- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- Engageny Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- enVision Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy

Big Ideas Math Algebra 1 Answers Chapter 5 Solving Systems of Linear Equations
If you are searching for instant help on the concepts of Algebra 1 Ch 5 Solving Systems of Linear Equations then this is the one-stop destination for all your needs. Make the most out of the BIM Book Algebra 1 Chapter 5 Solving Systems of Linear Equations Solutions Key provided and clarify your doubts on the same. You need not worry about the accuracy of the Solving Systems of Linear Equations Big Ideas Math Algebra 1 Answers Chapter 5 as they are given to you by subject experts.
To make it easy for you we have compiled the Big Ideas Math Algebra 1 Answers for Chapter 5 Textbook Questions via quick links available here. You can tap on them or download them free of cost and prepare effectively. Practice the BIM Textbook Algebra 1 Ch 5 Solving Systems of Linear Equations Answers on a regular basis so that your speed and accuracy will be improved in the actual exams.
Big Ideas Math Book Algebra 1 Answer Key Chapter 5 Solving Systems of Linear Equations
We have covered all the Questions from Exercises(5.1 to 5.7), Chapter Tests, Review Tests, Quiz, Assessment Tests, Cumulative Assessments, etc. in the Solving Systems of Linear Equations Big Ideas Math Algebra 1 Answer Key. You can understand the topics in it easily as they are explained in an elaborate manner keeping in mind your level of understanding.
- Solving Systems of Linear Equations Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency – Page 233
- Solving Systems of Linear Equations Mathematical Practices – Page 234
- Lesson 5.1 Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Graphing – Page(235-240)
- Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Graphing 5.1 Exercises – Page(239-240)
- Lesson 5.2 Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Substitution – Page(241-246)
- Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Substitution 5.2 Exercises – Page(245-246)
- Lesson 5.3 Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Elimination – Page(247-252)
- Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Elimination 5.3 Exercises – Page(251-252)
- Lesson 5.4 Solving Special Systems of Linear Equations – Page(253-258)
- Solving Special Systems of Linear Equations 5.4 Exercises – Page(257-258)
- Solving Systems of Linear Equations Study Skills: Analyzing Your Errors – Page 259
- Solving Systems of Linear Equations 5.1–5.4 Quiz – Page 260
- Lesson 5.5 Solving Equations by Graphing – Page(261-266)
- Solving Equations by Graphing 5.5 Exercises – Page(265-266)
- Lesson 5.6 Graphing Linear Inequalities in Two Variables – Page(267-272)
- Graphing Linear Inequalities in Two Variables 5.6 Exercises – Page(271-272)
- Lesson 5.7 Systems of Linear Inequalities – Page(273-280)
- Systems of Linear Inequalities 5.7 Exercises – Page(278-280)
- Solving Systems of Linear Equations Performance Task: Prize Patrol – Page 281
- Solving Systems of Linear Equations Chapter Review – Page(282-284)
- Solving Systems of Linear Equations Chapter Test – Page 285
- Solving Systems of Linear Equations Cumulative Assessment – Page(286-287)
Solving Systems of Linear Equations Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
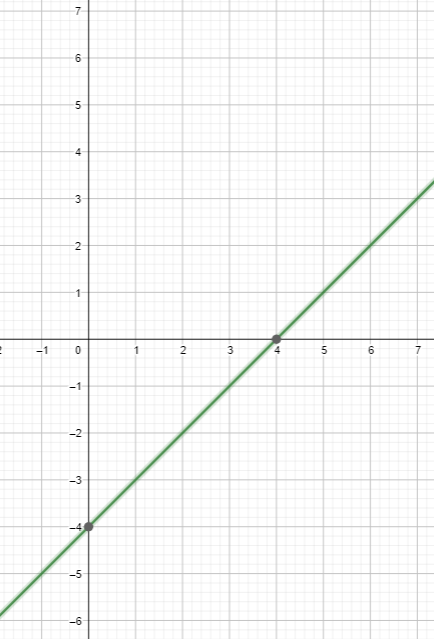
Question 11. ABSTRACT REASONING The graphs of the linear functions g and h have different slopes. The value of both functions at x = a is b. When g and h are graphed in the same coordinate plane, what happens at the point (a, b)? Answer:
Solving Systems of Linear Equations Mathematical Practices
Mathematically proficient students use technological tools to explore concepts.
Monitoring Progress
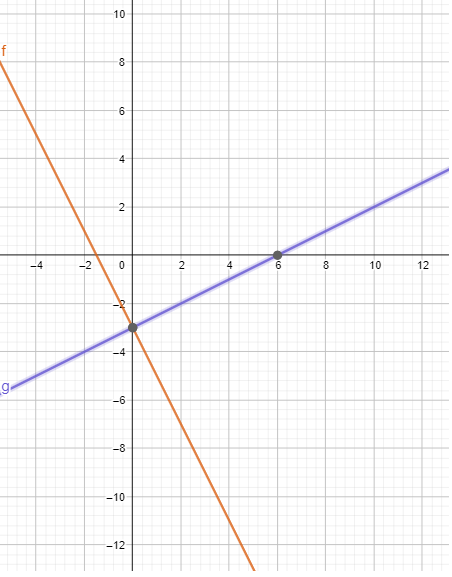
Lesson 5.1 Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Graphing
Essential Question How can you solve a system of linear equations?
EXPLORATION 1

EXPLORATION 2
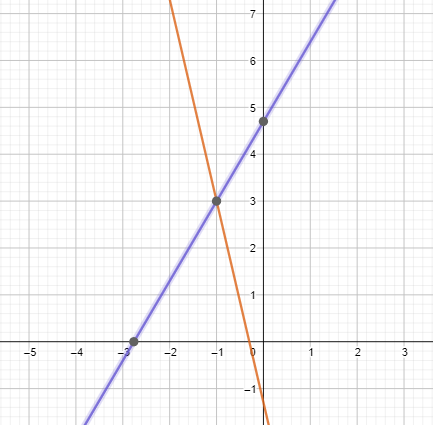
Communicate Your Answer
Question 3. How can you solve a system of linear equations? How can you check your solution? Answer:
Tell whether the ordered pair is a solution of the system of linear equations. Question 1. (1, -2); 2x + y = 0 -x + 2y = 5 Answer: 2x +y = 0 2(1) + (-2) = 0 2 – 2 = 0 The solution works on the first equation. -x + 2y = 5 -1 + 2(-2) = 5 -1 – 4 = 5 -5 = 5 The solution does not work in the second solution.
Question 2. (1, 4); y = 3x + 1 y = -x + 5 Answer: Given, (1, 4); y = 3x + 1 y = -x + 5 y = 3x + 1 4 = 3(1) + 1 4 = 4 The solution works on the first equation. y = -x + 5 4 = -1 + 5 4 = 4 The solution works on the second equation.
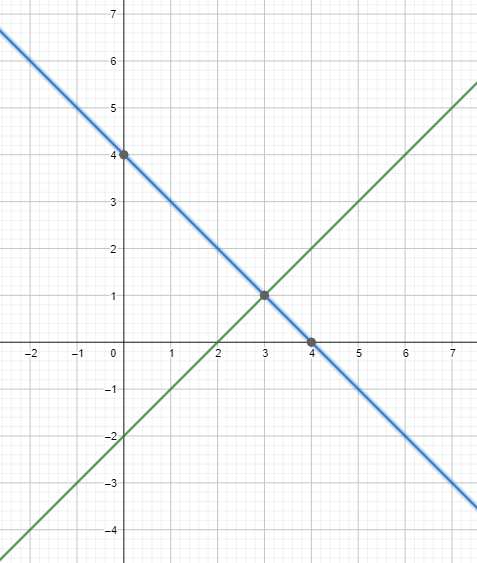
Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Graphing 5.1 Exercises

