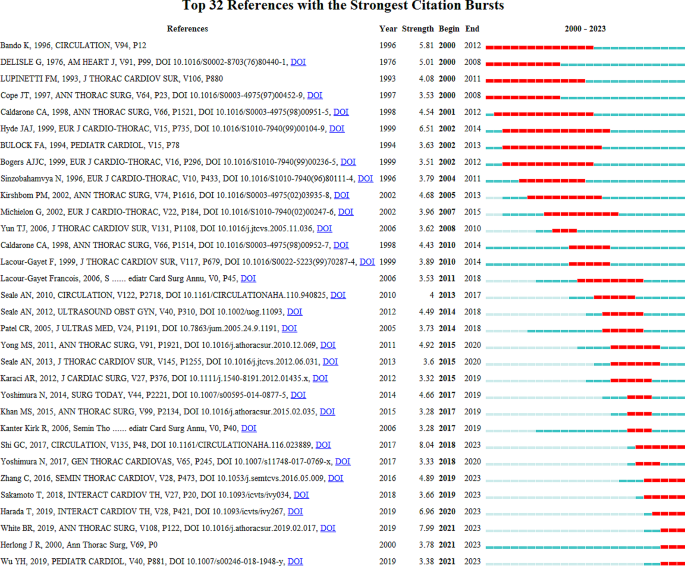
Citation burst detection identified 32 references with citation bursts
Frequency of keywords
Keywords were the high condensation and summary of the main contents of a publication, which could indicate the research theme. Frequency analysis of keywords can help researchers quickly identify the main research hotspots in a research field. Supplementary Fig. 7, Additional File 1 shows the top 20 keywords with the greatest frequency. There was no doubt that “total anomalous pulmonary venous connection” topped the lists with a frequency of 181, followed by “congenital heart disease” ( n = 60), “pulmonary vein stenosis” ( n = 41), “echocardiography” ( n = 20), “pulmonary vein” ( n = 20), “sutureless technique” ( n = 16), “prenatal diagnosis” ( n = 13), “surgery” ( n = 13), “fetal echocardiography” ( n = 12), and “single ventricle” ( n = 11).
Major research areas
Keyword co-occurrence analysis is an important approach for investigating the main research interests and hot issues in a specific research field. Among 546 keywords, 35 met the threshold of 5 occurrences. If keywords had the same meanings, they were merged. After merging duplicate keywords, 26 (threshold setting of 5) were displayed in the network visualization (Fig. 9 A). The node size represents the frequency of the keywords, and the distance between them represents the strength of the association. Closely related keywords were grouped into one cluster, and each cluster represented one research domain. The 26 keywords were grouped into six clusters. The red cluster was the largest and included the keywords “congenital,” “heart defects,” “infant,” “mortality,” “outcome,” “pulmonary vein,” and “surgery” This indicates that the most important topic was surgical repair of TAPVC. The green cluster included the keywords such as “total anomalous pulmonary venous connection,” “pulmonary vein stenosis,” “pulmonary hypertension,” and “stent” and was mainly associated with postoperative PVS, an important complication after surgical repair of TAPVC. The blue cluster included the keywords such as “anomalous pulmonary venous connection,” “congenital heart surgery,” and “heterotaxy” and was mainly related to the surgical repair of TAPVC patients with heterotaxy. The yellow cluster included the keywords such as “congenital heart disease” and “echocardiography” and was mainly related to the application of echocardiography in diagnosing TAPVC. The purple cluster included the keywords such as “fetal echocardiography” and “prenatal diagnosis” and was mainly related to the application of echocardiography in the prenatal diagnosis of TAPVC. Finally, the light blue cluster included the keywords “right atrial isomerism,” “single ventricle,” and “sutureless technique” and was mainly related to the application of the sutureless technique in the surgical repair of TAPVC patients with right atrial isomerism or a single ventricle.
