- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips

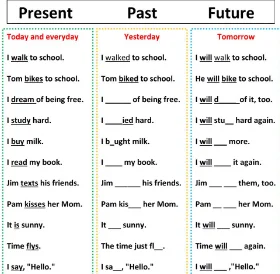
Tense Use in Academic Writing: Past, Present and Future
4-minute read
- 2nd December 2016
While the dreary constraints of physical reality mean that we’re stuck in the present for all practical purposes, in speech or writing we can skip from past to present to future at will.
To do this, you’ll need to master the past, present and future tense. These grammatical tenses are useful in all kinds of writing, but here we’ll focus on their use in academic work .
What is Grammatical Tense?
Before anything else, we need to quickly clarify what we mean by “grammatical tense.”
The main thing you need to know is that the form of the verb in a sentence changes depending on when the action described occurs.
As such, by modifying a sentence to adjust the tense, we can change its meaning:
Present Tense: Alfred burns the cakes.
Past Tense: Alfred burned the cakes.
Future Tense: Alfred will burn the cakes.
In the first example, the present tense verb “burns” suggests that it’s happening now. The past tense verb “burned”, however, shows that it has already happened. And by adding the helping verb “will,” we can instead suggest that the action is going to happen in the future.

The examples above are the simple forms of each of these tenses. There are many variations on these, however, so it’s worth checking how each form differs in practice.
The Past Tense in Academic Writing
In an academic paper, you could use the past tense to show that an idea is not widely accepted any more. In the following, for instance, the past tense “claimed” and “has since been disputed” both signal that the study no longer applies:
Cook and Moore (1964) originally claimed that profane language is amusing, although this has since been disputed by many experts.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.

The past tense is also commonly used in academic writing when describing the methods used in an experiment that has already been conducted:
The sample was tested using several techniques.
Some colleges have specific instructions for how a methodology chapter should be written, though, so make sure to check for rules about tense use in your style guide.
The Present Tense in Academic Writing
The present tense is dominant in most forms of academic work, since it applies when writing about current events or states of being. This includes describing:
- Existing facts and theories (e.g., “Profane language is common among young people…”)
- The findings of a study (e.g., “The results demonstrate that…”)
- The opinions or claims of other thinkers (e.g., “Cook and Moore argue that…”)
The present tense is usually correct even when describing a study that happened in the past, as long as the conclusions are still relevant in the present.
The Future Tense in Academic Writing
The future tense is less common in academic writing, but it still has a couple of important roles. One is in research proposals , since you’ll need to describe your research aims, predictions about results, and the methods you intend to use:
This study will examine the role of profane language in comedy. We predict that profane language will be considered hilarious by the majority of respondents.
The future tense is also useful when recommending fresh avenues of research or suggesting how the results of a study could be applied:
Our study suggests that further research should be conducted into the increasing use of profane language in everyday life.
The crucial thing is that the future tense is used when describing something that hasn’t yet happened or that is expected to occur in the future.

Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...
2-minute read
How to Cite the CDC in APA
If you’re writing about health issues, you might need to reference the Centers for Disease...
5-minute read
Six Product Description Generator Tools for Your Product Copy
Introduction If you’re involved with ecommerce, you’re likely familiar with the often painstaking process of...
What Is a Content Editor?
Are you interested in learning more about the role of a content editor and the...
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.

Verb Tenses
What this handout is about.
The present simple, past simple, and present perfect verb tenses account for approximately 80% of verb tense use in academic writing. This handout will help you understand how to use these three verb tenses in your own academic writing.
Click here for a color-coded illustration of changing verb tenses in academic writing.
Present simple tense
The present simple tense is used:
In your introduction, the present simple tense describes what we already know about the topic. In the conclusion, it says what we now know about the topic and what further research is still needed.
“The data suggest…” “The research shows…”
“The dinoflagellate’s TFVCs require an unidentified substance in fresh fish excreta” (Penrose and Katz, 330).
“There is evidence that…”
“So I’m walking through the park yesterday, and I hear all of this loud music and yelling. Turns out, there’s a free concert!” “Shakespeare captures human nature so accurately.”
Past simple tense
Past simple tense is used for two main functions in most academic fields.
“…customers obviously want to be treated at least as well on fishing vessels as they are by other recreation businesses. [General claim using simple present] De Young (1987) found the quality of service to be more important than catching fish in attracting repeat customers. [Specific claim from a previous study using simple past] (Marine Science)
We conducted a secondary data analysis… (Public Health) Descriptional statistical tests and t-student test were used for statistical analysis. (Medicine) The control group of students took the course previously… (Education)
Present perfect tense
The present perfect acts as a “bridge” tense by connecting some past event or state to the present moment. It implies that whatever is being referred to in the past is still true and relevant today.
“There have been several investigations into…” “Educators have always been interested in student learning.”
Some studies have shown that girls have significantly higher fears than boys after trauma (Pfefferbaum et al., 1999; Pine &; Cohen, 2002; Shaw, 2003). Other studies have found no gender differences (Rahav and Ronen, 1994). (Psychology)
Special notes
Can i change tenses.
Yes. English is a language that uses many verb tenses at the same time. The key is choosing the verb tense that is appropriate for what you’re trying to convey.
What’s the difference between present simple and past simple for reporting research results?
- Past simple limits your claims to the results of your own study. E.g., “Our study found that teenagers were moody.” (In this study, teenagers were moody.)
- Present simple elevates your claim to a generalization. E.g., “Our study found that teenagers are moody.” (Teenagers are always moody.)
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Biber, Douglas. 1999. Longman Grammar of Spoken and Written English . New York: Longman.
Hawes, Thomas, and Sarah Thomas. 1997. “Tense Choices in Citations.” Research into the Teaching of English 31 (3): 393-414.
Hinkel, Eli. 2004. Teaching Academic ESL Writing: Practical Techniques in Vocabulary and Grammar . Mahwah, NJ: Lawrence Erlbaum Associates.
Penrose, Ann, and Steven Katz. 2004. Writing in the Sciences: Exploring the Conventions of Scientific Discourse , 2nd ed. New York: Longman.
Swales, John, and Christine B. Feak. 2004. Academic Writing for Graduate Students: Essential Tasks and Skills , 2nd ed. Ann Arbor: University of Michigan Press.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Verb Tenses in Academic Writing | Rules, Differences & Examples
Verb Tenses in Academic Writing | Rules, Differences & Examples
Published on 20 October 2022 by Shane Bryson . Revised on 11 September 2023.
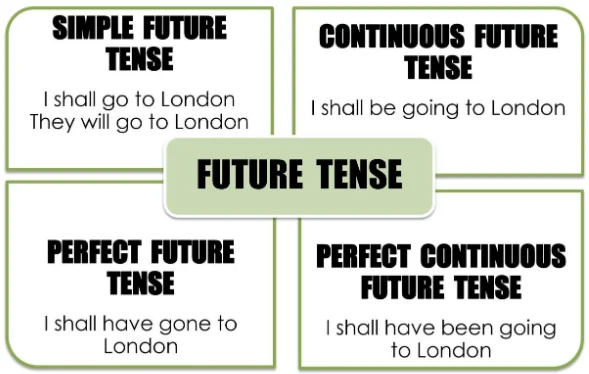
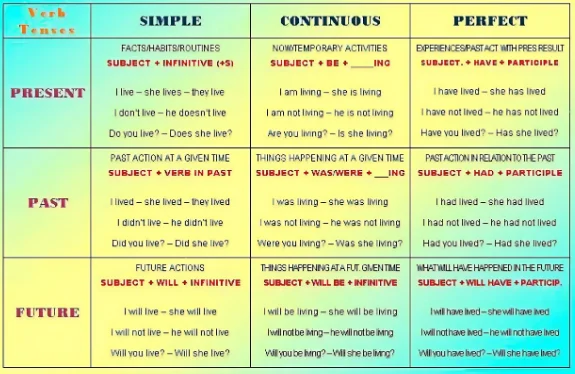
Tense communicates an event’s location in time. The different tenses are identified by their associated verb forms. There are three main verb tenses: past , present , and future .
In English, each of these tenses can take four main aspects: simple , perfect , continuous (also known as progressive ), and perfect continuous . The perfect aspect is formed using the verb to have , while the continuous aspect is formed using the verb to be .
In academic writing , the most commonly used tenses are the present simple , the past simple , and the present perfect .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Tenses and their functions, when to use the present simple, when to use the past simple, when to use the present perfect, when to use other tenses.
The table below gives an overview of some of the basic functions of tenses and aspects. Tenses locate an event in time, while aspects communicate durations and relationships between events that happen at different times.
It can be difficult to pick the right verb tenses and use them consistently. If you struggle with verb tenses in your thesis or dissertation , you could consider using a thesis proofreading service .
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
The present simple is the most commonly used tense in academic writing, so if in doubt, this should be your default choice of tense. There are two main situations where you always need to use the present tense.
Describing facts, generalisations, and explanations
Facts that are always true do not need to be located in a specific time, so they are stated in the present simple. You might state these types of facts when giving background information in your introduction .
- The Eiffel tower is in Paris.
- Light travels faster than sound.
Similarly, theories and generalisations based on facts are expressed in the present simple.
- Average income differs by race and gender.
- Older people express less concern about the environment than younger people.
Explanations of terms, theories, and ideas should also be written in the present simple.
- Photosynthesis refers to the process by which plants convert sunlight into chemical energy.
- According to Piketty (2013), inequality grows over time in capitalist economies.
Describing the content of a text
Things that happen within the space of a text should be treated similarly to facts and generalisations.
This applies to fictional narratives in books, films, plays, etc. Use the present simple to describe the events or actions that are your main focus; other tenses can be used to mark different times within the text itself.
- In the first novel, Harry learns he is a wizard and travels to Hogwarts for the first time, finally escaping the constraints of the family that raised him.
The events in the first part of the sentence are the writer’s main focus, so they are described in the present tense. The second part uses the past tense to add extra information about something that happened prior to those events within the book.
When discussing and analyzing nonfiction, similarly, use the present simple to describe what the author does within the pages of the text ( argues , explains , demonstrates , etc).
- In The History of Sexuality , Foucault asserts that sexual identity is a modern invention.
- Paglia (1993) critiques Foucault’s theory.
This rule also applies when you are describing what you do in your own text. When summarising the research in your abstract , describing your objectives, or giving an overview of the dissertation structure in your introduction, the present simple is the best choice of tense.
- This research aims to synthesise the two theories.
- Chapter 3 explains the methodology and discusses ethical issues.
- The paper concludes with recommendations for further research.
The past simple should be used to describe completed actions and events, including steps in the research process and historical background information.
Reporting research steps
Whether you are referring to your own research or someone else’s, use the past simple to report specific steps in the research process that have been completed.
- Olden (2017) recruited 17 participants for the study.
- We transcribed and coded the interviews before analyzing the results.
The past simple is also the most appropriate choice for reporting the results of your research.
- All of the focus group participants agreed that the new version was an improvement.
- We found a positive correlation between the variables, but it was not as strong as we hypothesised .
Describing historical events
Background information about events that took place in the past should also be described in the past simple tense.
- James Joyce pioneered the modernist use of stream of consciousness.
- Donald Trump’s election in 2016 contradicted the predictions of commentators.
The present perfect is used mainly to describe past research that took place over an unspecified time period. You can also use it to create a connection between the findings of past research and your own work.
Summarising previous work
When summarising a whole body of research or describing the history of an ongoing debate, use the present perfect.
- Many researchers have investigated the effects of poverty on health.
- Studies have shown a link between cancer and red meat consumption.
- Identity politics has been a topic of heated debate since the 1960s.
- The problem of free will has vexed philosophers for centuries.
Similarly, when mentioning research that took place over an unspecified time period in the past (as opposed to a specific step or outcome of that research), use the present perfect instead of the past tense.
- Green et al. have conducted extensive research on the ecological effects of wolf reintroduction.
Emphasising the present relevance of previous work
When describing the outcomes of past research with verbs like fi nd , discover or demonstrate , you can use either the past simple or the present perfect.
The present perfect is a good choice to emphasise the continuing relevance of a piece of research and its consequences for your own work. It implies that the current research will build on, follow from, or respond to what previous researchers have done.
- Smith (2015) has found that younger drivers are involved in more traffic accidents than older drivers, but more research is required to make effective policy recommendations.
- As Monbiot (2013) has shown , ecological change is closely linked to social and political processes.
Note, however, that the facts and generalisations that emerge from past research are reported in the present simple.
While the above are the most commonly used tenses in academic writing, there are many cases where you’ll use other tenses to make distinctions between times.
Future simple
The future simple is used for making predictions or stating intentions. You can use it in a research proposal to describe what you intend to do.
It is also sometimes used for making predictions and stating hypotheses . Take care, though, to avoid making statements about the future that imply a high level of certainty. It’s often a better choice to use other verbs like expect , predict, and assume to make more cautious statements.
- There will be a strong positive correlation.
- We expect to find a strong positive correlation.
- H1 predicts a strong positive correlation.
Similarly, when discussing the future implications of your research, rather than making statements with will, try to use other verbs or modal verbs that imply possibility ( can , could , may , might ).
- These findings will influence future approaches to the topic.
- These findings could influence future approaches to the topic.
Present, past, and future continuous
The continuous aspect is not commonly used in academic writing. It tends to convey an informal tone, and in most cases, the present simple or present perfect is a better choice.
- Some scholars are suggesting that mainstream economic paradigms are no longer adequate.
- Some scholars suggest that mainstream economic paradigms are no longer adequate.
- Some scholars have suggested that mainstream economic paradigms are no longer adequate.
However, in certain types of academic writing, such as literary and historical studies, the continuous aspect might be used in narrative descriptions or accounts of past events. It is often useful for positioning events in relation to one another.
- While Harry is traveling to Hogwarts for the first time, he meets many of the characters who will become central to the narrative.
- The country was still recovering from the recession when Donald Trump was elected.
Past perfect
Similarly, the past perfect is not commonly used, except in disciplines that require making fine distinctions between different points in the past or different points in a narrative’s plot.
Sources for this article
We strongly encourage students to use sources in their work. You can cite our article (APA Style) or take a deep dive into the articles below.
Bryson, S. (2023, September 11). Verb Tenses in Academic Writing | Rules, Differences & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 29 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/english-language/verb-tenses/
Aarts, B. (2011). Oxford modern English grammar . Oxford University Press.
Butterfield, J. (Ed.). (2015). Fowler’s dictionary of modern English usage (4th ed.). Oxford University Press.
Garner, B. A. (2016). Garner’s modern English usage (4th ed.). Oxford University Press.
Is this article helpful?
Shane Bryson
Shane finished his master's degree in English literature in 2013 and has been working as a writing tutor and editor since 2009. He began proofreading and editing essays with Scribbr in early summer, 2014.
Other students also liked
Subject-verb agreement | examples, rules & use, english mistakes commonly made in a dissertation | examples.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
Tense Use in Essays: Past vs. Present
2-minute read
- 16th April 2016
It’s mostly time travellers who worry about the more convoluted aspects of grammatical tense , but the issue of tense use in academic writing is, nonetheless, controversial.
To be specific, there is much disagreement about tense use in essays : specifically, is past or present tense best? Today, we look into this tricky problem.
Present Tense
The present tense is used when discussing current events or states. It will often be the dominant tense used in academic writing due to the number of situations to which it applies:
- Stating general principles or theories (e.g. ‘The third law of thermodynamics states …’)
- Describing a fact (e.g. ‘Catalysts increase the rate of a reaction…’)
- Expressing an opinion or making a claim (e.g. ‘I believe further research is required…’)
- Analysing the results of an experiment (e.g. ‘The results show that…’)
In all these cases, the present tense shows that something applies at the current time or emphasises its relevance to the present.
The present tense can also do this in a literature review, since it frames research in terms of its current significance. This shows that you’re engaged with ongoing debate in your field of study, not simply describing out-of-date research.
The past tense is used when describing events that have already happened. In academic writing, this could be writing up a completed experiment.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
For example, the past tense can be used in methodology and results sections. Likewise, the past tense is useful when writing a case study, since this is almost always about something that has already occurred.
While you can use the past tense in a literature review, saying that someone ‘believed’ something may imply that they changed their mind. As such, the past tense can be used for discussing ‘dead’ ideas (i.e. things that no-one holds true any more) or something that someone has since disavowed.
Future Tense
The future tense is useful for discussing things that are yet to happen, such as when we commit to doing something (e.g. ‘I will continue to research this issue’).
Generally, you won’t need to do this too often in academic writing. However, the future tense can be useful in the following situations:
- Making predictions about the future
- Offering recommendations based on your results
- Suggesting new avenues of research
In all these cases, the future tense will help you express yourself more clearly.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Get help from a language expert. Try our proofreading services for free.
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...
How to Cite the CDC in APA
If you’re writing about health issues, you might need to reference the Centers for Disease...
5-minute read
Six Product Description Generator Tools for Your Product Copy
Introduction If you’re involved with ecommerce, you’re likely familiar with the often painstaking process of...
What Is a Content Editor?
Are you interested in learning more about the role of a content editor and the...
4-minute read