Monitoring Progress and Modeling with Mathematics
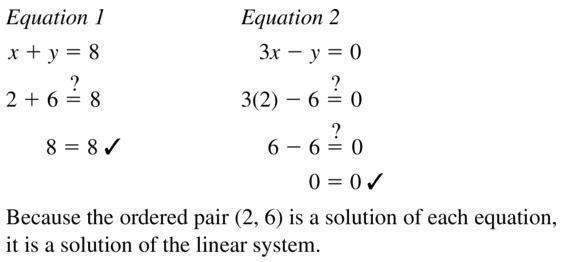
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
Solve the literal equation for y. Question 34. 10x + 5y = 5x + 20 Answer: 10x + 5y = 5x + 20 10x + 5y – 5x = 20 5x + 5y = 20 x + y = 4 y = 4 – x
Question 35. 9x + 18 = 6y – 3x Answer: 9x + 18 = 6y – 3x 9x + 3x + 18 = 6y 12x + 18 = 6y 2x + 3 = y So, the equation is y = 2x + 3
Question 36. \(\frac{3}{4}\) x + \(\frac{1}{4}\) y = 5 Answer: Given equation is \(\frac{3}{4}\) x + \(\frac{1}{4}\) y = 5 \(\frac{3}{4}\) x – \(\frac{3}{4}\) x + \(\frac{1}{4}\) y = 5 – \(\frac{3}{4}\) x \(\frac{1}{4}\) y = 5 – \(\frac{3}{4}\) x Multiply by 4 on both sides \(\frac{1}{4}\) y × 4 = (5 – \(\frac{3}{4}\) x)4 y = 20 – 3x
Lesson 5.2 Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Substitution
Essential Question How can you use substitution to solve a system of linear equations?
Using Substitution to Solve Systems Work with a partner. Solve each system of linear equations using two methods. Method 1 Solve for x first. Solve for x in one of the equations. Substitute the expression for x into the other equation to find y. Then substitute the value of y into one of the original equations to find x.
Method 2 Solve for y first. Solve for y in one of the equations. Substitute the expression for y into the other equation to find x. Then substitute the value of x into one of the original equations to find y. Is the solution the same using both methods? Explain which method you would prefer to use for each system a. x + y = -7 -5x + y = 5 Answer: x + y = -7 -5x + y = 5 Solve for x x + y = -7 -5x + y = 5 + – – 6x = -12 x = -2 -2 + y = -7 y = -7 + 2 y = -5
b. x – 6y = -11 3x + 2y = 7
Answer: x – 6y = -11 3x + 2y = 7— × 3 9x + 6y = 21
x – 6y = -11 9x + 6y = 21 10x = 10 x = 1 3(1) + 2y = 7 3 + 2y = 7 2y = 7 – 3 2y = 4 y = 2 So, x = 1 and y = 2
c. 4x + y = -1 3x – 5y = -18
Answer: 4x + y = -1 — × 5 ⇒ 20x + 5y = -5 3x – 5y = -18
20x + 5y = -5 3x – 5y = -18 23x = -23 x = -1 4x + y = -1 4(-1) + y = -1 -4 + y = -1 y = -1 + 4 y = 3
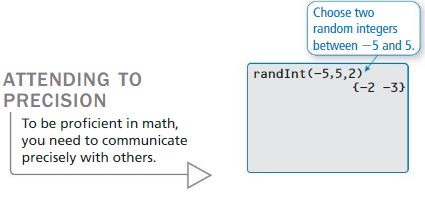
Question 3. How can you use substitution to solve a system of linear equations? Answer: Step 1 : First, solve one linear equation for y in terms of x . Step 2 : Then substitute that expression for y in the other linear equation. Step 3 : Solve this, and you have the x -coordinate of the intersection. Step 4 : Then plug in x to either equation to find the corresponding y -coordinate.
Question 4. Use one of the methods from Exploration 1 to solve each system of linear equations. Explain your choice of method. Check your solutions.
a. x + 2y = -7 2x – y = -9 Answer: x + 2y = -7—– × 2 ⇒ 2x + 4y = -14 2x – y = -9
2x + 4y = -14 2x – y = -9 – + + 5y = -5 y = -1 x + 2y = -7 x + 2(-1) = -7 x – 2 = -7 x = -7 + 2 x = -5
b.x – 2y = -6 2x + y = -2 Answer: x – 2y = -6 2x + y = -2 — × 2
x – 2y = -6 4x + 2y = -4 5x = -10 x = -2 x – 2y = -6 -2 – 2y = -6 -2y = -6 + 2 -2y = -4 y = 2
c.-3x + 2y = -10 -2x + y = -6 Answer: -3x + 2y = -10 -2x + y = -6 —- × 2 ⇒ -4x + 2y = -12
-3x + 2y = -10 -4x + 2y = -12 + – + x = 2 -2x + y = -6 -2(2) + y = -6 -4 + y = -6 y = -6 + 4 y = -2
d. 3x + 2y = 13 x – 3y = -3 Answer: 3x + 2y = 13 x – 3y = -3 — × 3 ⇒ 3x – 9y = -9
3x + 2y = 13 3x – 9y = -9 – + + 11y = 22 y = 2 x – 3(2) = -3 x – 6 = -3 x = -3 + 6 x = 3
e. 3x – 2y = 9 -x – 3y = 8 Answer: 3x – 2y = 9 -x – 3y = 8 —- × 3 ⇒ -3x – 9y = 24
3x – 2y = 9 -3x – 9y = 24 -11y = 33 y = -3 -x – 3(-3) = 8 -x + 9 = 8 -x = -1 x = 1
f. 3x – y = -6 4x + 5y = 11 Answer: 3x – y = -6 —– × 5 ⇒ 15x – 5y = -30 4x + 5y = 11
15x – 5y = -30 4x + 5y = 11 19x = -19 x = -1 3x – y = -6 3(-1) – y = -6 -3 – y = -6 -y = -6 + 3 -y = -3 y = 3
Solve the system of linear equations by substitution. Check your solution. Question 1. y = 3x + 14 y = -4x Answer: Given, y = 3x + 14 y = -4x -4x = 3x + 14 -4x – 3x = 14 -7x = 14 x = -14/7 x = -2 Substitute x value in y. y = -4x y = -4(-2) y = 8 Check: y = -4x 8 = -4(-2) 8 = 8
Question 2. 3x + 2y = 0 y = \(\frac{1}{2}\)x – 1 Answer: 3x + 2y = 0 y = \(\frac{1}{2}\)x – 1 \(\frac{1}{2}\)x – y = 1 —- × 2 x – 2y = 2 Solve 1 & 3 3x + 2y = 0 x – 2y = 2 4x = 2 x = 2/4 x = 1/2 3x + 2y = 0 3(\(\frac{1}{2}\)) + 2y = 0 \(\frac{3}{2}\) + 2y = 0 2y = –\(\frac{3}{2}\) y = –\(\frac{3}{4}\)
Question 3. x = 6y – 7 4x + y = -3 Answer: x = 6y – 7 4x + y = -3
x – 6y = -7—– × 4 ⇒ 4x – 24y = -28 4x + y = -3
4x – 24y = -28 4x + y = -3 -25y = -25 y = 1 x – 6y = -7 x – 6(1) = -7 x – 6 = -7 x = -7 + 6 x = -1
Solve the system of linear equations by substitution. Check your solution. Question 4. x + y = -2 -3x + y = 6 Answer: x + y = -2 -3x + y = 6 4x = -8 x = -8/4 x = -2 x + y = -2 -2 + y = -2 y = -2 + 2 y = 0 Check: x + y = -2 -2 + 0 = -2 -2 = -2
Question 5. -x + y = -4 4x – y = 10 Answer: -x + y = -4 4x – y = 10 3x = 6 x = 6/3 x = 2 -x + y = -4 -2 + y = -4 y = -4 + 2 y = -2 Check: -x + y = -4 -2 + (-2) = -4 -4 = -4
Question 6. 2x – y = -5 3x – y = 1 Answer: 2x – y = -5 3x – y = 1 -x = -6 x = 6 3(6) – y = 1 18 – y = 1 -y = 1 – 18 -y = -17 y = 17
Question 7. x – 2y = 7 3x – 2y = 3 Answer: x – 2y = 7 3x – 2y = 3 -2x = 4 x = -2 3x – 2y = 3 3(-2) – 2y = 3 -6 – 2y = 3 -2y = 3 + 6 -2y = 9 y = -9/2
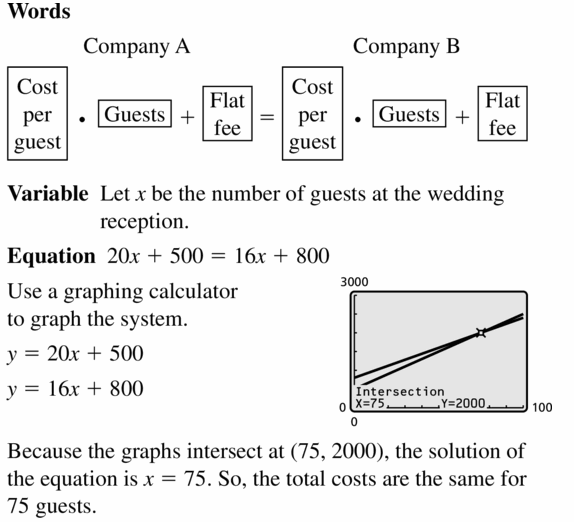
Question 8. There are a total of 64 students in a drama club and a yearbook club. The drama club has 10 more students than the yearbook club. Write a system of linear equations that represents this situation. How many students are in each club? Answer: Given, There are a total of 64 students in a drama club and a yearbook club. The drama club has 10 more students than the yearbook club. x = y + 10 y = 64 – x y = 64 – (y + 10) y = 64 – y – 10 y + y = 64 – 10 2y = 54 y = 27 x = y + 10 x = 27 + 10 x = 37 Check: x + y = 64 37 + 27 = 64 64 = 64
Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Substitution 5.2 Exercises
Vocabulary and Core Concept Check Question 1. WRITING Describe how to solve a system of linear equations by substitution. Answer: To solve a system of linear equations by substitution, solve one of the equations for one of the variables. Then substitute the expression for this variable into the other equation to find the value of the other variable. Finally, substitute this value into one of the original equations to find the value of the other variable.
Question 2. NUMBER SENSE When solving a system of linear equations by substitution, how do you decide which variable to solve for in Step 1? Answer: The solution does not depend on the choice of variable which is substituted. Any of the two variables can be solved in step 1 and then, substituted in the second equation.
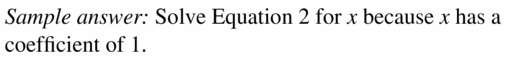
Question 16. 11x – 7y = -14 x – 2y = -4 Answer: Given equation is 11x – 7y = -14 x – 2y = -4 —- × 11 ⇒ 11x – 22y = -44
11x – 7y = -14 11x – 22y = -44 15y = 30 y = 2 x – 2y = -4 x – 2(2) = -4 x – 4 = -4 x = -4 + 4 x = 0 Check: x – 2y = -4 0 – 2 (2) = -4 -4 = -4
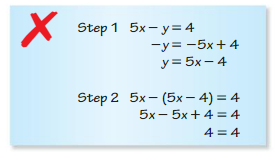
Question 30. MAKING AN ARGUMENT Your friend says that given a linear system with an equation of a horizontal line and an equation of a vertical line, you cannot solve the system by substitution. Is your friend correct? Explain. Answer: The equation of the vertical line is x = a The equation of the horizontal line is y = b We cannot substitute one of the variables into the other equation Therefore your friend is correct.

Find the sum or difference. Question 36. (x – 4) + (2x – 7) Answer: Given expression is (x – 4) + (2x – 7) x – 4 + 2x – 7 3x – 11 So, (x – 4) + (2x – 7) = 3x – 11
Question 37. (5y – 12) + (-5y – 1) Answer: Given expression is (5y – 12) + (-5y – 1) 5y – 12 – 5y – 1 = -12 – 1 = -13 So, (5y – 12) + (-5y – 1) = -13
Question 38. (t – 8) – (t + 15) Answer: Given expression is (t – 8) – (t + 15) t – 8 – t – 15 -8 – 15 -23 So, (t – 8) – (t + 15) = -23
Question 39. (6d + 2) – (3d – 3) Answer: Given expression is (6d + 2) – (3d – 3) 6d + 2 – 3d + 3 3d + 5 So, (6d + 2) – (3d – 3) = 3d + 5
Question 40. 4(m + 2) + 3(6m – 4) Answer: Given expression is 4(m + 2) + 3(6m – 4) 4(m) + 4(2) + 3(6m) + 3(-4) 4m + 8 + 18m – 12 22m + 8 – 12 22m – 4 So, 4(m + 2) + 3(6m – 4) = 22m – 4
Question 41. 2(5v + 6) – 6(-9v + 2) Answer: Given expression is 2(5v + 6) – 6(-9v + 2) 2(5v) + 2(6) – 6(-9v) – 6(2) 10v + 12 + 54v – 12 64v + 0 = 64v So, 2(5v + 6) – 6(-9v + 2) = 64v
Lesson 5.3 Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Elimination
Essential Question How can you use elimination to solve a system of linear equations?
b. 2x + y = 6 2x – y = 2 Answer: 2x + y = 6 2x – y = 2 4x = 8 x = 8/4 x = 2 2x + y = 6 2(2) + y = 6 4 + y = 6 y = 6 – 4 y = 2
c. x – 2y = -7 x + 2y = 5 Answer: x – 2y = -7 x + 2y = 5 2x = -2 x = -1 x + 2y = 5 -1 + 2y = 5 2y = 5 + 1 2y = 6 y = 3
EXPLORATION 3
Using Elimination to Solve a System Work with a partner. 2x + y = 7 Equation 1 x + 5y = 17 Equation 2 a. Can you eliminate a variable by adding or subtracting the equations as they are? If not, what do you need to do to one or both equations so that you can? b. Solve the system individually. Then exchange solutions with your partner and compare and check the solutions. Answer: Given, 2x + y = 7 Equation 1 x + 5y = 17 Equation 2—- × 2 We cannot eliminate by adding or subtracting the equations as they are, we need to multiply equation 2 by 2 2x + y = 7 (-)2x + 10y = 34 -10y = -27 y = 2.7 2x + y = 7 2x + 2.7 = 7 2x = 4.3 x = 2.15 2x + y = 7 2(2.15) + 2.7 = 7 4.3 + 2.7 = 7 7 = 7 So, LHS = RHS
Question 4. How can you use elimination to solve a system of linear equations? Answer: 1. Write given equations in the standard form. 2. Make the coefficients of one variable opposite. 3. Either subtract or add the equations to get an equation in one variable.
Question 5. When can you add or subtract the equations in a system to solve the system? When do you have to multiply first? Justify your answers with examples. Answer: The equations representing the first situation of directly adding or subtracting the equations are x + y = 5 x – y = 1 Adding equations 1 and 2, we observe that the variable y is eliminated and we are remained with linear equation in single variable 2x = 6 x = 3 Putting this value of x in any of the equations 1 or 2 will get the value of y, and thus we will get the required solution of the system of equations. 3 + y = 5 y = 5 – 3 y = 2 So, the required solution for the system of equations (x, y) = (3, 2) The equations representing the second situation of multiplying first and then adding or subtracting 2x + 3y = 8 —– × 3 3x + 2y = 7 —- × 4 6x + 9y = 24 6x + 4y = 14 5y = 10 y = 2 3x + 2y = 7 3x + 2(2) = 7 3x + 4 = 7 3x = 7 – 4 3x = 3 x = 1 Thus, the required solution for this system of equations is given by (x, y) = (1, 5).
Question 6. In Exploration 3, why can you multiply an equation in the system by a constant and not change the solution of the system? Explain your reasoning. Answer: You need to multiply one or both of the equations by a constant to get the same coefficient.
Solve the system of linear equations by elimination. Check your solution. Question 1. 3x + 2y = 7 -3x + 4y = 5 Answer: Given equations 3x + 2y = 7 -3x + 4y = 5 6y = 12 y = 2 3x + 2y = 7 3x + 2(2) = 7 3x + 4 = 7 3x = 7 – 4 3x = 3 x = 1 Check: 3x + 2y = 7 3(1) + 2(2) = 7 3 + 4 = 7 7 = 7 LHS = RHS
Question 2. x – 3y = 24 3x + y = 12 Answer: Given equations x – 3y = 24 3x + y = 12 —- × 3 ⇒ 36x + 3y = 36
x – 3y = 24 9x + 3y = 36 10x = 60 x = 60/10 x = 6 3x + y = 12 3(6) + y = 12 18 + y = 12 y = 12 – 18 y = -6 Check: 3x + y = 12 3(6) + (-6) = 12 18 – 6 = 12 12 = 12 LHS = RHS
Question 3. x + 4y = 22 4x + y = 13 Answer: Given equations x + 4y = 22 4x + y = 13 —- × 4 ⇒ 16x + 4y = 52
x + 4y = 22 16x + 4y = 52 -15x = -30 x = 30/15 x = 2 x + 4y = 22 2 + 4y = 22 4y = 22 – 2 4y = 20 y = 20/4 y = 5 Check: x + 4y = 22 2 + 4(5) = 22 2 + 20 = 22 22 = 22 LHS = RHS
Question 4. Solve the system in Example 3 by eliminating x. Answer:
Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Elimination 5.3 Exercises