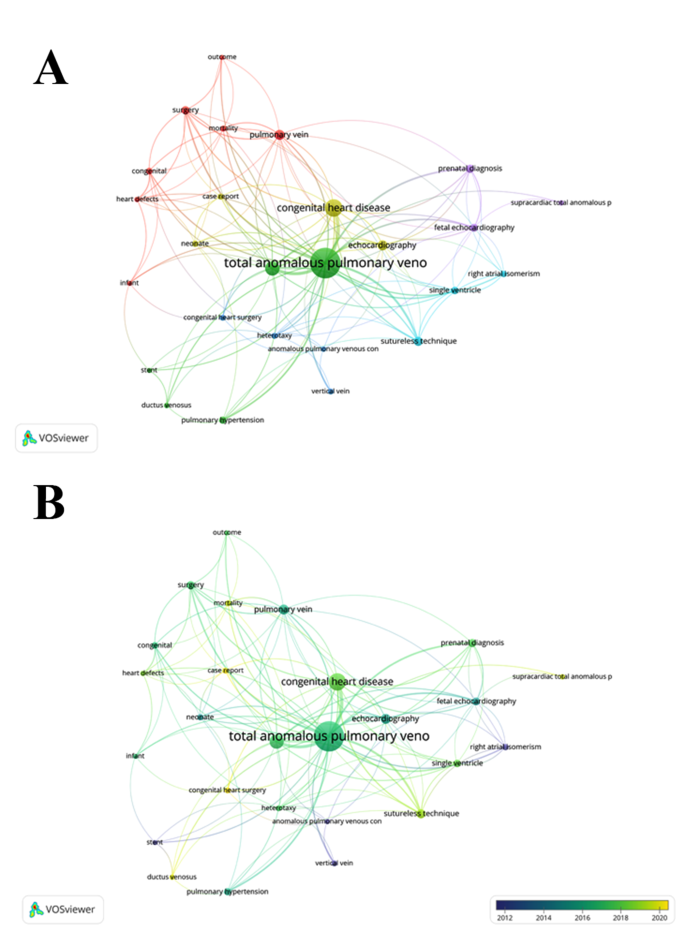
(A) Network clustering of keyword co-occurrence analysis; (B) Time-overlapping co-occurrence network of keywords
Figure 9 B shows the visualization of the time overlapping of keywords. Different nodes are marked with different colors based on the average occurrence year of these keywords. The keyword “case report” appeared most recently, with an average occurrence year of 2021.8.
Keyword bursts
Citation burst detection was conducted to explore the rapid increase in popularity of keywords over a specific period. In this study, there were no keywords with citation bursts. This suggests that research topics are relatively smooth in the field of TAPVC.
This bibliometric study quantitatively analyzed the characteristics of publications in the field of TAPVC and comprehensively reviewed its development history, current status, and future trends. The present study is important for several reasons. Scholars can be aware of research hotspots and set future study directions. This bibliometric study can serve as an educational tool for residents to familiarize themselves with TAPVC development. Journal editors can recognize potentially important manuscripts based on prior knowledge. Clinicians can apply the latest findings to clinical practice to achieve better results. The government may formulate future funding policies and research investment plans.
Research growth in the field of TAPVC has experienced two stages according to the increasing number of publications over time. Before 2016, there was a long, slow growth stage of knowledge accumulation, and it was essential to have practical clinical experience rather than technical improvement. In 2017, a publication published in Circulation used a large patient cohort to examine the current outcome of TAPVC patients [ 5 ]. Since 2017, TAPVC research has entered a rapid growth stage, indicating that it has entered a phase of rapid development. During the second stage, the importance of this medical condition is recognized, researchers have become interested in this topic, and research outputs in this field have substantially increased. Overall, the rapid growth trend in TAPVC research will likely continue. Despite the fast-growing trend of research outputs in the field of TAPVC, studies on TAPVC are generally still lagging behind those on other cardiovascular diseases, such as hypertension and arteriosclerosis. The rarity of this disease is to blame for the lower research activity in the field of TAPVC compared with more mature fields.