The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.

Tenses in writing
Verb tenses.
The present tense is used to express anything that is happening now or occurring in the present moment. The present also communicates actions that are ongoing, constant, or habitual. For example:
Use the past tense to indicate past events, prior conditions, or completed processes. For example:
The future tense indicates actions or events that will happen in the future. For example:
Aspect allows you to be more precise in your selection of verbs. Aspect falls into two categories: continuous and perfect. To indicate the continuous aspect, add a form of the verb "to be" and a present participle to your main verb. The perfect aspect is created with a form of the verb "to have" and a past participle. The following chart shows twelve forms of the verb "to write" that result from combining time with aspect.
( aspect summary )
A participle is a verb form that can be used as an adjective.
Aspect in Detail
The continuous aspect is created with a form of "to be" and a present participle ( about participles ). For example:
The perfect aspect is created with a form of the verb "to have" and a past participle. For example:
The perfect aspect is often the most challenging to understand, so here's a brief overview.
Past Perfect describes a past action completed before another. For example, the next two sentences describe one action followed by another, but each achieves a different rhetorical effect by using different verb forms.
"Wrote" and "reread" sound equally important in the first sentence. In the second, the past perfect form "had written" emphasizes the action "reread."
Present Perfect refers to completed actions which endure to the present or whose effects are still relevant.
Future Perfect refers to an action that will be completed in the future.
One final note: the terms used to describe aspect have changed over time, and different terms are often used to describe the same aspect. It may help to know that the following terms are equivalent:
- "simple present" (or) "present indefinite"
- "past continuous" (or) "past progressive" (or) "past imperfect"
- "past complete" (or) "past perfect"
- "past perfect continuous" (or) "past perfect progressive"
Verb Tenses in Context
Conventions governing the use of tenses in academic writing differ somewhat from ordinary usage. Below we cover the guidelines for verb tenses in a variety of genres.
Academic Writing
- Books, Plays, Poems, Movies, etc.
Historical Contrast
Research proposals, resumes and cover letters, stories/narrative prose.
1. Academic writing generally concerns writing about research. As such, your tense choices can indicate to readers the status of the research you're citing. You have several options for communicating research findings, and each has a different rhetorical effect. For example:
- 1.3 According to McMillan (1996), the most common cause of death was car accidents.
If you choose the present tense, as in Example 1.1, you're implying that the findings of the research are generally accepted, whereas the present perfect tense in 1.2 implies not only general acceptance but also current relevance and, possibly, the continuity of the findings as an authoritative statement on the causes of death. On the other hand, the past tense in Example 1.3 emphasizes the finding at the time the research was conducted, rather than its current acceptance.
However, if you are writing about specific research methods, the process of research and data collection, or what happened during the research process, you will more commonly use the past tense, as you would normally use in conversation. The reason is that, in this instance, you are not emphasizing the findings of the research or its significance, but talking about events that occurred in the past. Here is an example:
- 1.4 During the data collection process, Quirk conducted 27 interviews with students in his class. Prior to the interviews, the students responded to a brief questionnaire.
Books, Poems, Plays, Movies
2. When you are discussing a book, poem, movie, play, or song the convention in disciplines within the humanities is to use the present tense, as in:
- 2.1 In An Introduction to English Grammar (2006), Noam Chomsky discusses several types of syntactic structures.
- 2.2 In Paradise Lost , Milton sets up Satan as a hero who changes the course of history.
3. In cases where it is useful to contrast different ideas that originate from different periods , you can use the past and the present or present perfect tense to do so. The past tense implies that an idea or a theory has lost its currency or validity, while the present tense conveys relevance or the current state of acceptance.
For example, when you want to discuss the fact that a theory or interpretation has been supplanted by new perspectives on the subject:
- 3.1 Stanley Fish (1993) maintained a reader-response stance in his analysis of Milton's L'Allegro and Il Penseroso . However, recent literary critics consider/have considered this stance to be inappropriate for the two poems.
The verb tenses used above emphasize the contrast between the old view (by Stanley Fish), which is indicated by the past tense, and the new view (by "recent literary critics"), which is indicated by the present tense or the present perfect tense. The difference between the present tense and the present perfect (i.e. between consider and have considered ) is that the present perfect suggests that the current view has been held for some time.
4. The future tense is standard in research proposals because they largely focus on plans for the future. However, when writing your research paper, use the past tense to discuss the data collection processes, since the development of ideas or experiments— the process of researching that brings the reader to your ultimate findings—occurred in the past.
5. In a resume, the past tense is used for reporting past experience and responsibilities. However, in a statement of purpose, a personal statement, or a cover letter, the present perfect tense is commonly used to relate past experience to present abilities, e.g., "I have managed fourteen employees."
6. The past tense is commonly used when writing a narrative or a story , as in:
- 6.1 Once upon a time, there was a peaceful kingdom in the heart of a jungle . . .
Some writers use the present tense in telling stories, a technique called the "historical present" that creates an air of vividness and immediacy. For example:
- 6.2 Yesterday when I was walking around downtown, the craziest thing happened. This guy in a suit comes up to me, and says , "If you know what's good for you . . . "
In this example, the speaker switches from the past tense in giving context for the story to the present tense in relating the events themselves.
Back to Grammar in College Writing
- Have your assignments done by seasoned writers. 24/7
- Contact us:
- +1 (213) 221-0069
- [email protected]