Question 10. 3x – 30 = y 7y – 6 = 3x Answer:

Question 12. 8x – 5y = 11 4x – 3y = 5 Answer:
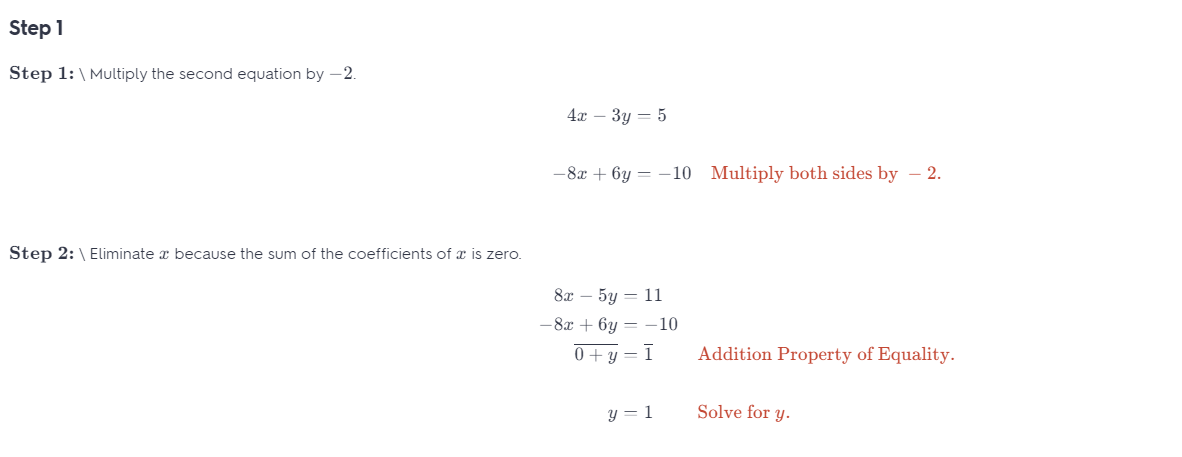
Question 24. -6y + 2 = -4x y – 2 = x Answer:
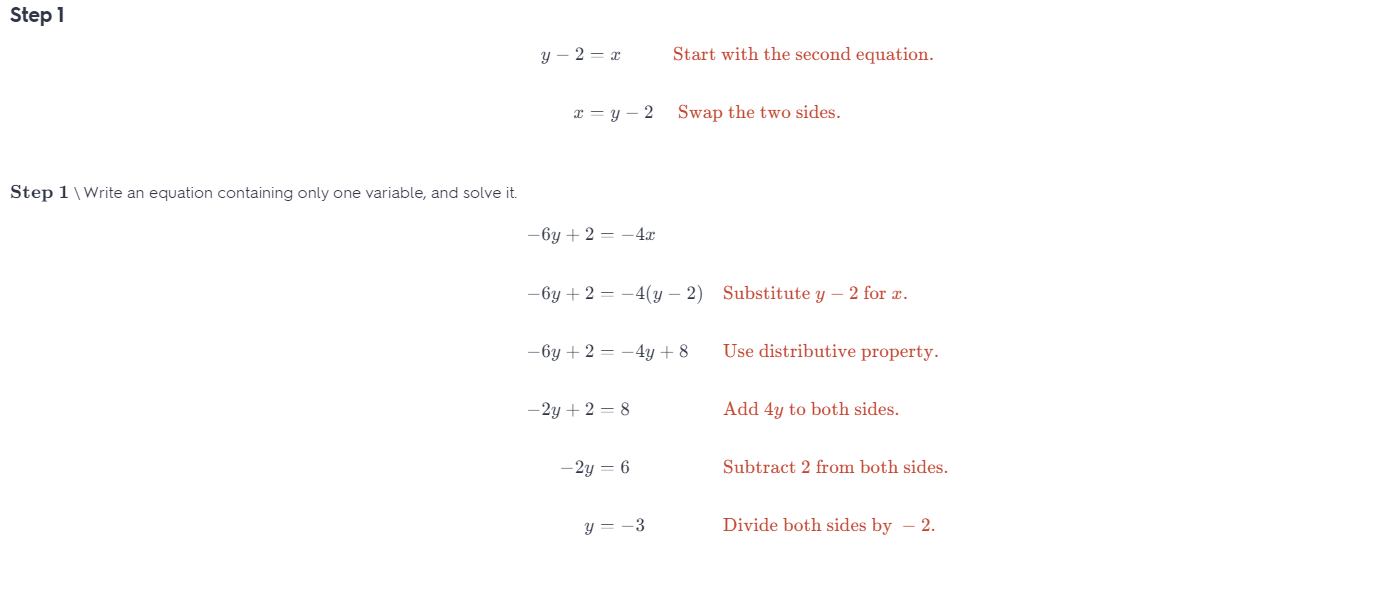
Question 26. 3x + y = \(\frac{1}{3}\) 2x – 3y = \(\frac{8}{3}\) Answer:
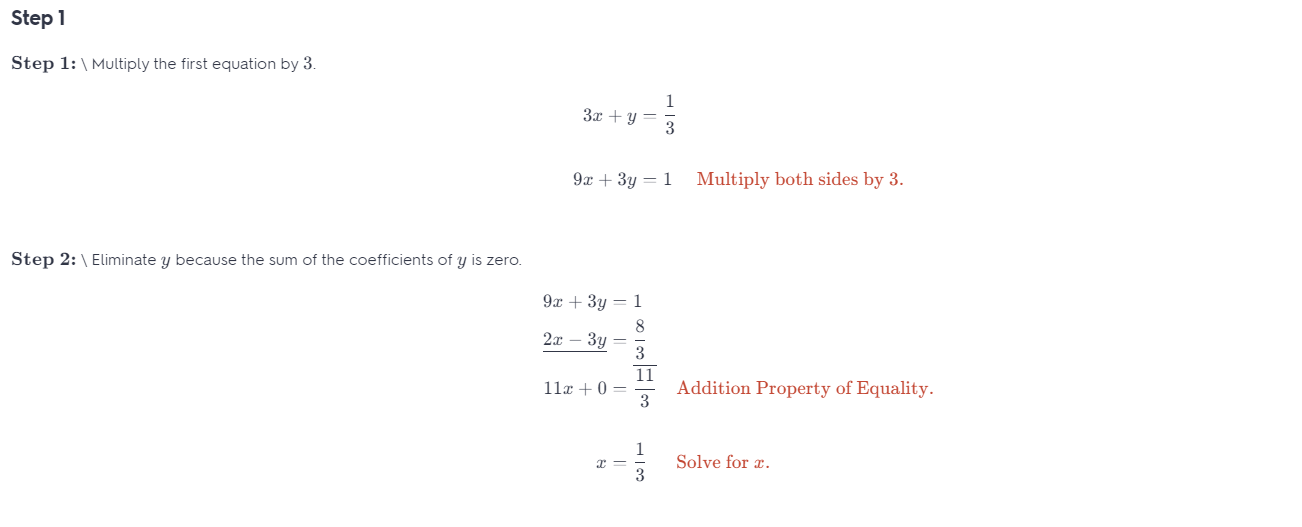
Question 29. MAKING AN ARGUMENT Your friend says that any system of equations that can be solved by elimination can be solved by substitution in an equal or fewer number of steps. Is your friend correct? Explain. Answer: No, If like terms are in the same respective positions and at least one pair of like terms has the same or opposite coefficients, then elimination is more efficient than substitution and will take fewer steps. On the other hand, if one of the variables in one of the equations is either isolated already or has a coefficient of 1 or -1, then substitution is more efficient and will take fewer steps.
Question 30. THOUGHT PROVOKING Write a system of linear equations that can be added to eliminate a variable or subtracted to eliminate a variable. Answer:
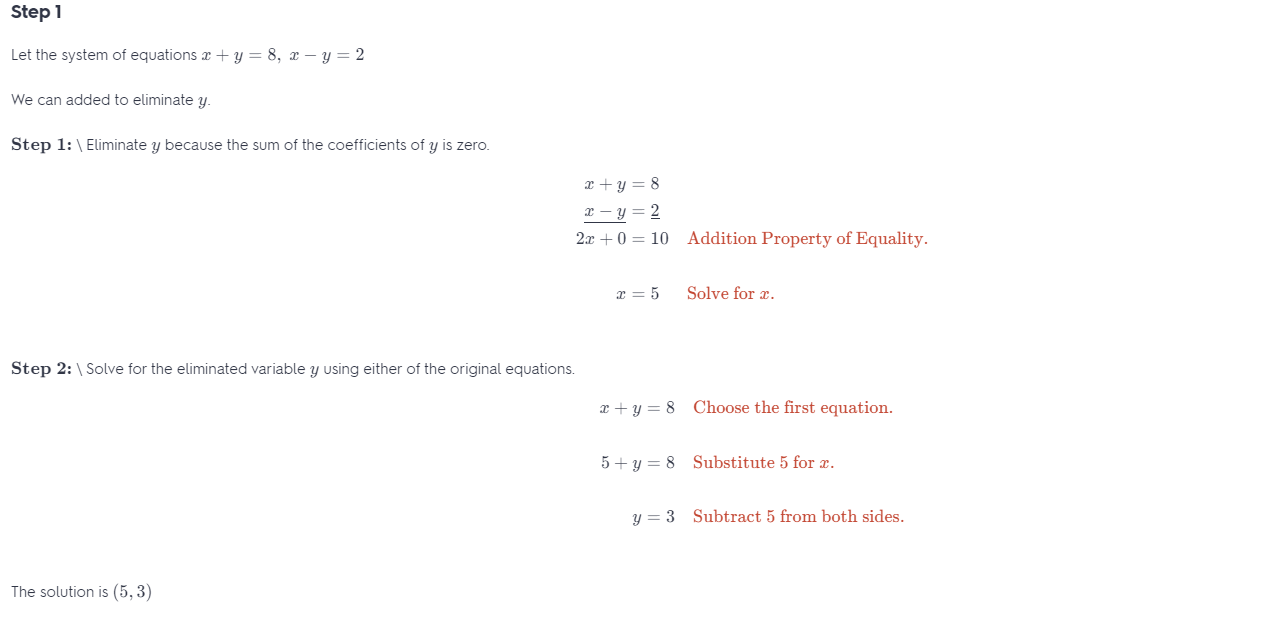
Question 34. PROBLEM SOLVING A motorboat takes 40 minutes to travel 20 miles downstream. The return trip takes 60 minutes. What is the speed of the current? Answer:

Solve the equation. Determine whether the equation has one solution, no solution, or infinitely many solutions. Question 36. 5d – 8 = 1 + 5d Answer:
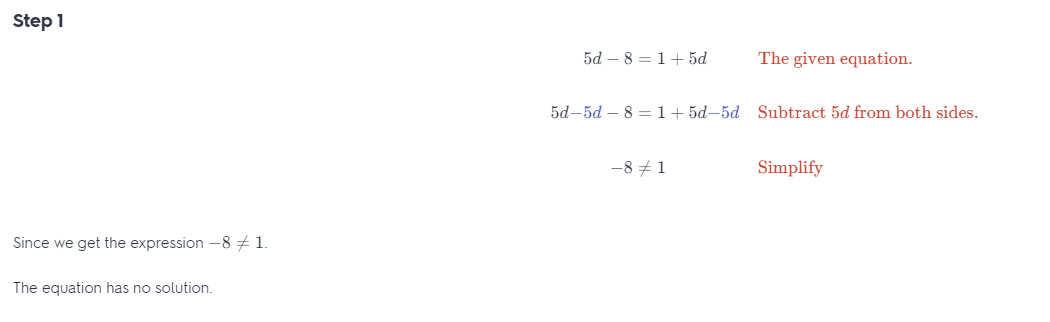
Write an equation of the line that passes through the given point and is parallel to the given line. Question 40. (4, -1); y = -2x + 7 Answer:
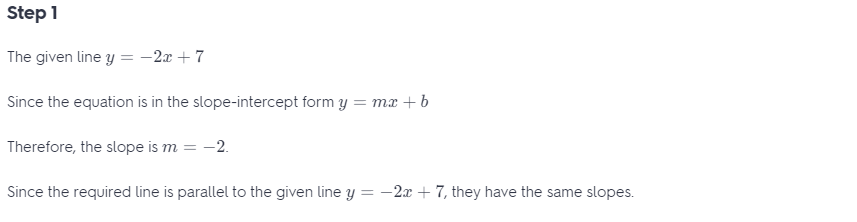
Question 42. (-5, -2); y = \(\frac{2}{3}\)x + 1 Answer:

Lesson 5.4 Solving Special Systems of Linear Equations
Essential Question Can a system of linear equations have no solution or infinitely many solutions?
| x | 1 | -0.5 |
| y | -5 | 5 |
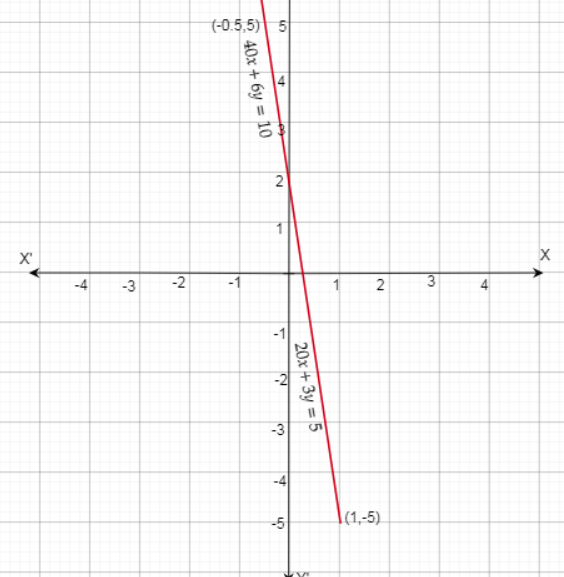
Question 3. Can a system of linear equations have no solution or infinitely many solutions? Give examples to support your answers. Answer: A system of linear equations can have infinitely many solutions or no solution. Example: 4x + 3y = 9 4x + 3y = -7 It has no solution 4x + 3y = 9 8x + 6y = 18 It has infinitely many solutions.
Solve the system of linear equations. Question 1. x + y = 3 2x + 2y = 6 Answer: Given equations x + y = 3 2x + 2y = 6 ⇒ x + y = 3 x + y = 3 x + y = 3 x + y – x – y = 3 – 3 0 = 0 It has infinitely many solutions.
Question 2. y = -x + 3 2x + 2y = 4 Answer: y = -x + 3 2x + 2y = 4 x + y = 3 2x + 2y = 4 ⇒ x + y = 2 x + y = 3 x + y = 2 It has no solution.
Question 3. x + y = 3 x + 2y = 4 Answer: x + y = 3 x + 2y = 4 x + y – x – 2y = 3 – 4 -y = -1 y = 1 It has one solution.
Question 4. y = -10x + 2 10x + y = 10 Answer: y = -10x + 2 ⇒ 10x + y = 2 10x + y = 10 10x + y – 10x – y = 2 – 10 0 = -8 It has no solution.
Question 5. WHAT IF? What happens to the solution in Example 3 when the perimeter of the trapezoidal piece of land is 96 kilometers? Explain. Answer: The trapezoidal land is changed from 48 kilometers to 96 kilometers. 6x + 12y = 96 and 18x + 36y = 144 18x + 36y = 188 18x + 36y – (18x + 36y) = 288 – 144 18x + 36y – 18x – 36y = 144 0 ≠ 144 Therefore, there is no solution to the given system of linear equations.
Solving Special Systems of Linear Equations 5.4 Exercises
Vocabulary and Core Concept Check Question 1. REASONING Is it possible for a system of linear equations to have exactly two solutions? Explain. Answer: Two lines cannot intersect at exactly two points. So, a system of linear equations cannot have exactly two solutions.
Question 2. WRITING Compare the graph of a system of linear equations that has infinitely many solutions and the graph of a system of linear equations that has no solution. Answer:
Question 4. 2x – 2y = 4 -x + y = -2 Answer: Given equations 2x – 2y = 4 -x + y = -2 —- × 2 ⇒ -2x + 2y = -4
2x – 2y = 4 -2x + 2y = -4 0 = 0 It has an infinite number of solutions.
Question 6. x – y = 0 5x – 2y = 6 Answer: Given equations x – y = 0 — × 2 ⇒ 2x – 2y = 0 5x – 2y = 6
2x – 2y = 0 5x – 2y = 6 -3x = -6 x = 2 Substitute x in eq. (1) x – y = 0 2 – y = 0 y = 2 It has one solution.
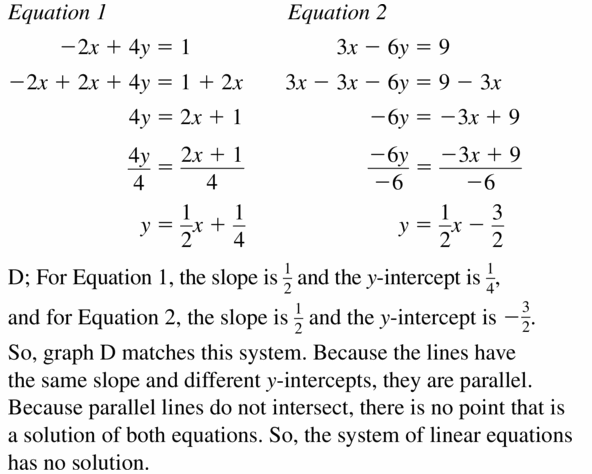
Question 8. 5x + 3y = 17 x – 3y = -2 Answer:
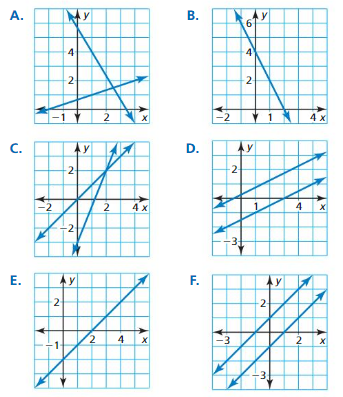
Question 10. y = -6x – 8 y = -6x + 8 Answer:
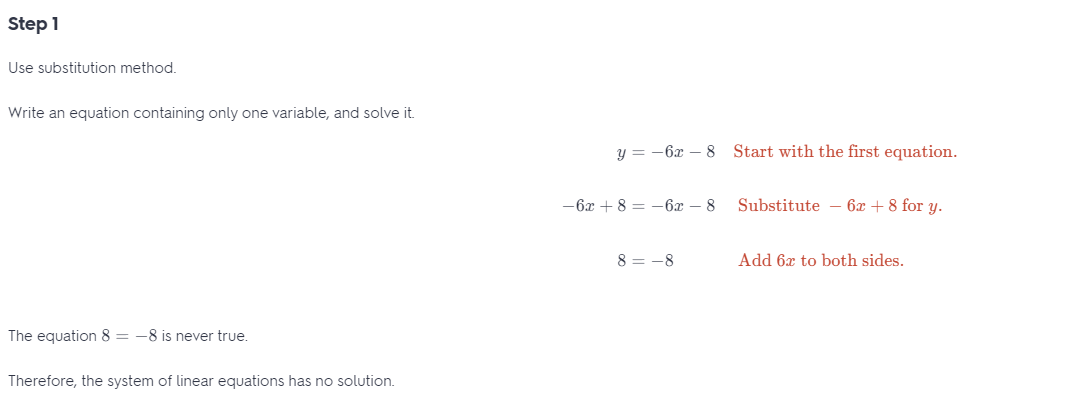
Question 12. -x + 2y = 7 x – 2y = 7 Answer:
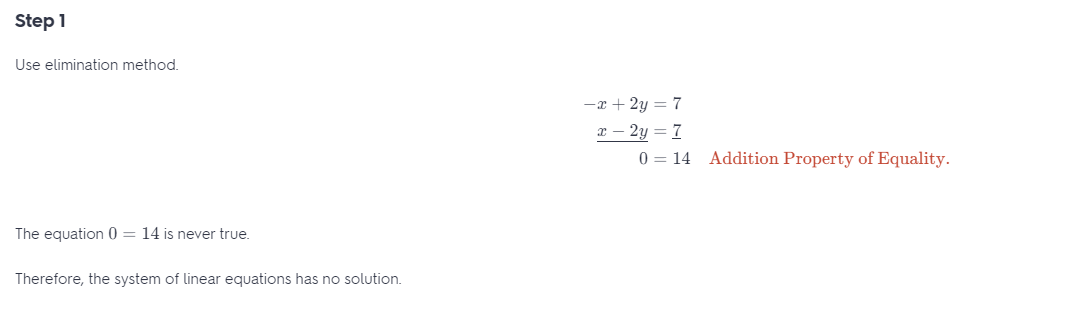
Question 14. 15x – 5y = -20 -3x + y = 4 Answer:
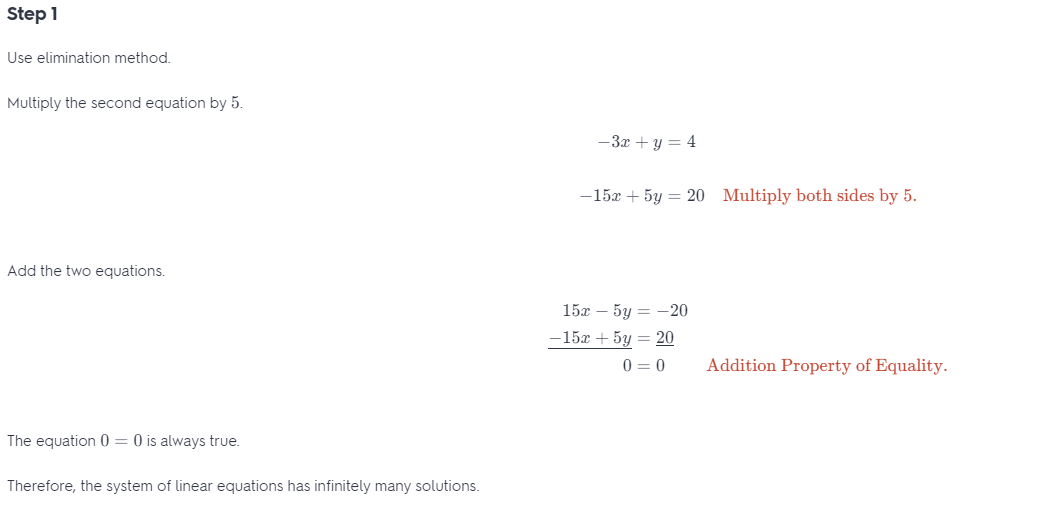
Question 16. 3x – 2y = -5 4x + 5y = 47 Answer:
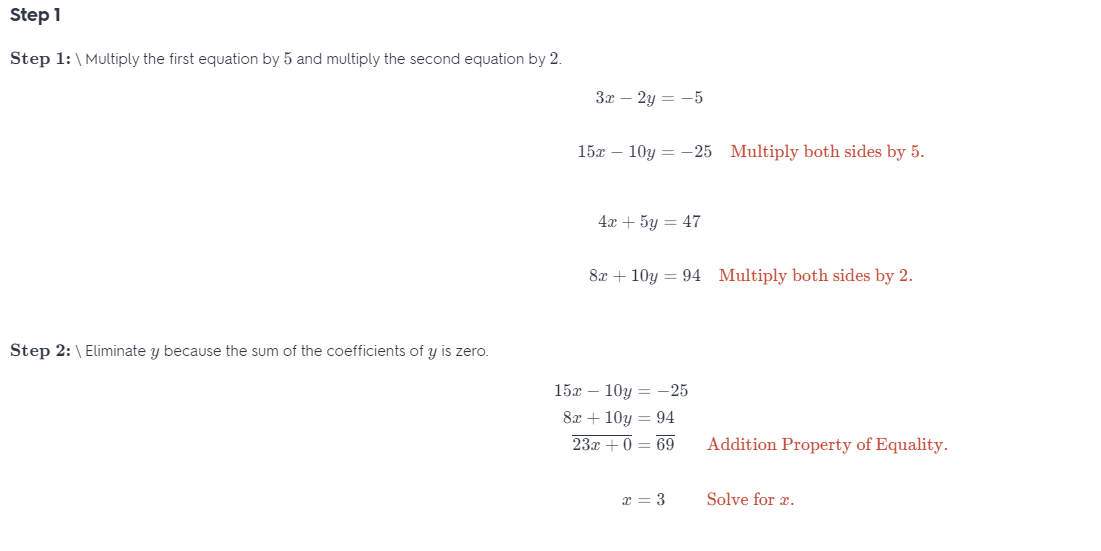
Question 18. y = -6x – 2 12x + 2y = -6 Answer:

Question 20. -7x + 7y = 1 2x – 2y = -18 Answer:
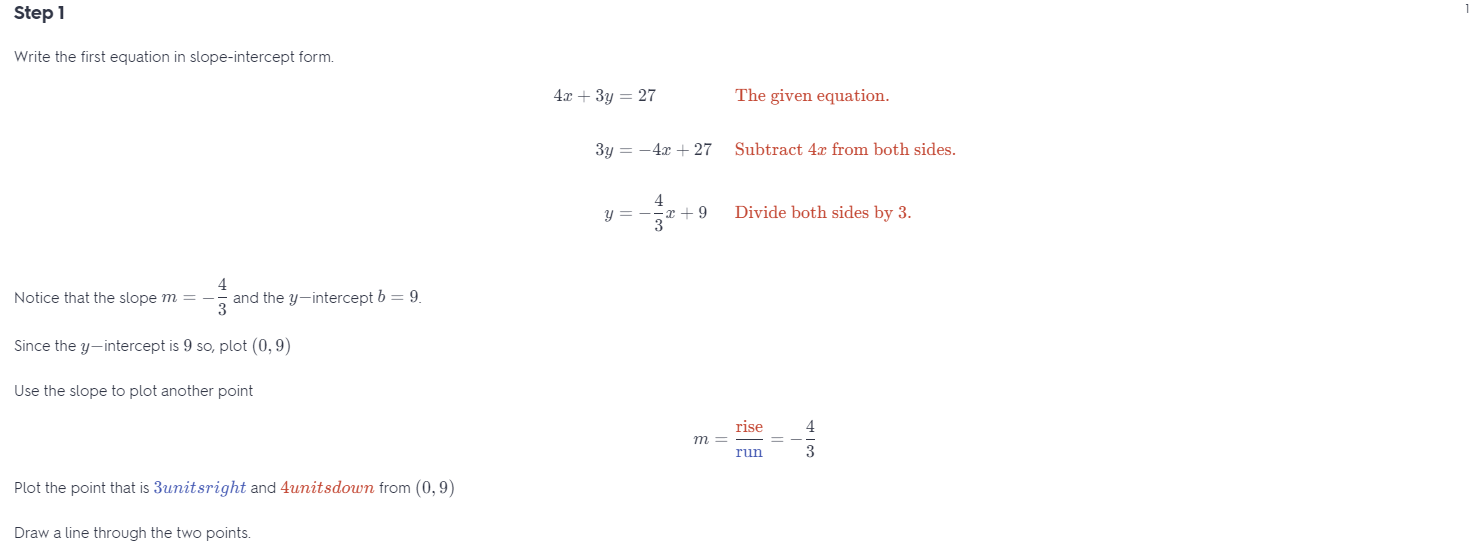
Question 26. MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS In a canoe race, Team A is traveling 6 miles per hour and is 2 miles ahead of Team B. Team B is also traveling 6 miles per hour. The teams continue traveling at their current rates for the remainder of the race. Write a system of linear equations that represents this situation. Will Team B catch up to Team A? Explain. Answer:

Question 28. THOUGHT PROVOKING Write a system of three linear equations in two variables so that any two of the equations have exactly one solution, but the entire system of equations has no solution. Answer:

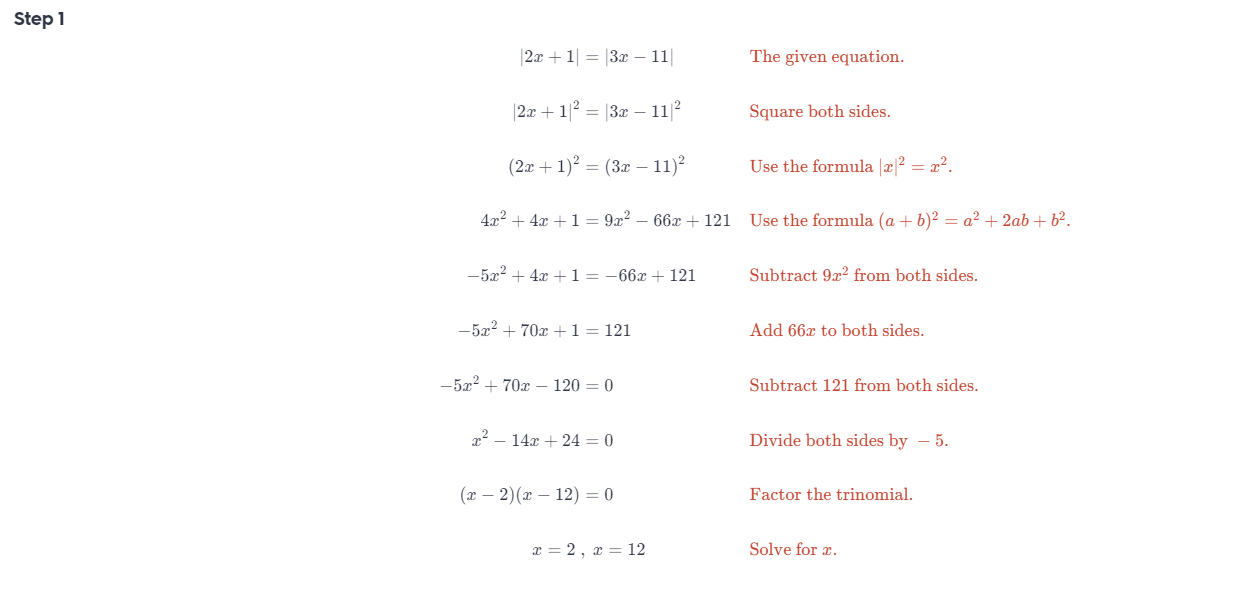
Question 34. |3x – 45| = |12x| Answer:
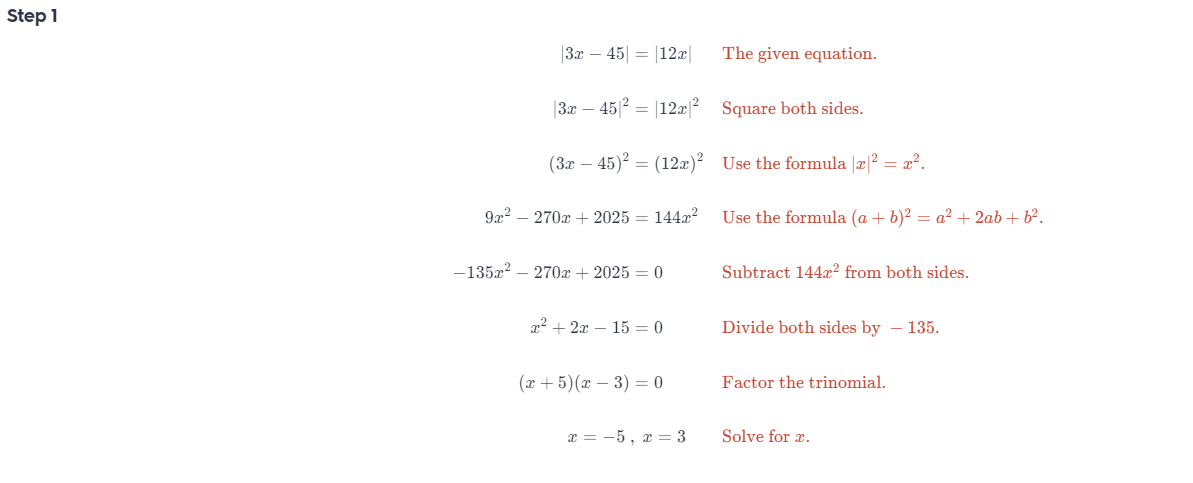
Question 36. |2x + 1| = |3x – 11| Answer:
Solving Systems of Linear Equations Study Skills: Analyzing Your Errors
5.1 – 5.4 What Did You Learn?
Core Vocabulary system of linear equations, p. 236 solution of a system of linear equations, p. 236
Core Concepts Section 5.1 Solving a System of Linear Equations by Graphing, p. 237
Section 5.2 Solving a System of Linear Equations by Substitution, p. 242
Section 5.3 Solving a System of Linear Equations by Elimination, p. 248
Section 5.4 Solutions of Systems of Linear Equations, p. 254
Mathematical Practices
Question 1. Describe the given information in Exercise 33 on page 246 and your plan for finding the solution. Answer:
Question 2. Describe another real-life situation similar to Exercise 22 on page 251 and the mathematics that you can apply to solve the problem. Answer:
Question 3. What question(s) can you ask your friend to help her understand the error in the statement she made in Exercise 32 on page 258? Answer:
Study Skills: Analyzing Your Errors