The United States is in a dominant position in terms of quantity and quality and is the core of international collaboration in the field of TAPVC. The United States is dominant in many other fields, indicating that the United States is at the cutting edge in the scientific community. The present study showed that greater number of journals, a greater GDP, a greater population, and greater R&D expenditure promote research productivity and impact in the field of TAPVC. GDP represents the total value of all productive activities over a time period and is the primary measure of a country’s strength. It is widely believed that the economic conditions of a country will affect its research output. The current study’s results align with previous research showing a link between GDP and scientific research output [ 20 ]. Policy-makers in less developed countries need to provide more support to maintain the growth trend of knowledge in the field of TAPVC. Only in this way could medical staff perform better clinical interventions and thus improve outcomes in clinical practice with the support of these strong-evidence studies [ 20 ]. The investment in R&D determines the level of infrastructure and resources for research, the contribution to scientific progress and innovation, and the creation of new knowledge [ 21 ]. Countries with limited research output should increase the proportion of R&D investment to improve scientific productivity and impact. Finding this correlation is particularly important in the current economic climate. The financial pressure on the government has contributed to a reduction in research funding. A direct correlation between research investment and scientific output could demonstrate the benefits of continued support for research funding. University and university hospitals are the birthplaces of medical knowledge. Countries with low research output should increase the number of universities and hospitals. Consistent with previous research, our study shows that countries with more indexed journals produce more scientific work [ 21 ]. Researchers tend to submit manuscripts to journals from their own countries and cite journals from their own countries. Countries with low research output should establish more internationally influential journals. The population is an important factor in TAPVC research. TAPVC is extremely rare; only an adequate population can accumulate enough cases. The extremely low incidence of TAPVC suggests that a sufficient number of patients can be included in studies based only on a sufficient population. A national medical center with centralized resources and knowledge should be established to collect cases scattered throughout the country. International collaboration and the sharing and exchange of patient data should be encouraged to increase the number of patients worldwide for research. In addition, registries and databases should be established to centralize dispersed patients [ 22 ]. When interpreting these results, however, some confounding factors need to be taken into account. Because domestic papers are published faster, it is possible that researchers from some countries tend to publish their findings in local journals. Such publications are not included in the present study. Only recently have some countries published papers in international journals. In addition, a previous study showed that proficiency in English facilitated the publication of articles in international journals [ 23 ]. Manuscripts from English-speaking countries have a greater chance of being accepted than those from non-native English-speaking countries.
Inadequate international research collaboration is a potential reason for the limited research outputs in the field of TAPVC. International collaboration is one of the future development directions. TAPVC is extremely rare, and a limited number of patients and researchers may hinder TAPVC research in many countries. International research collaboration will increase research productivity and impact in this field [ 24 ]. Collaborative works enhance the sharing of researchers and patients among countries to produce more research outcomes. The lack of international collaboration is difficult to explain but may be due to a lack of funding, communications, favorable circumstances, or international conferences in this field. Nonetheless, the included publications are limited to those published in English, which can distort the actual situation of international collaboration. To improve collaboration, we need to form societies on pediatric cardiac surgery, hold international and regional academic conferences, establish specialized journals on congenital heart surgery, create international databases on congenital heart surgery, provide global management for patients with congenital heart disease, strengthen education, research and community service, promote international exchange of trainees, provide educational programs for medical staff coming from different countries, facilitate international teaching and treatment, certify congenital heart surgeons globally to move surgeons to areas of need, promote international collaboration by contacting leading authors or research groups at the global level, encourage collaboration in intergovernmental organizations, give aid loans, donate equipment to hospitals, provide services and public infrastructures, offer training scholarships for foreign doctors, establish new pediatric cardiac surgery centres, and sponsor overseas medical missions [ 25 , 26 ].
The journal analysis showed that Annals of Thoracic Surgery had the largest number of publications and citations in this field of TAPVC. This journal has an IF of 4.6 (2022) and focuses on cardiothoracic surgery. Researchers tend to publish and cite publications in this journal because this journal is a highly ranked academic journal in the field of cardiothoracic surgery, and high-ranking academic journals are always looking for novel and valuable research. Bradford’s law showed that six core journals published 128 publications. The main idea of Bradford’s law is that core journals publish the most articles that are widely cited [ 27 ]. When researchers stray from core journals, the impact of published articles declines. This trend has resulted in the majority of highly cited papers coming from a small number of professional journals. There was a significant correlation between the number of citations and the IF of different journals. Our research obeys the well-known rule that most cited articles are published in journals with high IFs, which in turn leads to the high IFs of these journals.