Past, Present, and Future Tense in Essays: How to Switch

Past, Present, and the Future Tenses in Your Essay
Choosing the correct grammatical tense for your essay can be a challenge. You have to decide whether to use past, present, or future tense. A wrong choice impacts your essay negatively. It will lack clarity and flow. This is not a situation that you ought to find yourself in.
Most students struggle with choosing the right tense. For some, it is due to the lack of guidance on using grammatical tenses. Others are careless with their writing. The result is a poorly written essay that a reader cannot understand. However, it is a problem that you can deal with once and for all.

Reading the instructions will enlighten you on which tense to use in writing your essay. Your tutor can also guide you on how to use grammatical tenses. You get the guidelines of when to use a particular tense. The help prevents you from choosing the wrong tense.
The type of your essay also reveals which tenses you ought to use. All essays are not the same. They have some distinct rules that create a significant difference. You must be aware of those rules and follow them to the latter. For instance, using the right tense is something you must take seriously.
People Also Read: A Guide for Buying a College Essay: Without Being Caught
Should an Essay be in Present, Past, or Future Tense?
Many students might find it challenging to choose the right tense. Some are yet to learn by heart the rules governing the use of tenses. They end up making the wrong choice.
Ultimately, the impact of their essay score is negative. Fortunately, it is a problem you can work on.
Every essay needs to be clear and engaging, where the reader needs an easier time reading it. But, that is not the case with all students. Some find themselves using the wrong tenses.
Instead of using the present tense, they write essays in the past tense. But perhaps they do not know when to use a present, past, or future tense.
You can use present, past, and future tense in your essay. But there is a catch. Before you write your essay, you must know which tense fits it. You can either get guidance from your tutor or do your research. Above all, ensure the tense you use is consistent and clear.
Most essay writers use the present tense. It is simple and direct to the point. You can write short sentences that are easier to read and understand. The reader will use little time to read your essay. It will not be tiring to read it since the message is clear.
The present tense is common in academic writing. It allows you to write about current states of events more candidly. By using the present tense, you can easily describe theories. It will be easier to explain an event that is happening now. Generally, the present tense is ideal for writing essays.
People Also Read: How to Write an Email to a University: Admission or Information
Instances to Use Present Tense in an Essay

You do not have to write every essay in the present tense. There are instances under which it becomes a must. At that juncture, you have to play ball.
You must shun the past and future tenses to make your essay consistent. Deviating from the present tense might distort your sentence structure thereby complicating your essay.
The present tense is ideal for creating a sense of immediacy. The reader gets to experience every action as it unfolds. It is easier to grasp the information the writer is passing across. The clarity in the essay engages the reader .
This is one of the reasons why writing in the present tense is common.
Writing an essay in the present tense is much easier. You can write your essay within the shortest time possible, and meeting deadlines will not be an issue. Your essay will be simple and clear to the point, without any sophistication.
Use present tense in an essay where you refer to existing facts. The present tense shows that the fact is indeed true. It becomes easier for the reader to believe in what you are writing. Also, it describes the findings of a study in the present tense. That is also the case when expressing people’s claims and opinions .
Instances to Use Past Tense in an Essay
You must be careful with the tense you use in your essay. Each tense does come with its demands. For instance, past tense is ideal for emphasizing that people do not accept a particular idea. Use past tense to describe that idea for easier understanding.
If your essay describes historical events, you have to use past tense. It makes the description clearer to the reader. This is a clear indication that they can get a picture of the turn of events. This is very crucial for the flow of your essay.
Reading it becomes engaging and enjoyable without any sense of struggling to understand ideas.
People Also Read: Thesis Defense Steps: Full Guide How to Prepare and Present
Instances to Use Future Tense in an Essay
Not often do students use the future tense in essays. They either use present and past tenses, the former being the most common.
But some instances permit the use of future tense. It does play a significant role.
Use future tense to describe your essay’s research predictions, methods, and aims. It becomes easier to demystify what the researcher is up to.
Besides, if you recommend research sources or state the application of study findings, then use future tense. You can easily describe something that is yet to happen or likely to occur in the future.
Can You Combine All Tenses in Essay Writing?
You can also use all tenses in your essay. However, you need to take this step with a lot of caution. Remember, the reader needs to get your message. You have to do that with some pomp to make your essay an enticing read .
Combining all tenses will certainly do that job for you.
Describe the cause and impact of interlocking events in an essay by combining all tenses. Your target audience can now get the hang of the events from a much broader perceptive. However, you have to respect time settings.
It is crucial to avoid any confusion that might distort your message. Ensure you get rid of any sophistication bound to disturb the flow of thoughts in your write-up.
Combining all tenses can be a win or a loss for you. It depends on the context of your essay. Besides, you need to mind your reader.
Your essay should be on a standard that is easier to comprehend. Thus, proceed with caution.
Make your point in a manner that captures the reader’s attention. Using all tenses can help you achieve that feat. However, the tenses should not appear haphazardly. If you are not careful, you might make it hard for your reader to understand your insinuating description.
People Also Read: Can Literature Reviews Be Published: Can I Publish on my Own
Choosing the right tense for your essay is fundamental. It ensures that you can engage your reader in a comprehensive context easily. It starts by knowing when to use present, past, and future tense or combine them.
If your essay is about current events, it must be in the present tense. The reader gets to know what is happening at the very moment.
Use past tense to write an essay on past events. Describing those events will be much easier. You will do it with clarity hence not causing any confusion. On the other side, the future tense suits the description of events yet to occur.
You can also use the future tense to predict events that are about to happen. And if you want to polish your essay, care to combine all tenses, but do it with caution.
Watch this video to learn more about this.

When not handling complex essays and academic writing tasks, Josh is busy advising students on how to pass assignments. In spare time, he loves playing football or walking with his dog around the park.
Related posts

Check My Essay Grade
Check My Essay Grade: How To Rate Your Essay

Is Essay a Genre
Is Essay a Genre of Literature: Its Structure and Examples

check my essay
Check My Essay Free From Grammar, Plagiarism, To Quality
Writing tenses: 5 tips for past, present, future
Understanding how to use writing tenses is challenging. How do you mix past, present and future tense without making the reader giddy? What is the difference between ‘simple’ and ‘perfect’ tense? Read this simple guide for answers to these questions and more:
- Post author By Jordan
- 28 Comments on Writing tenses: 5 tips for past, present, future

What are the main writing tenses?
In English, we have so-called ‘simple’ and ‘perfect’ tenses in the past, present and future. The simple tense merely conveys action in the time narrated. For example:
Past (simple) tense: Sarah ran to the store. Present (simple) tense: Sarah runs to the store. Future (simple) tense: Sarah will run to the store
Perfect tense uses the different forms of the auxiliary verb ‘has’ plus the main verb to show actions that have taken place already (or will/may still take place). Here’s the above example sentence in each tense, in perfect form:
Past perfect: Sarah had run to the store. Present perfect: Sarah has run to the store. Future perfect: Sarah will have run to the store.
In the past perfect, Sarah’s run is an earlier event in a narrative past:
Sarah had run to the store many times uneventfully so she wasn’t at all prepared for what she saw that morning.
You could use the future perfect tense to show that Sarah’s plans will not impact on another event even further in the future. For example:
Sarah will have run to the store by the time you get here so we won’t be late.
(You could also say ‘Sarah will be back from the store by the time you get here so we won’t be late.’ This is a simpler option using the future tense with the infinitive ‘to be’.) Here are some tips for using the tenses in a novel:
1. Decide which writing tenses would work best for your story
The majority of novels are written using simple past tense and the third person:
She ran her usual route to the store, but as she rounded the corner she came upon a disturbing sight.
When you start drafting a novel or a scene, think about the merits of each tense. The present tense, for example, has the virtue of:
- Immediacy: The action unfolds in the same narrative moment as the reader experiences it (there is no temporal distance: Each action happens now)
- Simplicity: It’s undeniably easier to write ‘She runs her usual route to the store’ then to juggle all sorts of remote times using auxiliary verbs
Sometimes authors are especially creative in combining tense and POV. In Italo Calvino’s postmodern classic , If on a winter’s night a traveler ( 1979), the entire story is told in the present tense, in the second person. This has the effect of a ‘choose-your-own-adventure’ novel. To rewrite Sarah’s story in the same tense and POV:
You run your usual route to the store, but as you round the corner you come upon a disturbing sight.
This tense choice is smart for Calvino’s novel since it increases the puzzling nature of the story. In If on a winter’s night a traveler , you, the reader, are a character who buys Calvino’s novel If on a winter’s night a traveler , only to discover that there are pages missing. When you attempt to return it, you get sent on a wild goose chase after the book you want.
Tense itself can enliven an element of your story’s narration. In a thriller novel, for example, you can write tense scenes in first person, present tense for a sense of danger unfolding now . Tweet This
A muffled shot. He sits up in bed, tensed and listening. Can’t hear much other than the wind scraping branches along the gutter.