Solving Systems of Linear Equations 5.1–5.4 Quiz
Solve the system of linear equations by substitution. Check your solution. Question 4. y = x – 4 -2x + y = 18 Answer: Given equations y = x – 4 -2x + y = 18 x – y = 4 -2x + y = 18 -x = 22 x = -22 y = -22 – 4 y = -26 Check: -26 = -22 – 4 -26 = -26 The solution is correct.
Question 5. 2y + x = -4 y – x = -5 Answer: Given equations 2y + x = -4 y – x = -5 3y = -9 y = -9/3 y = -3 -3 – x = -5 -x = -5 + 3 -x = -2 x = 2 Check: 2y + x = -4 2(-3) + 2 = -4 -6 + 2 = -4 -4 = -4
Question 6. 3x – 5y = 13 x + 4y = 10 Answer: Given equations 3x – 5y = 13 x + 4y = 10 —- × 3 ⇒ 3x + 12y = 30
3x – 5y = 13 3x + 12y = 30 -17y = -17 y = 1 x + 4y = 10 x + 4(1) = 10 x + 4 = 10 x = 10 – 4 x = 6 Check: 6 + 4(1) = 10 6 + 4 = 10 10 = 10
Solve the system of linear equations by elimination. Check your solution. Question 7. x + y = 4 -3x – y = -8 Answer: Given equations x + y = 4 -3x – y = -8 -2x = -4 x = 2 2 + y = 4 y = 4 – 2 y = 2 Check: x + y = 4 2 + 2 = 4 4 = 4
Question 8. x + 3y = 1 5x + 6y = 14 Answer: x + 3y = 1 —- × 2 5x + 6y = 14
2x + 6y = 2 5x + 6y = 14 -3x = -12 x = 4 4 + 3y = 1 3y = 1 – 4 3y = -3 y = -1 Check: 2x + 6y = 2 2(4) + 6(-1) = 2 8 – 6 = 2 2 = 2
Question 9. 2x – 3y = -5 5x + 2y = 16 Answer: Given equations 2x – 3y = -5 — × 5 ⇒ 10x – 15y = -15 5x + 2y = 16 — × 2 ⇒ 10x + 4y = 32
10x – 15y = -25 (-)10x + 4y = 32 -19y = -57 y = 3 5x + 2(3) = 16 5x + 6 = 16 5x = 16 – 6 5x = 10 x = 2 Check: 5x + 2y = 16 5(2) + 2(3) = 16 10 + 6 = 16 16 = 16 LHS = RHS
Solve the system of linear equations. Question 10. x – y = 1 x – y = 6 Answer: x – y = 1 (-)x – y = 6 0 = 7 It has no solution.
Question 11. 6x + 2y = 16 2x – y = 2 Answer: Given equation 6x + 2y = 16 2x – y = 2 —- × 2 ⇒ 4x – 2y = 4
6x + 2y = 16 4x – 2y = 4 10x = 20 x = 20/10 x = 2 4x – 2y = 4 4(2) – 2y = 4 8 – 2y = 4 8 – 4 = 2y 2y = 4 y = 2 Check: 4x – 2y = 4 4(2) – 2(2) = 4 8 – 4 = 4 4 = 4 LHS = RHS
Question 12. 3x – 3y = -2 -6x + 6y = 4 Answer: 3x – 3y = -2 —- × 2 ⇒ 6x – 6y = -4 -6x + 6y = 4
6x – 6y = -4 -6x + 6y = 4 0 = 0 It has no solution.

Question 14. It takes you 3 hours to drive to a concert 135 miles away. You drive 55 miles per hour on highways and 40 miles per hour on the rest of the roads. a. How much time do you spend driving at each speed? b. How many miles do you drive on highways? the rest of the roads? Answer: Given, It takes you 3 hours to drive to a concert 135 miles away. You drive 55 miles per hour on highways and 40 miles per hour on the rest of the roads. Let x be the number of hour taken to drive on highway and y be the number of hour taken to drive on the rest of the road. 55x + 40y = 135 —- (1) x + y = 3 —–(2) —- 55 55x + 55y = 165 55x + 40y = 135 -10y = -15 y = 1.5 Hence 1.5 hours is spend to drive to speed of 55 miles per hour and 1.5 hours are spend to drive for 45 miles per hour.
Lesson 5.5 Solving Equations by Graphing
Essential Question How can you use a system of linear equations to solve an equation with variables on both sides?
Previously, you learned how to use algebra to solve equations with variables on both sides. Another way is to use a system of linear equations.
Solving Equations Algebraically and Graphically Work with a partner. Solve each equation using two methods. Method 1 Use an algebraic method. Method 2 Use a graphical method. Is the solution the same using both methods? a. \(\frac{1}{2}\)x + 4 = –\(\frac{1}{4}\)x + 1 b. \(\frac{2}{3}\)x + 4 = \(\frac{1}{3}\)x + 3 c. –\(\frac{2}{3}\) x – 1 = \(\frac{1}{3}\)x – 4 d. \(\frac{4}{5}\) x + \(\frac{7}{5}\) = 3x – 3 e. -x + 2.5 = 2x – 0.5 f. – 3x + 1.5 = x + 1.5 Answer: a. \(\frac{1}{2}\)x + 4 = –\(\frac{1}{4}\)x + 1 Given, \(\frac{1}{2}\)x + 4 = –\(\frac{1}{4}\)x + 1 Adding \(\frac{1}{4}\)x on both sides \(\frac{3}{4}\)x + 4 = 1 \(\frac{3}{4}\)x = -3 3x = -12 x = -12/3 x = -4 y = \(\frac{1}{2}\)x + 4 y = –\(\frac{1}{4}\)x + 1 y = \(\frac{1}{2}\)x + 4 x = 0 y = \(\frac{1}{2}\)(0) + 4 y = 4 Coordinates: (0, 4) Put x = 1 y = \(\frac{1}{2}\)(1) + 4 y = \(\frac{1}{2}\) + 4 y = 4.5 Coordinates: (1, 4.5) y = –\(\frac{1}{4}\)x + 1 put x = 0 y = –\(\frac{1}{4}\)(0) + 1 y = 1 Coordinates: (0, 1) Put x = 1 y = –\(\frac{1}{4}\)(1) + 1 y = -0.25 + 1 y = 0.75 Coordinates: (1, 0.75)
b. \(\frac{2}{3}\)x + 4 = \(\frac{1}{3}\)x + 3 \(\frac{2}{3}\)x + 4 = \(\frac{1}{3}\)x + 3 \(\frac{2}{3}\)x + 4 – \(\frac{1}{3}\)x = 3 \(\frac{1}{3}\)x + 4 – 3 = 0 \(\frac{1}{3}\)x + 1 = 0 \(\frac{1}{3}\)x = -1 x = -1 × 3 x = -3 y = \(\frac{2}{3}\)x + 4 y = \(\frac{1}{3}\)x + 3 y = \(\frac{2}{3}\)x + 4 put x = 0 y = \(\frac{2}{3}\)(0) + 4 y = 4 put x = 1 y = \(\frac{2}{3}\)(1) + 4 y = \(\frac{2}{3}\) + 4 y = 0.67 + 4 y = 4.67 Coordinates: (1, 4.67) y = \(\frac{1}{3}\)x + 3 put x = 0 y = \(\frac{1}{3}\)(0) + 3 y = 3 Coordinates: (0, 3) put x = 1 y = \(\frac{1}{3}\)(1) + 3 y = 0.33 + 3 y = 3.33 Coordinates: (1, 3.33)
c. –\(\frac{2}{3}\) x – 1 = \(\frac{1}{3}\)x – 4 –\(\frac{2}{3}\) x – 1 = \(\frac{1}{3}\)x – 4 –\(\frac{2}{3}\) x – 1 – \(\frac{1}{3}\)x = – 4 -1x – 1 = -4 -x = -4 + 1 -x = -3 x = 3 y = –\(\frac{2}{3}\) x – 1 y = \(\frac{1}{3}\)x – 4 y = –\(\frac{2}{3}\) x – 1 put x = 0 y = –\(\frac{2}{3}\) (0) – 1 y = -1 Coordinates: (0, -1) put x = 1 y = –\(\frac{2}{3}\) (1) – 1 y = -0.67 – 1 y = -1.67 Coordinates: (1, -1.67) y = \(\frac{1}{3}\)x – 4 put x = 0 y = \(\frac{1}{3}\)(0) – 4 y = -4 Coordinates: (0, -4) put x = 1 y = \(\frac{1}{3}\)(1) – 4 y = 0.33 – 4 y = -3.66 Coordinates: (1, -3.66)
d. \(\frac{4}{5}\) x + \(\frac{7}{5}\) = 3x – 3 \(\frac{4}{5}\) x + \(\frac{7}{5}\) = 3x – 3 \(\frac{4}{5}\) x + \(\frac{7}{5}\) = 3x – 3 \(\frac{7}{5}\) = \(\frac{11}{5}\) x – 3 \(\frac{22}{5}\) = \(\frac{11}{5}\) x \(\frac{5}{11}\) × \(\frac{22}{5}\) = \(\frac{5}{11}\) × \(\frac{11}{5}\)x 2 = x y = \(\frac{4}{5}\) x + \(\frac{7}{5}\) y = 3x – 3 y = \(\frac{4}{5}\) x + \(\frac{7}{5}\) put x = 0 y = \(\frac{4}{5}\) (0) + \(\frac{7}{5}\) y = \(\frac{7}{5}\) y = 1.4 Coordinates: (0, 1.4) put x = 1 y = \(\frac{4}{5}\) (1) + \(\frac{7}{5}\) y = \(\frac{11}{5}\) y = 2.2 Coordinates: (1, 2.2) y = 3x – 3 put x = 0 y = 3(0) – 3 y = -3 put x = 1 y = 3(1) – 3 y = 0 Coordinates: (1, 0)
e. -x + 2.5 = 2x – 0.5 -x + 2.5 = 2x – 0.5 -x – 2x = -2.5 – 0.5 -3x = -3 x = 1 y = -x + 2.5 y = 2x – 0.5 y = -x + 2.5 put x = 0 y = 0 + 2.5 y = 2.5 put x = 2 y = -2 + 2.5 y = 0.5 Coordinates: (2, 0.5) y = 2x – 0.5 x = 0 y = 2(0) – 0.5 y = -0.5 Coordinates: (0, -0.5) x = 2 y = 2(2) – 0.5 y = 4 – 0.5 y = 3.5 Coordinates: (2, 3.5)
f. – 3x + 1.5 = x + 1.5 – 3x + 1.5 = x + 1.5 1.5 = 4x + 1.5 4x = 0 y = -3x + 1.5 and y = x + 1.5 y = -3x + 1.5 put x = 2 y = -3(2) + 1.5 y = -6 + 1.5 y = -4.5 Coordinates: (2, -4.5) put x = 1 y = -3(1) + 1.5 y = -3 + 1.5 y = -1.5 Coordinates: (1, -1.5) y = x + 1.5 put x = 1 y = 1 + 1.5 y = 2.5 Coordinates: (1, 2.5) put x = 2 y = 2 + 1.5 y = 3.5 Coordinates: (2, 3.5)
Question 3. How can you use a system of linear equations to solve an equation with variables on both sides? Answer: 1. First we choose left side to be the variable side and then the right will be the constant side. 2. Next we collect the variable terms to the variable side and the constants to the other side, using the addition or subtraction property of equality. 3. Now we make the coefficient of the variable using multiplication or division property of equality. 4. In the final step we substitute this value in the original equation to check the solution.
Question 4. Compare the algebraic method and the graphical method for solving a linear equation with variables on both sides. Describe the advantages and disadvantages of each method. Answer: It helps you to graph quickly, having both equations in Y form makes this method useful. In contrast, if neither equation has Y isolated, you are better off using substitution or elimination.
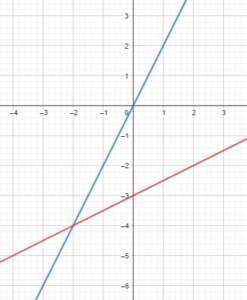
Solving Equations by Graphing 5.5 Exercises
Question 32. 2.1x + 0.6 = -1.4x + 6.9 Answer: Given, 2.1x + 0.6 = -1.4x + 6.9 2.1x + 1.4x = 6.9 – 0.6 3.5x = 6.3 x = 6.3/3.5 x = 1.8 The solution is x = 1.8
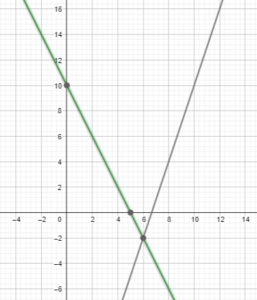
Question 36. MAKING AN ARGUMENT The graphs of y = -x + 4 and y = 2x – 8 intersect at the point (4, 0). So, your friend says the solution of the equation -x + 4 = 2x – 8 is (4, 0). Is your friend correct? Explain. Answer: Given, The graphs of y = -x + 4 and y = 2x – 8 intersect at the point (4, 0). So, your friend says the solution of the equation -x + 4 = 2x – 8 is (4, 0). -x + 4 = 2x – 8 -x + 4 – (4 + 2x) = 2x – 8 – (4 + 2x) -3x = -12 x = 4 So, the solution is x = 4.
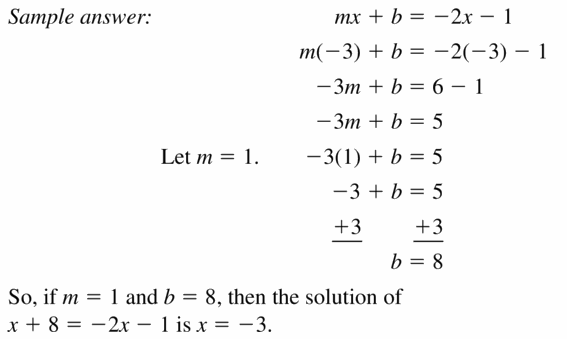
b. From the graph we can see that x & y axis represents time and amount of money respectively. 19/3 = 6.3 million dollars.
Question 40. THOUGHT PROVOKING A car has an initial value of $20,000 and decreases in value at a rate of $1500 per year. Describe a different car that will be worth the same amount as this car in exactly 5 years. Specify the initial value and the rate at which the value decreases. Answer: Given, A car has an initial value of $20,000 and decreases in value at a rate of $1500 per year. Describe a different car that will be worth the same amount as this car in exactly 5 years. 1500 × 5 = $7,500 v = -7500y + 20,000