Co-occurrence analysis of keywords identified six themes: surgical repair of TAPVC, postoperative PVS, surgical repair of TAPVC patients with heterotaxy, application of echocardiography in diagnosing TAPVC, application of echocardiography in the prenatal diagnosis of TAPVC, and application of sutureless technique in the surgical repair of TAPVC patients with right atrial isomerism or a single ventricle.
Without intervention, the mortality rate during the first year of life is as high as 80%. Surgery is the only effective treatment for this disease. Due to improved diagnostic accuracy, surgical approaches, and perioperative management, early mortality is steadily decreasing, but there is still considerable variability. The early mortality rate reported in recent publications ranges between < 10% and 20%. Surgical management of TAPVC remains a challenge [ 28 ].
PVS is the most common complication after surgical repair of TAPVC with an incidence of 10–20%, and remains an issue. PVS is associated with high morbidity and mortality following surgical repair. PVS usually occurs within a few months after surgical repair and progresses rapidly. The effective methods for preventing postoperative PVS are still unknown and are worth exploring [ 28 ].
Heterotaxy syndrome is frequently associated with TAPVC. The outcomes of patients with heterotaxy syndrome who undergo TAPVC repair remain unclear, and there are limited data. Some studies have reported that heterotaxy syndrome is a significant risk factor, while others have found no significant difference in the survival of heterotaxy patients [ 29 ].
The surgical results of TAPVC depend on a detailed understanding of the anatomical morphology. Echocardiography remains the first-line diagnostic modality for TAPVC because of its safety and accessibility. However, echocardiography has disadvantages, such as poor spatial resolution, an acoustic window, and poor interpretation accuracy. Echocardiography exhibits good performance in diagnosing isolated TAPVC but has limited accuracy in diagnosing mixed or infracardiac TAPVC and TAPVC associated with obstruction, heterotaxy syndrome, or right atrial isomerism. Improving the diagnostic accuracy of echocardiography in challenging cases remains to be addressed [ 30 ].
Prenatal diagnosis of TAPVC, especially obstructive TAPVC, is essential for birth planning and postpartum management and decreases morbidity and mortality in the perinatal period. Fetal heart echocardiography is the primary diagnostic modality. However, the prenatal diagnosis of TAPVC is very challenging, and misdiagnosis and missed diagnosis are extremely common [ 31 ].
Single ventricle and right atrial isomerism are frequently associated with TAPVC. In such patients, abnormal localization of thoracic structures, such as the great arteries and systemic veins, results in compression of pulmonary venous drainage. The outcomes of patients with a single ventricle or right atrial isomerism who undergo surgical repair of TAPVC remain poor and are associated with a high risk of postoperative PVS and mortality [ 32 , 33 ]. The effective treatment for these patients remains elusive. The sutureless technique has been introduced to reduce the risk of postoperative PVS. In this technique, the pulmonary venous confluence and the left atrium were opened, and the left atrium wall was sutured to the mediastinal pleura. The sutureless technique was favored because of its broad applicability to different anatomical morphologies and avoidance of direct anastomosis of the pulmonary vein endothelium. The efficacy, applicability, and indications of the sutureless technique are still not well established [ 34 ]. The favorable results of the sutureless technique in some recent studies have extended the indications of this technique to difficult patients, such as those with a single ventricle or right atrial isomerism [ 33 ]. However, the outcomes of the sutureless technique in such patients remain uncertain.
There are some limitations to this present bibliometric analysis. First, the search strategy was performed only in the WoSCC database. Because the WoSCC database includes most high -quality publications, it does not distort the overall trend of the research results. Second, this study included only publications written in English and omitted those written in native languages. Second, recently published high-quality studies may not have received sufficient attention due to citation delays and need to be updated in subsequent studies. Third, more citations do not always mean higher quality and controversial publications tend to have more citations. Fourth, only articles and reviews were included. However, these two types of publications are more likely to represent contributions to a research field. Finally, some limitations inherent in bibliometrics should be considered. For example, the importance of recently published publications is underestimated because there is not enough time to accumulate citations.