2. Avoid losing clarity when mixing tenses
Because stories show us chains and sequences of events, often we need to jump back and forth between earlier and present scenes and times. This is especially true in novels where characters’ memories form a crucial part of the narrative.
It’s confusing when an author changes tense in the middle of a scene. The fragmented break in continuity makes it hard to place actions in relation to each other. For example:
Sarah runs her usual route to the store. As she turned the corner, she came upon a disturbing scene.
This is wrong because the verbs do not consistently use the same tense , even though it is clear (from context) that Sarah’s run is a continuous action in a single scene.
Ursula K. Le Guin offers excellent advice on mixing past and present in her writing manual, Steering the Craft :
It is highly probable that if you go back and forth between past and present tense, if you switch the tense of your narrative frequently and without some kind of signal (a line break, a dingbat,a new chapter) your reader will get all mixed up as to what happened before what and what’s happening after which and when we are, or were, at the moment. Ursula K. Le Guin, Steering the Craft
In short, make sure there are clear breaks between sections set in different tenses and that actions in the same timeline don’t create confusion by using different tenses for the same scene’s continuous events.
These 10 exercises for practicing tenses provide a fun way to focus on mastering the basics.
Get a professional edit for perfect tense
Get a no-obligation quote for a manuscript evaluation, developmental editing, copy-editing or proofreading.
3: Mix the tenses for colour and variety
Le Guin raises a good point about writing tenses. Le Guin describes the downside of telling a story almost exclusively in present tense:
It all rather sounds alike…it’s bland, predictable, risk-free. All too often, it’s McProse. The wealth and complexity of our verb forms is part of the color of the language. Using only one tense is like having a whole set of oil paints and using only pink. Le Guin, Steering the Craft
Instead mix different tenses where appropriate, but signal changes between time settings:
For example:
That morning, she had run her usual route to the store. As she turned the corner, she had come upon a disturbing scene. Apart from the glass and metal sprayed across the road like some outgoing tide’s deposit, there were what looked like two stretchers, mostly eclipsed from view by a swarm of emergency workers. Now, safely home, she decided to lie down, all the while trying to get that scene out of her mind.
Mixing the tenses can help to show the cause and effect of interlocking events. The use of the past perfect to describe the scene of an accident in the example above is effective because the past perfect shows what is already complete. It gives it an irrevocable quality, the quality of a haunting, living-on-in-memory event. Finished, but not finished in the character’s mind’s eye.