Lesson 5.6 Graphing Linear Inequalities in Two Variables
Essential Question How can you graph a linear inequality in two variables? A solution of a linear inequality in two variables is an ordered pair (x, y) that makes the inequality true. The graph of a linear inequality in two variables shows all the solutions of the inequality in a coordinate plane.
Question 4. How can you graph a linear inequality in two variables? Answer: We need to plot the line y = ax + b. According to given symbols we need a pick point form graph and put it in the inequality is a condition that arises is true then the region of the point is shaded and it represents the inequality. All the points lying on the shaded region of inequality are its solutions.
Question 5. Give an example of a real-life situation that can be modeled using a linear inequality in two variables. Answer: Example: If we have a total of $50 that could be spent on kiwi and apples which are $25/kg and $30/kg for making a desert, then we have to find the linear inequation in two variables of how much would be the quality that we should buy that would not exceed the budget. Amount of kiwi . Rate of kiwi + amount of apples . rate of apples ≤ 50
Tell whether the ordered pair is a solution of the inequality. Question 1. x + y > 0; (-2, 2) Answer: x + y > 0 The ordered pair = (-2, 2) -2 + 2 > 0 0 > 0 It is not the solution to inequality.
Question 2. 4x – y ≥ 5; (0, 0) Answer: 4x – y ≥ 5 4(0) – 0 ≥ 5 0 ≥ 5 It is not the solution to inequality.
Question 3. 5x – 2y ≤ -1; (-4, -1) Answer: 5x – 2y ≤ -1 (-4, -1) 5(-4) – 2(-1) ≤ -1 -20 + 2 ≤ -1 -18 ≤ -1 It is the solution to inequality.
Question 4. -2x – 3y < 15; (5, -7) Answer: -2x – 3y < 15; (5, -7) -2(5) – 3(-7) < 15 -10 + 21 < 15 11 < 15 It is the solution to inequality.
Question 9. You can spend at most $12 on red peppers and tomatoes for salsa. Red peppers cost $4 per pound, and tomatoes cost $3 per pound. Write and graph an inequality that represents the amounts of red peppers and tomatoes you can buy. Identify and interpret two solutions of the inequality. Answer: Given, You can spend at most $12 on red peppers and tomatoes for salsa. Red peppers cost $4 per pound, and tomatoes cost $3 per pound. 4x + 3y ≥ 12
Graphing Linear Inequalities in Two Variables 5.6 Exercises
Vocabulary and Core Concept Check Question 1. VOCABULARY How can you tell whether an ordered pair is a solution of a linear inequality? Answer: To tell whether an ordered pair is a solution to a linear inequality, substitute the values into the linear inequality. If they make the inequality true, then the ordered pair is a solution to the linear inequality. If they make the inequality false, then the ordered pair is not a solution to the linear inequality.
Question 2. WRITING Compare the graph of a linear inequality in two variables with the graph of a linear equation in two variables. Answer: The general linear equation in two variables is ax + by + c = 0 where a, b, c are constants. To find the graph of ax + bx + c = 0, assume a set of values for x and calculate the respective set of values for y. The coordinates are (x, y). Plot the points on the graph and join them. The graph formed will be a straight line.

Question 4. x – y ≤ 0; (5, 2) Answer: x – y ≤ 0 5 – 2≤ 0 3 ≤ 0 So, (5, 2) is not a solution to inequality.
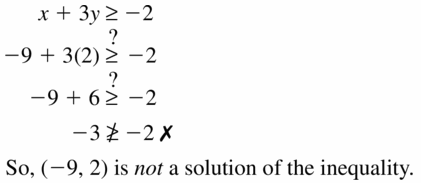
Question 6. 8x + y > -6; (-1, 2) Answer: 8x + y > -6 8(-1) + 2 > -6 -8 + 2 > -6 -6 > -6 So, (-1, 2) is not a solution to inequality.
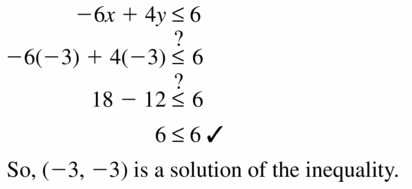
Question 8. 3x – 5y ≥ 2; (-1, -1) Answer: 3x – 5y ≥ 2 3(-1) – 5(-1) ≥ 2 -3 + 5 ≥ 2 2 ≥ 2 So, (-1, -1) is a solution of the inequality.
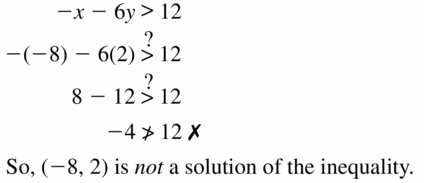
Question 10. -4x – 8y < 15; (-6, 3) Answer: -4x – 8y < 15 -4(-6) – 8(3) < 15 24 – 24 < 15 0 < 15 So, (-6, 3) is a solution of the inequality.
Question 12. (-1, 3) Answer: Yes, (-1, 3) is a solution because it lies in the shaded half-plane.
Question 14. (0, 0) Answer: Yes, (0, 0) is a solution because it lies in the shaded half-plane.
Question 16. (2, 1) Answer: No, (2, 1) is not a solution because it lies in the shaded half-plane.