This bibliometric analysis identified the most influential publications and identified the most prominent countries, institutions, authors, and journals in the field of TAPVC. The field of TAPVC is still in a period of rapid growth and development. A greater number of journals, GDP, population, and research & development expenditure promote research productivity and impact. International collaboration in the field of TAPVC should be encouraged. The research themes in this field are focused on six areas: surgical repair of TAPVC, postoperative pulmonary vein stenosis, surgical repair of TAPVC patients with heterotaxy, application of echocardiography in diagnosing TAPVC, application of echocardiography in the prenatal diagnosis of TAPVC, and application of the sutureless technique in the surgical repair of TAPVC patients with right atrial isomerism or a single ventricle. This study is the first bibliometric analysis to provide a comprehensive overview of TAPVC research. Our findings could provide valuable information on the development history, current status, and future trends, as well as new ideas for promoting development in this field.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection
Pulmonary vein stenosis
Web of Science core collection
Impact factor
Journal Citation Report
Gross national product
Research & development
Herlong JR, Jaggers JJ, Ungerleider RM. Congenital heart surgery nomenclature and database project: pulmonary venous anomalies. Ann Thorac Surg. 2000;69(4 Suppl):S56–69.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Files MD, Morray B. Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection: preoperative anatomy, physiology, imaging, and Interventional Management of postoperative pulmonary venous obstruction. Semin Cardiothorac Vasc Anesth. 2017;21(2):123–31.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Burroughs JT, Edwards JE. Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection. Am Heart J. 1960;59(913 – 31.
Vanderlaan RD, Caldarone CA. Surgical approaches to total anomalous pulmonary venous connection. Semin Thorac Cardiovasc Surg Pediatr Card Surg Annu. 2018;21:83–91.
Shi G, Zhu Z, Chen J, Ou Y, Hong H, Nie Z, et al. Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection: the current management strategies in a Pediatric Cohort of 768 patients. Circulation. 2017;135(1):48–58.
Mukherjee D, Lim WM, Kumar S, Donthu N. Guidelines for advancing theory and practice through bibliometric research. J Bus Res. 2022;148(101 – 15.
Wen C, Liu W, Fang C, Shentu J, Ma R, Zhang H, et al. The 100 most cited papers on total anomalous pulmonary venous connection: a bibliometric analysis. J Cardiothorac Surg. 2023;18(1):187.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Yeung AWK. Comparison between Scopus, web of Science, PubMed and publishers for mislabelled review papers. Curr Sci. 2019;116(11):1909–.
Article Google Scholar
Garfield E. Journal impact factor: a brief review. CMAJ. 1999;161(8):979–80.
CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
van Eck NJ, Waltman L. Software survey: VOSviewer, a computer program for bibliometric mapping. Scientometrics. 2010;84(2):523–38.
Chen CM, CiteSpace II. Detecting and visualizing emerging trends and transient patterns in scientific literature. J Am Soc Inform Sci Technol. 2006;57(3):359–77.
Aria M, Cuccurullo C. Bibliometrix: an R-tool for comprehensive science mapping analysis. J Informetrics. 2017;11(4):959–75.
Radhakrishnan S, Erbis S, Isaacs JA, Kamarthi S. Novel keyword co-occurrence network-based methods to foster systematic reviews of scientific literature. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(3):e0172778.
Karamlou T, Gurofsky R, Al Sukhni E, Coles JG, Williams WG, Caldarone CA, et al. Factors associated with mortality and reoperation in 377 children with total anomalous pulmonary venous connection. Circulation. 2007;115(12):1591–8.
Seale AN, Uemura H, Webber SA, Partridge J, Roughton M, Ho SY, et al. Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection: morphology and outcome from an international population-based study. Circulation. 2010;122(25):2718–26.