4. Practice showing shadowy past or present actions using verb forms
In addition to simple and perfect tenses, there are different ‘moods’ that show verbs as hypothetical or possible actions. In addition to the indicative mood (‘she runs to the store’) there is also the subjunctive mood (‘If she runs to the store’) and the potential mood (‘she may run to the store’).
The different moods are useful because they can show possibilities and scenarios that might have happened, or might still happen, under different circumstances. Here are examples for correct uses for each of the tenses (in active voice):
Subjunctive mood:
Present tense: If she runs to the store… Past tense: If she ran to the store… Future tense: If she should run to the store… Present perfect tense: If she has run to the store… Past perfect tense: If she had run to the store… Future perfect tense: If she should have run to the store….
Think of this mood as setting up a possibility. For example: ‘If she runs to the store, she better be quick because we’re leaving in 5.’
The potential mood helps us show shadowy, more hypothetical, uncertain scenarios:
Present tense: She may run to the store. Present perfect tense: She may have run to the store. Past perfect: She might have run to the store.
In each of these examples, the action is a possibility and the mood (using the various forms of ‘may’) shows this.
These verb moods in conjunction with tense are useful. They help us describe situations in which a narrator or character does not have full knowledge of events, or is wondering how events might pan out. They help to build suspense in the build-up to finishing a book .
5. Practice rewriting paragraphs in different tenses
It’s often easiest to get the hang of tense by doing. Pick a paragraph by an author and rewrite in each of the tenses. Here, for example, is a paragraph from David Sedaris’ essay, ‘Buddy, Can you Spare a Tie?’:
The only expensive thing I actually wear is a navy blue cashmere sweater. It cost four hundred dollars and looks like it was wrestled from the mouth of a tiger. “What a shame,” the dry cleaner said the first time I brought it in. The sweater had been folded into a loaf-sized bundle, and she stroked it, the way you might a freshly dead rabbit. David Sedaris, ‘Buddy, Can you Spare a Tie?’ , When You Are Engulfed in Flames
Rewritten in past simple tense:
The only expensive thing I actually wore was a navy blue cashmere sweater. It cost four hundred dollars and looked like it was wrestled from the mouth of a tiger. “What a shame,” the dry cleaner said the first time I brought it in. The sweater was folded into a loaf-sized bundle, and she stroked it, the way you might a freshly dead rabbit.’
Here is the same passage in past perfect:
The only expensive thing I had actually worn was a navy blue cashmere sweater. It had cost four hundred dollars and had looked like it had been wrestled from the mouth of a tiger. “What a shame,” the dry cleaner had said, the first time I brought it in. The sweater had been folded into a loaf-sized bundle, and she had stroked it, the way you might a freshly dead rabbit.
The effect is of a character describing the defining experiences before another event (before buying an even more expensive item of clothing, for example). For example, you could write ‘Before I bought that lavish suit…’ before the paragraph.
To perfect writing tenses, make your own exercises and practice rewriting extracts from your story in each tense to see the changing effect this has on your narrative.
Do you need feedback on your use of tense in a story? Get novel help from our writing community or your own, experienced writing coach.
Related Posts:
- How the future will impact your fantasy story characters
- Future technology books: Q&A with author Kate Baucherel
- Writing styles: 10 tips to master ways of writing
- Tags how to write tense , tense and narration , writing tenses
Jordan is a writer, editor, community manager and product developer. He received his BA Honours in English Literature and his undergraduate in English Literature and Music from the University of Cape Town.
28 replies on “Writing tenses: 5 tips for past, present, future”
A fine explanation of tenses. A subject often ignored, having been overlooked except by students of language. In short, changes in tense are great aids to tension.
Thanks, Bob! It’s true that it’s not discussed as commonly as certain other topics such as characterization.
Reading such articles clear all the confusion. Thanks!
I have question though, I am writing in past tense, all the events are happening in past tense. But, say, my protagonist is in a situation where she has to decide something and she is anticipating something, in short, it’s future for her, how do we go about that.
She was still sitting on the same bench, as she didn’t want to leave the light. She was sure that ………………………………………………………………….
What I want to write here is, she knew that she will not find any cab at this hour. a. She was sure that she will not find any cab at this hour. b. She was sure that she was not going to any cab at this hour. c. She was sure that she couldn’t get a cab at this hour.
In my current scene, I am trying to show the thought process of the protagonist and I have encountered 2 or 3 places where I have come across this situation. Am I doing something wrong? Should I not come across such situation at all if I am writing in past tense?
I understand reading helps, but at this moment, my mind is blank and I am not able to recollect anything that I (must) have read.
Please suggest.
Hi Jayendra,
Thanks for your question and the feedback. Number a. would be incorrect because ‘will’ is in the simple future tense (it would be correct in ‘She is sure she will not find any cab at this hour’). B would be correct with a few small tweaks: ‘She was sure she wasn’t going to find any cab at such a late hour’ (or ‘…any cab so late at night.’) Incidentally, ‘this’ implies present, continuous time so it is a little jarring in past tense (hence the alternatives above). c. Similarly, this option would be better as ‘She was sure she wouldn’t find a cab at such a late hour.’ ‘Would not’ is the right past tense form here, in present tense it would be ‘will not’. It implies future action in relation to the present time of the narration.
I hope that helps!
Hey Bridget, thanks for your reply. It feels silly now. If I was able to come up with “could”, why couldn’t I think of “would”! 🙂
Thank you for this article. Tense has been driving me insane as it feels like there are hundreds of exceptions when it comes to usage of “simple present verbs” in past tense narratives. It makes me want to disregard the entire subject and rely on an editor to catch any mistakes that I don’t naturally leave out.
For example. When you said, “Past perfect: Sarah had run to the store.” “Run” is a present (simple) tense verb, which would make you think that it can’t be used at all in a past tense narrative, but it clearly can if you phrase it correctly. This holds true with literally dozens of other verbs, adverbs, and other “tense” related words. I’m finding my work being hampered by this as I literally stumble over myself thinking I buggered up a word in my narrative, only to later find out it was a perfectly acceptable usage. I’m really at the breaking point over this, and I’m close to just disregarding it all together and relying on pure instinct and proofreading, then review by an editor at a later date. Then of course, there’s the whole deal with acceptable tense shifting…
Am I incorrect for thinking this way? Will this kind of mindset bar me from any chance of ever getting published or even being given an offer by an agent? Is there room in this world for easily confusable writers? I don’t know, and I can’t imagine how confusing this must be for foreign speakers, either. As I’ve been speaking english all my life and writing as a hobby for nearly a decade.
Anyway, sorry for the rant. I actually do have an actual question. How do you use simple present tense usages of “being” when writing in second person past tense? Because the phrase, “You are…(whatever character’s name) comes up quite a bit. However, there’s no way to get around the fact that you have to use “are,” in the past tense continuous, and I can’t find any info on if that is correct or not.
I have a question. Would it be incorrect if my story is in first person point of view and narrated in the past tense, but the internal monologue of my narrator is in the present tense?
Ex. “Don’t you ever go anywhere else, Red?” My name isn’t Red. I can’t remember where that nickname came from. “I go to school.” I said. I could feel him rolling his eyes at me. I think he’s done that before. “Come with me today.” I looked at him then, a little puzzled. It was a bad idea and yet I said: “Okay.”
It sounds right in my head but I feel like the tenses are too all over the place to be correct. The narrator has memory problems so I want what he’s thinking to be read but I’m just not sure if this is correct. I’m more comfortable with past tense writing but should I switch to present tense?
I have the same question!
Hi Hannah, this comment slipped by, my sincere apologies for that.
Regarding your question, the tense switching does jolt the reader out of the story. If you’re more comfortable with past tense, I’d suggest putting the internal monologue in past, too. For example:
“I go to school,” I said. I could feel him rolling his eyes at me. He’d done that before.’ Similarly, for ‘I can’t remember where that nickname came form’, you could simplify it to make past tense less clunky as: ‘Where did that nickname come from?’
I hope your story is much further along now!
I’m a translator struggling with getting the past perfect correct in the story I’m working on. I find your article very helpful. Thank you 🙂
I have one question:
That morning, she had run her usual route to the store. As she turned the corner, she had come upon a disturbing scene. Apart from the glass and metal sprayed across the road like some outgoing tide’s deposit, there were what looked like two stretchers, mostly eclipsed from view by a swarm of emergency workers.
The above example sentences describe an event that had happened in the past from the narrator’s perspective, and that’s why the past perfect is used. Okay, no problem. But why isn’t everything in the past perfect? Why is it okay to leave some parts in simple past?
“As she turned the corner” instead of “As she had turned the corner” “there were what looked like two stretchers” instead of “there had been what looked two stretchers”
This is the exact issue I’m having in my story. When I put every single verb in the past perfect, the sentences sound very heavy, especially when the section describing the past event is long. But I’m not sure which parts are okay to leave in simple past.
Thank you for the feedback and for your question. You struck the exact reason there – stylistically, to put every single verb in past perfect does read clunkier and isn’t necessary. As long as there is a past-perfect verb establishing the time-frame of events, the rest of the events that are still contextually happening in the earlier time period don’t necessarily need past perfect. For example:
‘It happened last week. I had stopped by the vet shop to get my dog’s flea tablet [past perfect – prior action is established]. I was standing at the counter waiting to pay when I saw the new vet through the back entrance.’ If you wrote ‘I had been standing at the counter waiting to pay when I had seen the new vet…’ each instance of past perfect situates the action in a time period before the ‘main action’. Whereas the scene the narrator is describing is the main event unfolding after a prior action (stopping at the vet shop) situated before this encounter by past perfect tense.
There’s a useful article explaining past perfect further here: http://www.englishlessonsbrighton.co.uk/use-past-perfect-build-narratives/
Thank you so much for your quick response, Jordan! Your explanation and the link you shared are very helpful 😀
It’s a pleasure 🙂 Glad I could help! Good luck with your story.
Hi Jordan. I have a question regarding exceptions. Are there any? I’m busy writing a short and it currently starts out as “I live on the top floor of a two storey apartment complex.” I then proceed to recollect in past tense. The entire story takes place over the course of 1 night and ends with the protagonist still living there. I think – as I’m typing this out – I should probably change it to past tense right? The rest of story is written in past tense. I should treat the entire event as a recollection rather than get caught up in the fact that the protagonist is still currently living there. It just felt like I was setting it up as a “Once upon a time I lived on the top floor…” which is not really my intention. It’s part of series so “I” will still be living there. It just seemed like a nice opener using present tense. Any ideas on how I can achieve the same effect?
Thank you for sharing this interesting question. I can’t see any reason why you couldn’t begin and end on present. As long as the cuts between present and past are clear/signaled to your reader it should be fine. For example:
‘I live on the top floor of a two-storey apartment complex. You’ll know why I’ve shared this detail soon, as it connects to what I’m about to tell you about a strange event that happened two weeks ago.
I was….’
If you bookend a section in present tense this way, with a clear transition between the tenses using narration, it should be fine. The main thing with tenses is not to hop between tenses within the same narrative time-frame (for example ‘I am running down a dark street. I heard footsteps behind me.’ Here, there’s nothing to signal the passage between present and past and it’s confusing.
I hope this helps!
Hey! I’m a self-taught proofreader, not a writer myself (haven’t a creative bone in my body, sadly), and I’m having a great deal of difficulty learning present tense. Up until now, all the stories I’ve proofread have been in past tense, so I’m trying to teach myself how to correct tense errors.
However, many of the websites I’ve come across aren’t tutorials, they’re essays about why not to use present tense in fiction! Well, that’s up to the author to decide! The issue I’m having is mostly with knowing when to allow usage of past tense to go and when to correct it.
For instance, in this sentence: “Thrown by the jump in numbers, most viewers click back in the video just to double-check that Danny had indeed jumped from #3 to #6, before shrugging and continuing to watch.” I’m thinking that “had” needs to be “has”, but I’m not 100% sure. I like to be mostly sure before suggesting a change. Thanks. 🙂
Hi Tracy! Here the past perfect tense (‘had’) is acceptable because it describes an action completed before the present narrative time-frame (e.g. ‘I’m walking to the store now which had been closed this morning’ would be correct if the narrator were walking in the afternoon). If you wrote ‘I’m walking to the store now which has been closed this morning’ this would imply that it is still morning in the time of narration, due to ‘has’ here being in the present perfect tense (describing a past action or condition (‘being closed’) stretching into the present time).
‘Has’ in your example would read a little strangely as it could imply that Danny ‘has’ (in the present, continuing moment) jumped from #3 to #6.
I would say, since the video has already been recorded, that ‘had’ makes sense because Danny’s error (jumping from #3 to #6) ‘had’ been made at the time of recording, and had been viewed prior to the viewer’s realization. So both moments are squarely in the past rather than stretching into the present.
Does that make sense? 🙂 Tense will get you!
It absolutely does, thank you! I’m going to have to go back and reread certain things now, but I definitely understand this. So things that happened prior to the time frame in the story can be past tense, even in a present tense story! Thank you again, so very much, I’m trying so hard to learn this, but I just find it difficult. xD Your explanation certainly simplified it for me, though! ^_^
This post also sums up the differences very well: https://www.dailywritingtips.com/has-vs-had/
So, in short, can I use different tenses in my work of a story writing? In direct speech inverted commas are needed.Isn’t it?
MIXING PAST AND PRESENT TENSES
The following paragraph has a mixture of past and present tense. I believe it to be grammatically wrong but, to my mind, it doesn’t jar when I read it back and it gives the reader a sense of immediacy. My question is: Is it an absolute no-no or is there a degree of artist license here?
Archie flicked on the chainsaw’s master switch and pumped the primer a few times. Resting the saw on the ground he gave the cord a good hard yank. It clacked through its gears but didn’t catch. The second pull bit and snapped back stinging his fingers as it recoiled. “Son of a….” he yelped. The third pull sprung the chainsaw into life with a metallic shrill sending out a cloud of blue smoke that wafted across the laundry. Archie let it idle in a high pitched grumble and then tested it with a few pumps of the throttle that sent the chain shinning around the blade. “Seems okay” he yelled over the noise before killing the master switch. “I guess the real test will be half way through a tree.
Thank you for sharing that, there’s a great descriptive density to it and a clear sense of scene.
I’m curious as to why you think it mixes tenses? To my eyes, it’s all in past tense. You do have a participle phrase or two (e.g. ‘Resting the saw on the ground’) that provide a present/unfolding action, but these are used correctly within past tense for the overall narration (you do use it correctly to show one action that is ongoing during another – the finite verb ‘he gave…’ after that participle phrase still keeps the tense within past as expected).
It would be mixed if you had finite verbs in different tenses for events occurring in the same time-frame, e.g. ‘He rests the saw on the ground and gave the cord a good hard yank.’ This would be jarring because there would appear to be two different time-frames for actions unfolding within the same scene, thanks to present verb ‘rests’ and past verb ‘gave’. I hope this helps!
Great article, many thanks!
Brief question – when writing in the past tense, can you still use present tense for general statements? For example:
I woke up as usual at 5:47 station time when air supply unit number five, that occupied the majority of the level below our quarters, sprang into action, producing a constant humming that would last for the next eight hours. It is never completely quiet on a space station, there are always sounds, vibrations and audible movements, and you learn to live with it. It never bothered me, it was the only life I knew.
Hi Stephan, it’s a pleasure. I’m glad you found it helpful.
Thank you for sharing your question. That does scan fine. In the first instance, there is a participle phrase which creates the sense of a presently unfolding action within the past time-frame (‘producing a constant humming…’). This is correct usage.
Then the flip to present informs the reader of a general, ongoing state of affairs which is where we would use present tense. It depends on the site in time from which the narrator is speaking. If they are no longer living in the quarters when narrating this, then perhaps ‘It was never completely quiet on the space station…’ would make more sense (past tense for recounting conditions no longer being experienced). But if they are still based at the station, then present tense narration for a general state of affairs in their environment fits, as presumably it still isn’t ever completely quiet when they’re narrating this.
I hope this helps! Thanks for the great question.
Thank you for this article. I found it helpful. Both of my main characters at one point recall their dreams. Since they are recalling them, I would write them in past tense correct?
Hi Chelsea, it’s a pleasure! Not necessarily. I find authors often use present tense for this (especially if the main narration is in past tense). It would look something like:
But then I remembered the dream I had…
I’m standing in a wide, open field. I hear someone calling from the other side …
Present tense does create a sense of the unfolding moment that suits the sense of reenacting an interesting event, so personally I would lean towards that. I hope this helps. Just remember whichever tense you’re using to have a narrative link that clarifies that the narration is now crossing over into the dream description (in my example above, it’s the words ‘But then I remembered the dream I had).
Thank you for reading our blog!
Wow, This was fantastic
Hi Danny, thank you for reading our blog and for your feedback!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Pin It on Pinterest
Past simple or simple past is one of the essentials in English language. You can tell a story or write a story using the past simple tense.
I drove my dad's car yesterday.
I washed my face last night
So basically the simple past uses the past tense of the verb plus one of these:
Last holiday
Last ....etc
Of course you need to know the past simple of the irregular verbs
Irregular verbs read more
The regular verbs end with ed like
Work worked
Walk walked
Wash washed
and so on... etc
After you got familiar with your regular and irregular verbs then you can start writing
For example:
Write about your last holiday
What did you do?
Where did you go?
My last holiday was fantastic. I went to the mountains in a place called Salalah in Oman. The mountains were so green and the people were so friendly. I visited many places like, forts, beaches, the hotels at night and went shopping in the grand mall. I stayed there for 10 days. The weather was really nice and it was great for camping. So we went camping on the mountains and made a small fire for BBQ.
This is a sample paragraph for the past simple tense
Now it is your turn to try writing
_________________________________________________________________________
Free writing samples
Go to short writing2
Go to short writing1
Go to short writing3
Go to short writing4
Ellen Brock
Professional freelance novel editor, how to avoid errors in tense (past or present).
Tense comes easier to some writers than to others. If you’re a writer that struggles with sticking to one tense, here are some tips that will help.