Hancock Friesen CL, Zurakowski D, Thiagarajan RR, Forbess JM, del Nido PJ, Mayer JE, et al. Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection: an analysis of current management strategies in a single institution. Ann Thorac Surg. 2005;79(2):596–606. discussion 596–606.
White BR, Ho DY, Faerber JA, Katcoff H, Glatz AC, Mascio CE, et al. Repair of total anomalous pulmonary venous connection: risk factors for postoperative obstruction. Ann Thorac Surg. 2019;108(1):122–9.
Harada T, Nakano T, Oda S, Kado H. Surgical results of total anomalous pulmonary venous connection repair in 256 patients. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2019;28(3):421–6.
Wu Y, Xin L, Zhou Y, Kuang H, Jin X, Li Y, et al. Is sutureless technique Beneficial in the primary repair of total anomalous pulmonary venous connection? A systematic review and Meta-analysis. Pediatr Cardiol. 2019;40(5):881–91.
Fan G, Zhou Z, Zhang H, Gu X, Gu G, Guan X et al. Global scientific production of robotic surgery in medicine: a 20-year survey of research activities. Int J Surg. 2016;30(126 – 31.
Meo SA, Al Masri AA, Usmani AM, Memon AN, Zaidi SZ. Impact of GDP, spending on R&D, number of universities and scientific journals on research publications among Asian countries. PLoS ONE. 2013;8(6):e66449.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Jia J, Shi T. Towards efficiency in rare disease research: what is distinctive and important? Sci China Life Sci. 2017;60(7):686–91.
Man JP, Weinkauf JG, Tsang M, Sin DD. Why do some countries publish more than others? An international comparison of research funding, English proficiency and publication output in highly ranked general medical journals. Eur J Epidemiol. 2004;19(8):811–7.
Bordons M, Gomez I, Fernandez MT, Zulueta MA, Mendez A. Local, domestic and international scientific collaboration in biomedical research. Scientometrics. 1996;37(2):279–95.
Jonas RA. Strengthening international collaboration in congenital heart surgery. World J Pediatr Congenit Heart Surg. 2018;9(4):383–91.
Frigiola A, Moussaidi N, Giamberti A, Pome G, Isgro G, Youssef T, et al. International cooperation in healthcare: model of IRCCS Policlinico San Donato and Bambini Cardiopatici Nel Mondo Association for congenital heart diseases. Eur Heart J Suppl. 2016;18(Suppl E):E72–8.
Brookes BC. Bradford’s law and the bibliography of science. Nature. 1969;224(5223):953–6.
Yoshimura N, Fukahara K, Yamashita A, Doki Y, Takeuchi K, Higuma T, et al. Current topics in surgery for isolated total anomalous pulmonary venous connection. Surg Today. 2014;44(12):2221–6.
Khan MS, Bryant R 3rd, Kim SH, Hill KD, Jacobs JP, Jacobs ML et al. Contemporary Outcomes of Surgical Repair of Total Anomalous Pulmonary Venous Connection in Patients With Heterotaxy Syndrome. Ann Thorac Surg. 2015;99(6):2134-9; discussion 9–40.
Ali F, Qureshi S, Amanullah M, Atiq M. Accuracy of echocardiography in diagnosing total anomalous pulmonary venous return. Pak J Med Sci. 2018;34(5):1094–8.
Bravo-Valenzuela NJM, Peixoto AB, Araujo Junior E. Prenatal diagnosis of total anomalous pulmonary venous connection: 2D and 3D echocardiographic findings. J Clin Ultrasound. 2021;49(3):240–7.
Hoashi T, Kagisaki K, Oda T, Kitano M, Kurosaki K, Shiraishi I, et al. Long-term results of treatments for functional single ventricle associated with extracardiac type total anomalous pulmonary venous connection. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2013;43(5):965–70.
Yoshimura N, Oshima Y, Henaine R, Matsuhisa H. Sutureless pericardial repair of total anomalous pulmonary venous connection in patients with right atrial isomerism. Interact Cardiovasc Thorac Surg. 2010;10(5):675–8.