Choose Your Natural Tense
Unless there is a very good reason not to, write your novel in the tense that comes most naturally to you. This will save you a ton of time in revisions, because no matter how hard you try, you will always (at least occasionally) veer back towards your natural tense if you try to write in a tense you’re not as comfortable with.
The majority of writers are weak in present tense. Even after dozens of rounds of revisions, their writing still has glaring errors. In the typical past tense novel I edit, I see maybe 4-12 issues with the tense across the entire manuscript. But in every single present tense novel, I see hundreds of errors in tense, sometimes 4-12 per page.
There are some writers, though rare, that have an easier time sticking to present tense than past. There are also some writers who don’t make mistakes in either tense. Know what kind of writer you are. Be aware of which tense comes more naturally to you and use it!
Check Around Dialogue
One of the most common places I find tense errors is directly following dialogue that is in the opposite tense of the narration. For example:
I shove my hands on my hips and scowl. “It wasn’t like that,” I said.
Since the dialogue is in the past tense, it tricks the writer’s brain into thinking that “said” is correct. This should really be written:
I shove my hands on my hips and scowl. “It wasn’t like that,” I say.
Here’s an example in past tense:
I marched across the room and grabbed her by the shoulders. “We need to get out of here now,” I say and wipe the sweat from my brow.
Again, the tense has shifted after the dialogue. It should be written:
I marched across the room and grabbed her by the shoulders. “We need to get out of here now,” I said and wiped the sweat from my brow.
Mistakes in tense around dialogue are extremely common so make sure to spend extra time on these areas.
Imagine Talking to a Friend
This is a trick that can help the writers who truly can’t identify whether something is in past or present tense.
If you’re not sure whether a line is written correctly, imagine that rather than reading a story, you are talking to a friend.
If you are trying to write in the present tense, imagine you are talking to a friend and narrating what you’re doing right this second. For example:
I turn around and walk to the counter. The clerk smiled at me as I picked out a pack of gum.
If you imagine that you are narrating your every move as it happens, you will realize that “the clerk smiled” doesn’t make sense. It should be “the clerk smiles.”
If you’re trying to write in the past tense, imagine you are telling a story to your friend about something that happened last week. For example:
I ran down the street and bumped into Mrs. Duncan. She scowls at me and nearly faints.
When reading that out loud as if you’re telling a story about last week, it’s obvious that “she scowls” doesn’t make sense and that it should be “she scowled.”
Proofread, Proofread, then Proofread Again
If you’re writing in present tense or if you struggle with the past tense, you need to proofread your novel multiple times. Read through the entire thing looking for nothing but tense errors. Read it backwards if you have to. But make sure that you catch every single error in tense.
Though the mistakes may be simple to fix, errors in tense jar readers out of the story , which means that agents and editors will be more likely to chuck your manuscript into the rejection pile.
Get a Beta Reader or Hire an Editor
If worst comes to worst and you feel that you aren’t able to iron out your tense issues on your own, seek out a capable beta reader or hire an editor.
For more thoughts on tense, check out my article: Present Tense Might be a Bad Idea.
Need help with tense, plot, or other problems? Check out my editing services or pick up a free 1,000 word edit .

Share this:
12 thoughts on “ how to avoid errors in tense (past or present) ”.
I have trouble with tense all the time, I am hoping this works out with more practice. Thank you for sharing.
One thing that helps me is reading my paragraph/section aloud. If I hear it, I can often tell what is off and then I can fix it.
That’s a good idea. Actually, it’s good practice to read your writing out loud in any situation as it gives you a different sort of perspective to judge it by.
The one thing I’ve noticed that a lot of writers have issues with is making their sentences in tense and number. If you have a singular present tense noun you can’t have a plural past tense verb. I’ve edited a lot of academic articles and that is one of the biggest problems I’ve seen. Fun post
Good points! Thanks!
I just discovered your blog today and am enjoying reading through your ‘Ultimate Guide’ series. One thought here: I was thrown off by the first example (‘I thrust my hands…’) because ‘thrust’ can be either present or past. (Whether the latter use is correct, I don’t know, but I’ve seen it many times.) Perhaps a less ambiguously present verb might serve you better.
It didn’t occur to me that it would be confusing since “scowl” is obviously in the present tense, but I will change it. Thanks.
(My comment of 13 Dec. seems never to have been approved. Perhaps it’s caught in a spam filter? If so, I can repost it; otherwise, go ahead and delete this followup comment.)
Yes, it was in the spam filter. Sorry.
Thanks! The post has really helped but I still can’t turn “the silence was shattered” into present tense. Does anyone have any suggestions?
The silence is shattered… I would venture. “The silence is shattered by the sound of fireworks.”
Leave a comment Cancel reply

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar

How to Use Present and Past Tense in Essay Writing
Today we look at how we use present and past tenses in our essay writing to convery our message through our best of knowledge with a proper tone.
Essay writing! You might be thinking that why is a blog post on essay writing? It is something everyone can do. Yes, you are very correct everyone can do it but the point is who does it in the right way.

Suppose you need to write an essay in an exam in your answer sheet. The most important thing is that you need to keep the content relevant and keep a check on your verb tenses. While you would be moving fro tense to tense it may create some confusion while writing or while transitioning the content. Often you would need to switch tense which might upset the sequence of narration.
1. Try to Write the Essays in Present Tense
Generally, while writing essays, the writer must always use the present tense. If you wish to use the past tense then you need to refer to the events of the past. It shows the author’s ideas in a historical context. There is an exception to all these rules which explains that it is a narrative essay through which a writer can choose the past or present tense in the writing style. But the point that needs to consider is that the tense should remain consistent throughout the content.
When you are completely indulging in the writing process then it shows your effectiveness in every essay possible. Simple said, the answer would depend on the type of essay where you would be writing. When you are shifting tense from one to another, it becomes a bit distracting to the reader and they might leave it in the middle.
If you are discussing the narrative essay then it might become a bit of exception to the rule just because they will tell a fiction (a story). If you are relying on the tense (which will be past) to narrate some incidents or events then you need to refer to the writer’s perspective and his ideas just like historical entities.
If in an essay you are trying to state some facts which would refer to some perpetual or actions then you need to use the present tense. Suppose you are discussing your own ideas or expressing a particular work then also you can use the present tense.
You can use the present tense to describe the action in the work. It can also be some narrative fictional.
2. If you are trying to use multiple tenses in your essay then make sure that you do not lose the clarity in the work.
It often happens when the writer is trying to mix the tense while explaining two or three multiple situations or stories. The break between the tenses will confuse your audience or readers. Hence you need to be very careful while making that smooth transition between the tenses.
3. You can Mix the tenses For Bringing Out Various Colors And Variety
It is very important to mix tenses wherever it is necessary and appropriate but it should signal the changes between the time setting. When you mix the tenses it will show the major cause and effect of inter-locking events. The beautiful use of past and perfect is mainly used to show or describe the scene of an accident being very effective. It will give you a quality that will help you in haunting, live-on-memory, or any other event.
4. Practice Practice Practice….
When you are dealing with multiple sentences in a single content then you must practice using such sentences in your normal article writing routine. It will provide you a platform where you can try out your hand then proofread it to make sure everything is correct. Once this is done use can do the same for your main content. This way you will have a good practice of things and you won’t make any mistake.
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Subscriber-only Newsletter
Frank Bruni
Chris christie and bill barr have some explaining to do.

By Frank Bruni
Mr. Bruni is a contributing Opinion writer who was on the staff of The Times for more than 25 years.
I admired the vigor and even eloquence with which Chris Christie, quixotically campaigning for the 2024 Republican presidential nomination, made the case against Donald Trump. And I wrote as much .
But what he warrants today isn’t praise. It’s a lesson in chemistry. It’s a tutorial on beverages.
A little more than a week ago, during a public appearance at the University of Chicago’s Institute of Politics, Christie told Leigh Ann Caldwell of The Washington Post that he would never back Trump in November but that he also couldn’t bring himself to vote for President Biden. To explain his Biden aversion, Christie used a vocabulary more appropriate for spoiled milk.
“President Biden, in my view, is past the sell-by date,” he said .
The sell-by date matters when you’re purchasing dairy and you have better, fresher alternatives. But when you’re choosing a president and the other candidate is arsenic?
That’s pretty much how Christie spent much of last year describing Trump — as a civic toxin, a poison to us all. And if drinking spoiled milk is the protection against arsenic, you drink the spoiled milk. One means a possible tummy ache. The other can lead to lesions, cancer, even death.
In 2016 and 2020, Trump was a catalyst for bizarre moral relativism and pitiable moral surrender, and it’s happening again.
Christie calculates a false equivalence between Biden, whose policies he opposes and whose years are showing, and Trump, whose character and conduct Christie professedly reviles.
Bill Barr, the former attorney general who saw up close how Trump tried to subvert the peaceful transfer of power and who said in August that Trump “shouldn’t be anywhere near the Oval Office,” now supports his return to it . Barr’s position, it seems, is that Trump’s lawlessness pales beside Biden’s liberalism and that authoritarianism is a small price to pay for keeping the woke social justice warriors at bay.
Then there’s Chris Sununu, the New Hampshire governor, who was all in for Nikki Haley until she was all out of hope. He’s now on Team Trump, as he confirmed last month during an inexpressibly depressing interview on the ABC News show “This Week” with George Stephanopoulos, who was dumbfounded, given Sununu’s past characterizations of Trump.
“You support him for president, even though you believe he contributed to an insurrection,” Stephanopoulos said, trying to make sure he understood Sununu correctly. “You support him for president, even though you believe he’s lying about the last election.”
“Yeah,” Sununu answered. “Me and 51 percent of America.”
That “51 percent” part gets to me as much as the rest of it: Trump is tolerable because many Americans (if not the “51 percent” that Sununu essentially invented) say he is. Must give the people whatever they want. I’m reminded of what our parents said to us when we argued for permission for something because all our friends were being allowed to do it: If those friends are jumping off a bridge, should you? Sununu’s answer, it seems, is yes. He’s jumping, along with all the other Republicans in moral free fall.
The conservative Daily Beast columnist Matt Lewis recently looked at a few of the most prominent of those Republicans , venting disgust over the rationalizations of not only Barr and Sununu but also Mitch McConnell, the Senate Republican leader, who once strongly denounced Trump’s part in the events of Jan. 6, 2021. Shocker of shockers: McConnell will vote for him in November.
“Keep in mind, following Trump’s second impeachment trial in 2021, McConnell said that ‘Trump’s actions preceding the riot were a disgraceful dereliction of duty’ and that ‘there is no question that President Trump is practically and morally responsible for provoking the events of that day,’” Lewis wrote. “Supporting a man McConnell has clearly deemed unfit for the office may make McConnell craven, cynical or absurd, but he’s not alone in his decision.” Far from it.
Christie at least isn’t supporting Trump. That’s something. And it’s a reason that he can hold his head higher than Sununu, Barr or McConnell can. But we’re talking inches, not yards, because his joint dismissals of Trump and Biden as similarly unsavory options gut his own appraisal, during that appearance in Chicago, of Trump as someone “wholly unfit to be president of the United States in every way you think.”
I’m not saying that Christie should be enthusiastic about Biden, that I don’t understand his qualms about the president or that I expect Christie and other longtime Republicans to have some sudden ideological conversion because their party’s nominee is such a grave threat. I’m asking Christie to remember that less than six months ago, he called Trump “a dictator.” And seemed to believe that.
But last week in Chicago he lumped Trump and Biden together: “If the American people are stupid enough to nominate these two guys, doesn’t mean I have to be stupid, too.” No, but the smart way to bar someone “wholly unfit” from the White House is to vote for that person’s opponent. That’s how elections work. “None of the above” isn’t a principled stand. It’s a moral cop-out — and its own dereliction of duty.
For the Love of Sentences
Much like Gary Shteyngart’s article on the world’s biggest cruise ship a few weeks back, Ron Charles’s appraisal in The Washington Post of Danielle Steel’s new novel, “Only the Brave,” was a start-to-finish jamboree of shining sentences: “By my count, ‘Only the Brave’ is Steel’s 152nd novel, but her publicist tells me, ‘It is closer to her 170th.’ Apparently, the actual number can only be guessed at, in the same way the total mass of dark matter in the universe is estimated by how it bends light.” Also: “In the months leading up to this week’s publication, Steel’s publicist reached out repeatedly to insist that I not mention that the author is a 76-year-old romance novelist. As always, we’re never ashamed of the right things.” (Thanks to Joan Pantsios of Chicago and William Harrison of Kelowna, British Columbia, among others, for drawing attention to Charles’s review.)
Speaking of book reviews — my Times colleague Dwight Garner weighed in memorably on both a memoir and a collection of essays by Joseph Epstein: “Epstein favors tasseled loafers and bow ties, and most of his sentences read as if they were written by a sentient tasseled loafer and edited by a sentient bow tie.” (Kevin Callahan, Forest Hills, N.Y., and Elinor Nauen, Manhattan)
Sticking with The Times, which was the source of most of your nominations over the past week — Margaret Lyons perfectly described the main character of the messy but mesmerizing “Baby Reindeer,” a new Netflix series about an aspiring stand-up comedian and his stalker: “Donny recognizes and articulates the dangers of wanting fame, how it warps his judgment but also could solve his problems. (One person knowing your darkest secret is unbearable, but a million people knowing it is stardom.) Agony and attention are bound together here — Look at me! No, not like that! — twin snakes choking the life out of their prey.” (Linda Trocki, La Quinta, Calif., and Stephen Ranger, Toronto)
And Maggie Haberman and Jonah E. Bromwich used a wide-angle lens to look at Trump’s current criminal trial. “Eventually, the case could threaten not only Mr. Trump’s freedom but also the central tenets of a lifelong ethos ever-present in the former president’s patter: a convenient disregard for the truth, the blunt denial of anything damaging and a stubborn insistence that his adversaries are always acting in bad faith,” they wrote. (Cynthia Croasdaile, Portland, Ore., and Veronica Stinson, Halifax, Nova Scotia, among others)
In The Atlantic, Thomas Chatterton Williams rued the “impersonal, tech-saturated” sameness of a new generation of cars: “Could a child ever dream about a Lucid or Rivian? These are generically good-looking, low-emissions vehicles that only a cyborg could lust over. They are songs sung through Auto-Tune, with clever and forgettable lyrics composed by ChatGPT.” (Marjorie Ivey, St. Louis)
In The Guardian, Ryan Busse pivoted from Kristi Noem to another Republican governor with animals in his sights, Greg Gianforte of Montana: “In 2021, Gianforte illegally shot and killed a collared Yellowstone wolf that had its leg caught in a steel-jawed trap. He wanted to stuff the wolf and display it in his office — presumably without its radio collar, which would have dampened the effect he was going for.” (Kurt Griffin, Sioux Falls, S.D.)
To return to The Washington Post — Michael Dirda’s review of Anne Curzan’s “Says Who? A Kinder, Funner Usage Guide for Everyone Who Cares About Words” included this rumination on writing: “Effective prose, in truth, doesn’t resemble conversation. It’s more like sculpting with clay. You start with an inchoate mass, shape it a bit, hate the result, start over, try this, try that, give up, slink away in disgust, come back, work some more and eventually end up with something that looks vaguely like a pot or an essay.” (James Martin Thompson, Washington)
Having begun with Ron Charles, I’ll also end with him. In a recent Washington Post newsletter, he marveled at the actress Judi Dench’s astonishing ability to recite most of the lines from her long-ago parts in Shakespeare plays. “Such memorization is a lost art,” he wrote, adding that when he stares at the ceiling at night, “My mind is a tangle of bits of string, and all I can come up with is something like: ‘The Lord is my shepherd, I shall not want. Won’t you lay me down in the tall grass and let me do my stuff?’” For those of you not fluent in Fleetwood Mac, that last sentence is a lyric from the song “ Second Hand News .” (Denise Showers, Janesville, Wis.)
To nominate favorite bits of recent writing from The Times or other publications to be mentioned in “For the Love of Sentences,” please email me here and include your name and place of residence.
What I’m Doing, Planning and Reading
I spoke about my new book, “The Age of Grievance,” which came out this week, on “The Bulwark Podcast” with Tim Miller, and The Free Press just published the latest excerpt from it , about some of the particular ways in which the modern American economy sows envy and resentment. As someone whose diminished eyesight has made him a big and grateful consumer of audiobooks, I found it meaningful to do “The Age of Grievance” narration myself; here are its first five minutes . In the coming days and weeks, I’ll be making appearances in Montclair, N.J. ; Philadelphia ; and Washington, among other cities: My full schedule is on my website, where you’ll also find a range of information about the book. Also, I just added another event near my Chapel Hill, N.C., home, at McIntyre’s Books in Fearrington Village, on May 23; more details on that here .
Two Times colleagues whom I like and respect immensely have books of their own coming out in the next few weeks. “ Chasing Hope” is Nick Kristof’s look back at his extraordinary journalism career, including his travels to places most of us have never been and will never see. “ Trippy: The Perils and Promise of Medicinal Psychedelics ” is Ernesto Londoño’s mix of candid personal reflection and deep reporting, illuminating a growing trend in mental health that many of us don’t understand.
Campus protests have riveted and divided Americans and led to bitterly tense scenes such as the arrests on Tuesday night of protesters who had barricaded themselves inside Hamilton Hall at Columbia University. How to make sense of it all? Two of the best recent takes came from George Packer in The Atlantic and Lydia Polgreen in The Times . I don’t agree with every paragraph or sentence that each of them wrote, but that’s not what I’m looking for in a piece of journalism, especially one covering such an important topic. I’m looking to be made smarter and to understand the dynamics of a situation more fully, and I’m looking for analysis that seeks to lower rather than raise the temperature. Both articles fill that bill.
On a Personal Note
I was happy to include a few lines about the Netflix series “Baby Reindeer” in this week’s For the Love of Sentences section not only because the lines in question are terrific but also because they reminded me to say a few words of my own about the show.
It’s definitely not for everyone. It’s harrowingly dark, and it’s also repetitive, revisiting or lingering on developments and details that have been amply examined. Streaming services these days seem to take the approach that any story that can be told in X number of hours or installments should be given 25 to 50 percent more time than that. Bloat is a given.
But little that I’ve watched lately gripped and haunted me the way “Baby Reindeer” did. It’s the story, based on real events, of a struggling (really, failing) comedian and his stalker, and it is so raw and so true on the subject of human neediness that it’s a gut punch. Who among us hasn’t felt some version of the desperation that these characters do? Hasn’t made awful choices just for the sake of having company, of being seen, of being admired, no matter the flaws, delusions and demands of the admirer?
“Baby Reindeer” isn’t a simple perpetrator-and-victim tale. It examines how we see and don’t see what’s right in front of us, depending on what we’re intent on believing. That’s true in politics, as the past few years have vividly demonstrated. But it’s even truer when we’re looking for love. Or hope. Or just the barest smidgen of affirmation.
Frank Bruni is a professor of journalism and public policy at Duke University, the author of the book "The Age of Grievance" and a contributing Opinion writer. He writes a weekly email newsletter . Instagram Threads @ FrankBruni • Facebook
An underappreciated era in Black literature gets its due
Harvard scholar jesse mccarthy shines new light on revelatory books published in the middle of the 20th century..

L ately, in English departments the idea of grouping works of literature by when they were written has started to feel outdated, or at least old-fashioned. This might sound odd since the field is organized around such literary periods, with historical labels like “Victorian” or “Modernist” defining its conferences, course titles, journals, and job listings. But some professors now see such categories as blunt and tired. One even wrote a book called “ Why Literary Periods Mattered ,” past tense.
Which makes it rather surprising that a young star professor in Harvard’s English department has written a new book defending literary periodization — and proposing a new period of his own.
In “The Blue Period,” Jesse McCarthy zooms in on Black authors who lived and wrote between 1945 and 1965. During these decades, roughly the first half of the Cold War, most of the world sided with either America or the Soviet Union. But many Black Americans felt torn. “What is so distinctive, compelling, and politically potent about black writing from this era,” McCarthy writes, “is its dissent from both of the hegemonic Cold War ideological blocks.” Instead of turning toward Washington or Moscow, Black authors turned inward. Alongside Black painters and Black musicians, they produced ambiguous and emotional art that McCarthy calls “blue.”
It’s an exciting new window into well-known writers like Ralph Ellison and Gwendolyn Brooks, and it offers a chance to rediscover forgotten figures like Vincent O. Carter. It’s also a reminder that in our own period — one marked by distraction and information and a reflexive obsession with the present — the quaint act of thinking historically, of thinking periodically, remains valuable, even radical.
Thanks to some wonderful authors and some diligent academics, modern Black literature now feels rich with periodization. There’s Toni Morrison, who looms as a period unto herself. There are current writers like Jesmyn Ward and Colson Whitehead, who extend and revise Morrison’s historical approach. Moving backward, there’s the Black Arts Movement, with writers like Nikki Giovanni and Amiri Baraka, and the Harlem Renaissance, with writers like Langston Hughes and Zora Neale Hurston.
Advertisement
But what about the gap between the Harlem Renaissance and the Black Arts Movement? McCarthy found himself pondering those missing decades one day when he was a graduate student at Princeton, browsing the library shelves.
It started when McCarthy pulled down a copy of Vincent O. Carter’s obscure and experimental memoir “The Bern Book,” a striking volume with its cover illustration of a single piercing eye. “I was immediately intrigued,” McCarthy says.
Part of this intrigue was the unknown author and the brilliant prose, and part of it was that McCarthy didn’t know how to contextualize this fascinating book. “We didn’t really have a sense of who Carter was, how to read his books, why they mattered, how they fit into the field,” McCarthy says. What he needed as a reader, and what Carter needed as an author, was an interpretive framework: a literary period.
“The Blue Period” sketches this framework, often through the words of the authors themselves. In 1948, soon after he’d emigrated to Paris, Richard Wright published an essay on the front page of a French newspaper. “My body was born in America,” Wright wrote. “My heart was born in Russia; and today I stand contritely ashamed between my two parent countries.”