Wang Z, Ding N, Yi H, Zhu Y, Li Z, Yan D, et al. Application of sutureless technique in total anomalous pulmonary venous connection repair. J Card Surg. 2022;37(11):3769–75.
Download references
Acknowledgements
Not applicable.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Cardiothoracic Surgery, Shanghai Children’s Medical Center, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
Division of Cardiology, Peking University First Hospital, Beijing, China
Department of Neurosurgery, Shanghai Children’s Medical Center, School of Medicine, Shanghai Jiao Tong University, Shanghai, China
Chenhao Fang
Department of Pulmonary and Critical Care Medicine, Fujian Medical University Union Hospital, Fuzhou, China
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
CW has made substantial contributions to the conception and design of the work, and the acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of data, and has drafted the work and substantively revised it; GS, CF, LT have made substantial contributions to the acquisition, analysis, and interpretation of data. All authors have approved the submitted version (and any substantially modified version that involves the author’s contribution to the study). All authors have agreed both to be personally accountable for the author’s own contributions and to ensure that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work, even ones in which the author was not personally involved, are appropriately investigated, resolved, and the resolution documented in the literature.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Chen Wen .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate, consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplementary Material 1
Rights and permissions.
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Wen, C., Shen, G., Fang, C. et al. Insight into the research history and trends of total anomalous pulmonary venous connection: a bibliometric analysis. J Cardiothorac Surg 19 , 285 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13019-024-02787-8
Download citation
Received : 16 September 2023
Accepted : 30 April 2024
Published : 11 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13019-024-02787-8
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Bibliometrics
- Research progress
Journal of Cardiothoracic Surgery
ISSN: 1749-8090
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Developing countries share certain unique common characteristics. It is evident that most of these nations still grapple with issues concerning health, social amenities, and education. Challenges associated with public health include some of the common characteristics that may be noted within developing states (Todaro & Stephen 12).
Characteristic # 5. Lower Levels of Human Capital: Human capital - education, health and skills - are of crucial importance for economic development. In our analysis of human development index (HDI) we noted that there is great disparity in human capital among the developing and developed countries.
A developing country is a sovereign state with a less developed industrial base and a lower Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries. However, this definition is not universally agreed upon. There is also no clear agreement on which countries fit this category. The terms low and middle-income country (LMIC) and newly emerging economy (NEE) are often used interchangeably but ...
In many developing countries, agriculture accounts for more than a quarter of GDP. Its dominance in employment is even more striking. In many developing countries, majority of male and female are employed in agriculture. Low Level of Urbanization -- Most of the people in developed countries live in urban areas.
The Many Definitions of an Underdeveloped Country. In economic terms, a developed country is one that has a per capita Gross National Income (GNI) of over $11,095. A developing country has a GNI ...
The Third World, which is popularly referred to the countries of the south or developing countries, consists of many states in Africa, Caribbean, South America, Asia, and those in Central America. Corruption is the leading cause of underdevelopment and challenging economic conditions in Africa's developing countries.
Write an essay of approximately three to four paragraphs that explains the characteristics of the economy in developing countries, and that describes how health and political instability can ...
Scope of the Chapter. This chapter surveys the characteristics of developing countries, with particular emphasis on low-income economies. It looks at income distribution, political framework, family system, relative size of agriculture and industry, technology and capital levels, saving rates, dualism, international trade dependence, export ...
Developing countries have experienced an extraordinary period of economic development over the last couple of decades. Besides India and China, which registered record economic growth rates, countries in sub-Saharan Africa and Latin America have managed to match or exceed their performance of the 1960s and first half of the 1970s.
Over 65% are rurally based, compared to less than 27% in economically developed countries. Similarly, 62% of the labor force is engaged in agriculture, compared to only 7% in developed nations. Agriculture contributes about 20% of the GNP of developing nations but only 3% of the GNP of developed nations.
fundamental reforms in agricultural trade. phasing out quotas on developing countries' exports of textiles and clothing. reductions in customs duties on industrial products. expanding the number of products whose customs duty rates are "bound" under the WTO, making the rates difficult to raise.