Many Black intellectuals shared Wright’s alienation. On one side, there was the version of communism that had once energized them — but also Stalin and his brutal assault on freedom. On the other side, there was America and its avowed liberalism — but also the reality lived by so many Black people of Jim Crow and its brutal assault on freedom.
To Wright, both sides deserved blame: “The present nationalism, in America and in Russia, forces a man to abandon his human heritage.” But Wright also believed Black people could carve out a refuge from the dominant national politics, an interior space to discuss their feelings and fears and desires. “Our weapons are not their weapons,” Wright wrote. “For us there still exists room for liberty, and that room is your spirit and mine.”
The weapon many writers chose was a “blue” style, an adjective McCarthy borrows from Miles Davis and several of his 1950s albums, including “Kind of Blue.” “Davis would turn his back to the audience when he performed,” McCarthy says. Then he would play music that was intense, meditative, and inwardly focused — music that was reserved but still fiery.
“When I think of Black life in the 1950s,” McCarthy says, “it has this kind of sound.”
Once McCarthy understood the political dynamic and the aesthetic response to it, he began to see examples everywhere. Take Ralph Ellison’s “Invisible Man.” Critics have often read the novel as Ellison’s turn from communism toward liberalism. But McCarthy believes this reading is too simple. “Ellison sees Black people being instrumentalized by both sides,” he says. “Invisible Man” doesn’t end with the main character choosing a team. It ends with him retreating to his books and jazz records — with him turning his back to the audience and adopting a blue style.
One benefit of a literary period is that it can cast major figures in a fresh light. Another is that it can elevate minor figures. Vincent O. Carter is a good example. Although he wrote “The Bern Book” near the start of the blue period, in the ’50s, he couldn’t find a publisher until 1973. “By then it was the height of the Black Arts Movement,” McCarthy says, referring to the decade-long period of overtly political Black writing. “No one wanted this kind of book from a Black writer.” “The Bern Book” describes leaving America and ultimately settling in rural Switzerland. “Carter meditates on what Blackness means,” McCarthy says, “especially in the heart of Europe.” For his next book, “Such Sweet Thunder,” a novel centered on a Black working-class neighborhood that will be erased by an Eisenhower interstate, Carter couldn’t find any publisher at all. It appeared in 2003, two decades after his death.
By restoring both Carter titles to the 1950s, when they were largely written, McCarthy can argue for their importance and illuminate their themes.
Perhaps the best benefit of a literary period, though, is the way it connects authors major and minor. “The Bern Book” makes a fascinating counterpoint to “Stranger in the Village,” James Baldwin’s classic essay on his own time living in Switzerland. Why did Baldwin leave? Why did Carter stay, ultimately for 30 years? How did each author try to carve out space for Black interiority and emotion? Reading Carter and Baldwin alongside each other as works of the same literary period, and realizing that the authors were pursuing similar goals at similar times, enriches our understanding of them both.
In 1959, Baldwin wrote another important essay, which echoed Wright’s frustrations with the Cold War. “The world has shrunk to the size of several ignorant armies,” Baldwin wrote. The problem was he didn’t know which army was right: “I share, for example, the ideals of the West — freedom, justice, brotherhood — but I cannot say that I have often seen these honored.”
McCarthy hopes literary connections like these, so persuasively laid out in “The Blue Period,” will give scholars and students new approaches to Black writers of the 1950s and 1960s. At Harvard, he wants to teach a class that will focus on a number of blue texts. “If you’re teaching a whole class instead of a survey,” he says, “then in addition to Baldwin and Ellison you can assign, say, ‘Brown Girl, Brownstones’” — a 1959 novel by Paule Marshall about a family of immigrants with a fierce emotional life. Bookworms can do the same thing at home, pairing Marshall with Gwendolyn Brooks or Carter with Baldwin.
In addition to making a case for the blue period, McCarthy wants to advocate for a certain style of reading and thinking. “My students are extremely bright,” he says. “In many ways they know more than I did when I was in college, and if they don’t know something, they can look it up.” But sometimes he wonders if this information has become not just a crutch but an obstacle. “They don’t always know where all of this information fits in an actual trajectory,” he says. “They struggle to think historically.”
Thinking historically matters for any subject, but it especially matters for someone trying to understand the Black experience in America. As McCarthy writes in his book, “mores and political attitudes, fashion and taste, idiom and vocabulary — most notoriously the very words black people use to describe themselves — what it means to and how it feels to be black in the modern world have swung wildly.”
The swings and breaks of the past often provide its most revealing moments — but also the ones that are easiest to misinterpret or simply to forget. This is where thinking periodically can help.
Craig Fehrman is a journalist and historian. He is at work on a revisionist history of the Lewis and Clark expedition for Simon & Schuster.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The different tenses are identified by their associated verb forms. There are three main verb tenses: past , present , and future. In English, each of these tenses can take four main aspects: simple , perfect , continuous (also known as progressive ), and perfect continuous. The perfect aspect is formed using the verb to have, while the ...
There are three tenses that make up 98% of the tensed verbs used in academic writing. The most common tense is present simple, followed by past simple and present perfect. These tenses can be used both in passive and active voice. Below are the main functions that these three tenses have in academic writing.
As the name suggests, the past continuous tense is used to refer to an ongoing action in the past: Newton was sitting under a tree. The key phrase here is "was sitting," which combines the simple past tense "was" with the present participle "sitting.". This gives us a sense of a continuous action ("sitting") occurring in the past.
Here, the past simple tense (decreased) is used to discuss the results of a scientific investigation that was completed in the past. The writer switches to present simple ( suggest and contribute ) to describe a conclusion that is unlikely to change—even if consulted at a later date, the data gathered in the study will continue to suggest ...
The main thing you need to know is that the form of the verb in a sentence changes depending on when the action described occurs. As such, by modifying a sentence to adjust the tense, we can change its meaning: Present Tense: Alfred burns the cakes. Past Tense: Alfred burned the cakes. Future Tense: Alfred will burn the cakes.
The present simple, past simple, and present perfect verb tenses account for approximately 80% of verb tense use in academic writing. This handout will help you understand how to use these three verb tenses in your own academic writing. Click here for a color-coded illustration of changing verb tenses in academic writing.
Revised on 11 September 2023. Tense communicates an event's location in time. The different tenses are identified by their associated verb forms. There are three main verb tenses: past , present , and future. In English, each of these tenses can take four main aspects: simple , perfect , continuous (also known as progressive ), and perfect ...
Expressing an opinion or making a claim (e.g. 'I believe further research is required…') Analysing the results of an experiment (e.g. 'The results show that…') In all these cases, the present tense shows that something applies at the current time or emphasises its relevance to the present. The present tense can also do this in a ...
The past tense is commonly used when writing a narrative or a story, as in: 6.1 Once upon a time, there was a peaceful kingdom in the heart of a jungle . . . Some writers use the present tense in telling stories, a technique called the "historical present" that creates an air of vividness and immediacy.
The flexible use of tenses brings the reader the joy of being "in the present" for many moments while, in other moments, gaining the benefit of the insights and reflection that only a past-tense narrator can provide. Here's an example from a wonderful essay by Tim Hillegonds, "And Then We Are Leaving," published in the literary ...
It starts by knowing when to use present, past, and future tense or combine them. If your essay is about current events, it must be in the present tense. The reader gets to know what is happening at the very moment. Use past tense to write an essay on past events. Describing those events will be much easier.
Here are some tips for using the tenses in a novel: 1. Decide which writing tenses would work best for your story. The majority of novels are written using simple past tense and the third person: She ran her usual route to the store, but as she rounded the corner she came upon a disturbing sight.
Past simple or simple past is one of the essentials in English language. You can tell a story or write a story using the past simple tense. Examples: I drove my dad's car yesterday. I washed my face last night. So basically the simple past uses the past tense of the verb plus one of these: Yesterday. Last year.
Quick answer: In general, when writing most essays, one should use present tense, using past tense if referring to events of the past or an author's ideas in an historical context. An exception to ...
One of the most common places I find tense errors is directly following dialogue that is in the opposite tense of the narration. For example: I shove my hands on my hips and scowl. "It wasn't like that," I said. Since the dialogue is in the past tense, it tricks the writer's brain into thinking that "said" is correct.
1. "He went home. But before that he had eaten a sandwich." - the most technically correct answer - you use past perfect tense in its intended purpose. "He went home. But before that he *has been eating a sandwich." - incorrect by the grammar rules, and I don't think present perfect continuous tense is very common in casual speech in this case.
Past simple. The past simple is used to describe the events in a story in the chronological order that they happened. You can use several past tense verbs in one sentence if the events happen one after the other. When I got to my hotel room and opened the suitcase, I saw lots of small bags.
1. Try to Write the Essays in Present Tense. Generally, while writing essays, the writer must always use the present tense. If you wish to use the past tense then you need to refer to the events of the past. It shows the author's ideas in a historical context. There is an exception to all these rules which explains that it is a narrative ...
3. When you are writing about a certain historical event (even the creation of a literary or artistic work), use the past tense. Example: "Henry Fielding wrote in the eighteenth century.". Example: "Picasso produced a series of sculptures.". 4. When discussing events in a literary work (novel, story, play, or poem) always use the ...
Literary works, paintings, films, and other artistic creations are assumed to exist in an eternal present. Therefore, when you write about writers or artists as they express themselves in their work, use the present tense. The Basic Rule: You should use the past tense when discussing historical events, and you should use the literary present ...
"President Biden, in my view, is past the sell-by date," he said. The sell-by date matters when you're purchasing dairy and you have better, fresher alternatives.
Harvard scholar Jesse McCarthy shines new light on revelatory books published in the middle of the 20th century. Vincent O. Carter, one of the midcentury authors whose work is explored in "The ...