Countries in North America, Europe and the former U.S.S.R., Japan, Australia and New Zealand are said to be "developed.". All others are "developing.". By dividing the world into two large blocks, the above system tends to obscure the differences within each group and to emphasize differences between them. In its.
The countries in which the process of development has started but is not completed, have a developing phase of different economic aspects or dimensions like per capita income or GDP per capita, human development index (HDI), living standards, fulfillment of basic needs, and so on. The UN identifies developing countries as a country with a relatively low standard of living, underdeveloped ...
A developing country is one with a low living standard, underdeveloped industrial base, and low Human Development Index (HDI) relative to other countries ( Sheffrin et al , 2003). Developing countries are, in general, countries that have not achieved a significant degree of industrialization relative to their populations, and have, in most ...
Common Characteristics of Developing Economies. 1. Low Per Capita Real Income. Low per capita real income is one of the most defining characteristics of developing economies. They suffer from low per capita real income level, which results in low savings and low investments. It means the average person doesn't earn enough money to invest or ...
However, some countries are still developing and they share the same characteristics regardless of which continent they are on. Africa has the largest number of developing countries. Developing countries have the following characteristics. First of all, these are high population rates. Population growth is very high in some developing countries.
Diverse Structures and Common Characteristics of Developing Nations. It is hazardous to try to generalize too much about the 145 member countries of the United Nations (U.N.) that constitute the Third World. While almost all are poor in money terms, they are diverse in culture, economic conditions, and social and political structures.
Diversity of problems with in communality are the fundamental characteristics of the developing world. The problems in developing countries also have shared in common, on average, in comparison with the developed world. Developing countries has significant historical and economic communalities that derived to economic development challenges.
207. Characteristics of Developing Countries BY Hafeez260 The theme of this essay is: the importance of a study of other semi-developed countries as they struggle for economic growth, the elimination of mass poverty and, at the political level, for democratisation and the reduction of reliance on coercion. New countries are finding their voices ...
The developing countries are also known as underdeveloped countries, least developed countries, and third world countries. Many developing countries are differing from each other in physical, cultural, characteristics, but there are some common characteristics of developing countries which are as follows: 1. General poverty: There is widespread ...
Characteristics of Developing Countries Introduction: The total major countries of the world are 182 out of which only 34 are developed and remaining 148 are under developed. Developing Country (DC) is a nation which, compare to developed nations, lacks industrialization, infrastructure, developed agriculture developed natural resources, and ...
Scope of the Chapter. This chapter surveys the characteristics of developing countries, with particular emphasis on low-income economies. It looks at income distribution, political framework, family system, relative size of agriculture and industry, technology and capital levels, saving rates, dualism, international trade dependence, export ...
Developing country is defined as a country having a standard of living or level of industrial. production well below that possible with financial or technical aid; a country that is not yet. highly industrialized. A developing country also called a less developed country or emerging ma rket —ha s a. lower gross domestic product (GDP) than ...
We show how the standard social welfare framework can be used to assess the performance of social safety nets (SSNs) in terms of targeting efficiency and budget effort. We apply this framework to the World Bank's ASPIRE database and find that the variation in poverty alleviation achieved by SSNs in emerging markets and developing economies (EMDEs) is driven mainly by variation in budget effort.
The process of urbanization has accelerated economic growth while also presenting social challenges. Urban renewal is crucial for achieving sustainable urban development, especially by preserving traditional villages as cultural heritage sites within cities. This study employs Python algorithm programming and visual analysis functions to conduct a bibliometric analysis of 408 research papers ...
Total anomalous pulmonary venous connection (TAPVC) is a rare congenital heart disease characterized by the inability of all pulmonary veins to connect to the left atrium. Our previous bibliometric article summarized the characteristics of only the 100 most cited papers in TAPVC research. The purpose of this study was to use comprehensive bibliometric analysis to examine the development ...
An IoT agricultural Greenhouse System that will enable farmers to carry out automated irrigation and to remotely view the activities in the greenhouse and a user interface to monitor the temperature and soil humidity, and display the activities in the agricultural Greenhouse System were developed. The Greenhouse system provides a controlled environment for breeding high-value crops, medical ...