Question 18. MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS The inequality 3x + 2y ≥ 93 represents the numbers x of multiple- choice questions and the numbers y of matching questions you can answer correctly to receive an A on a test. You answer 20 multiple-choice questions and 18 matching questions correctly. Do you receive an A on the test? Explain. Answer: The ordered pair is (20, 18) 3x + 2y ≥ 93 3(20) + 2(18) ≥ 93 60 + 36 ≥ 93 96 ≥ 93 So, the inequality is true.
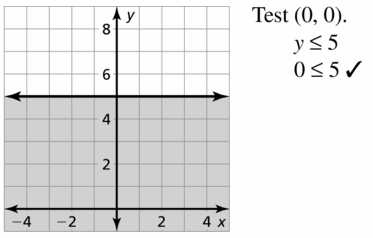
Question 41. REASONING When graphing a linear inequality in two variables, why must you choose a test point that is not on the boundary line? Answer: You have to know which side of the boundary line to shade. So, you need to choose a point on one side or the other of the boundary line to know which region contains the solutions of the inequality.
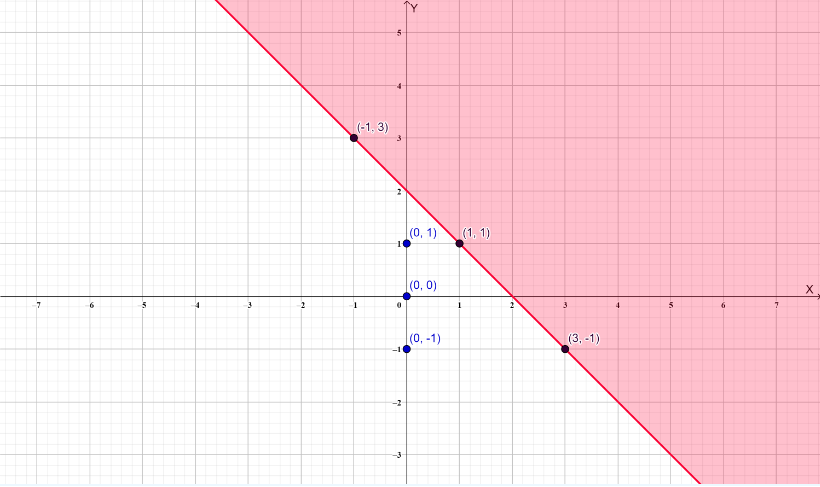
CRITICAL THINKING In Exercises 44 and 45, write and graph an inequality whose graph is described by the given information. Question 44. The points (2, 5) and (−3, −5) lie on the boundary line. The points (6, 5) and (−2, −3) are solutions of the inequality. Answer: The points (2, 5) and (−3, −5) lie on the boundary line. The points (6, 5) and (−2, −3) are solutions of the inequality. Find the equation of the boundary line Since the boundary line intersect the y-axis at (0, 1) So, the y-intercept is b = 1. m = y2-y1/x2-x1 m = -5-5/-3-2 m = 2 y = 2x + 1 Substitute x = 6 and y = 5 5 = 2(6) + 1 5 = 12 + 1 5 ≤ 13 So, y ≤ 2x + 1
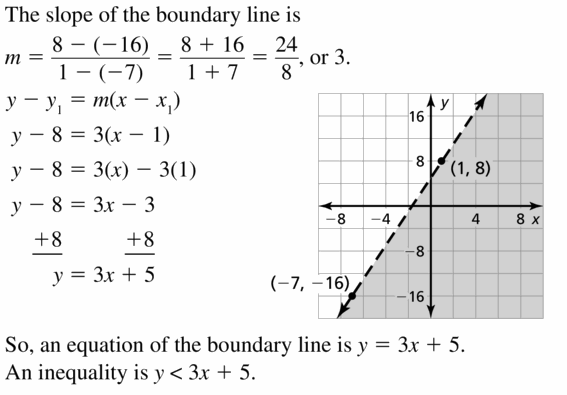
Write the next three terms of the arithmetic sequence. Question 46. 0, 8, 16, 24, 32, . . . Answer: 0, 8, 16, 24, 32, . . . a1 = 0 and the second term a2 = 8 d = a1 – a2 = 8 – 0 = 8 an = a + (n – 1)d a6 = a + (6 – 1)d = a + 5d = 0 + 5(8) = 0 + 40 a7 = a + (7 – 1)d = a + 6d = 0 + 6(8) = 48 a8 = a + (8 – 1)d = a + 7d = 0 + 7(8) = 0 + 56 = 56 The next three terms in the arithmetic sequence are 40, 48, 56.
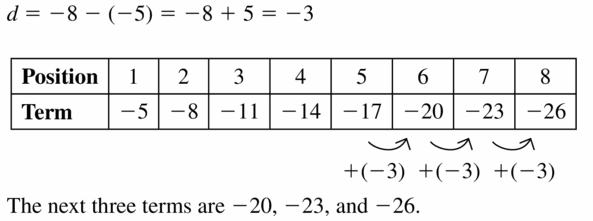
Question 48. \(-\frac{3}{2},-\frac{1}{2}, \frac{1}{2}, \frac{3}{2}, \frac{5}{2}, \ldots\) Answer: a1 = -3/2 a2 = -1/2 d = -1/2 – (-3/2) d = 1 a6 = 5/2 + 1 = 7/2 a7 = a6 + d = 7/2 + 1 = 9/2 a8 = 9/2 + 1 = 11/2 So, the next three terms are 7/2, 9/2, 11/2
Lesson 5.7 Systems of Linear Inequalities
Essential Question How can you graph a system of linear inequalities?
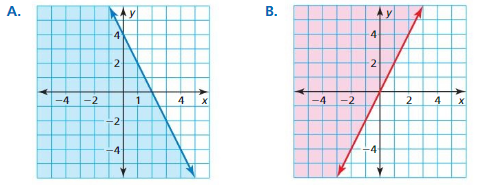
Question 4. When graphing a system of linear inequalities, which region represents the solution of the system? Answer: The inequality sign indicates the region that is part of the solution.
Question 6. Write a system of linear inequalities represented by the graph. Answer: Let the line passes through the points (0, 2) and (1, -1) y – y1 = y2-y1/x2-x1(x-x1) y – 2 = -1-2/1-0(x-0) y – 2 = -3x y = -3x + 2 y ≥ -3x + 2 Let the line passes through the points (0, -2) and (3, 0) y – (-2) = 0 – (-2)/3-0(x- 0) y + 2 = 2/3x y = 2/3x – 2 y ≥ 2/3x – 2
Tell whether the ordered pair is a solution of the system of linear inequalities. Question 1. (-1, 5); y < 5 y > x – 4 Answer: y < 5 (-1, 5) 5 < 5 (-1, 5) is the solution of the system of linear inequalities. y > x – 4 5 > -1 – 4 5 > -5 (-1, 5) is the solution of the system of linear inequalities.
Question 2. (1, 4); y ≥ 3x + 1 y > x – 1 Answer: y ≥ 3x + 1 (1, 4) 4 ≥ 3(1) + 1 4 ≥ 4 (1, 4) is the solution of the system of linear inequalities. y > x – 1 4 > 1 – 1 4 > 0 (1, 4) is the solution of the system of linear inequalities.
Question 8. Name another solution of Example 6. Answer:
Systems of Linear Inequalities 5.7 Exercises
Vocabulary and Core Concept Check Question 1. VOCABULARY How can you verify that an ordered pair is a solution of a system of linear inequalities? Answer: You can substitute the values into each inequality of the system and verify that the values make the inequalities true.
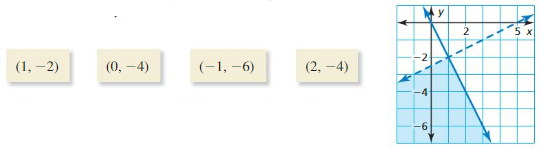
Question 4. (-3, -1) Answer: Yes, the ordered pair (-3, -1) is the solution of one inequality. It is in the shaded region.
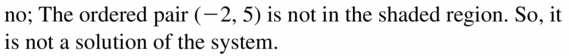
Question 6. (1, 1) Answer: No, the ordered pair (1, 1) is not in the shaded region. So, it is not the solution of the system.

Question 8. (1, -1); y > -2 y > x – 5 Answer: y > -2 -1 > -2 y > x – 5 -1 > 1 – 5 -1 > -4 Because the ordered pair (1, -1) is a solution of each inequality, it is a solution of the system.
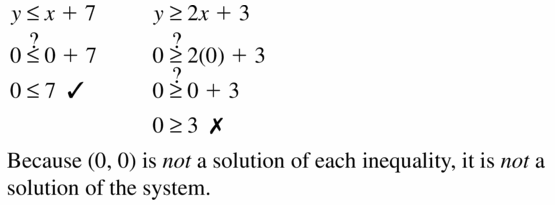
Question 10. (4, -3); y ≤ -x + 1 y ≤ 5x – 2 Answer: y ≤ -x + 1 -3 ≤ -4 + 1 -3 ≤ -3 y ≤ 5x – 2 -3 ≤ 5(4) – 2 -3 ≤ 20 – 2 -3 ≤ 18
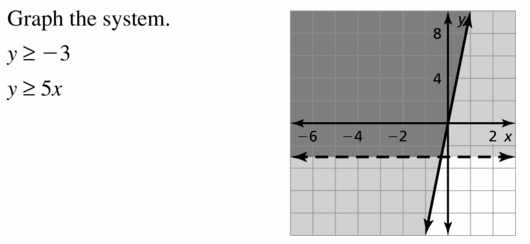
Question 36. PROBLEM SOLVING On a road trip with a friend, you drive about 70 miles per hour, and your friend drives about 60 miles per hour. The plan is to drive less than 15 hours and at least 600 miles each day. Your friend will drive more hours than you. How many hours can you and your friend each drive in 1 day? Answer: Given, On a road trip with a friend, you drive about 70 miles per hour, and your friend drives about 60 miles per hour. The plan is to drive less than 15 hours x + y < 15 and at least 600 miles each day. 70x + 60y ≥ 600 A = (0, 15), B = (0, 10), C = (8.571, 0), D = (10, 0) x = 0, y = 10 Distance = 70 × 0 + 60 × 10 = 600 600 ≥ 600 and x + y = 0 + 0 < 15 We drive for 0 hours and our friend drives 10 hours.

OPEN-ENDED In Exercises 42−44, write a system of linear inequalities with the given characteristic. Question 42. All solutions are in Quadrant I. Answer: If all solutions are points in Quadrant -1 then the x-coordinates and y-coordinates of all those points are all positive.
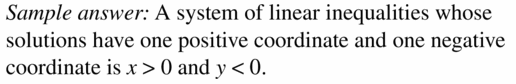
Question 46. THOUGHT PROVOKING You receive a gift certificate for a clothing store and plan to use it to buy T-shirts and sweatshirts. Describe a situation in which you can buy 9 T-shirts and 1 sweatshirt, but you cannot buy 3 T-shirts and 8 sweatshirts. Write and graph a system of linear inequalities that represents the situation. Answer:
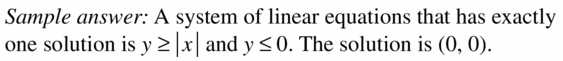
Write the product using exponents. Question 49. 4 • 4 • 4 • 4 • 4 Answer: 4 • 4 • 4 • 4 • 4 = 4 5
Question 50. (-13) • (-13) • (-13) Answer: (-13) • (-13) • (-13) = (-13)³
Question 51. x • x • x • x • x • x Answer: x • x • x • x • x • x = x 6
Write an equation of the line with the given slope and y-intercept. Question 52. slope: 1 y-intercept: -6 Answer: Equation of the line is y = mx + b m = 1 b = -6 y = (1)x + (-6) y = x – 6
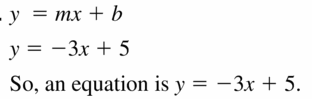
Question 54. slope: –\(\frac{1}{4}\) y-intercept: -1 Answer: Equation of the line is y = mx + b m = –\(\frac{1}{4}\) b = -1 y = –\(\frac{1}{4}\)x + (-1) y = –\(\frac{1}{4}\)x – 1
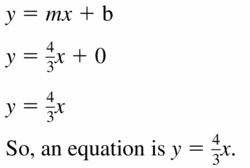
Solving Systems of Linear Equations Performance Task: Prize Patrol
5.5–5.7 What Did You Learn?

Core Concepts Section 5.5 Solving Linear Equations by Graphing, p. 262 Solving Absolute Value Equations by Graphing, p. 263
Section 5.6 Graphing a Linear Inequality in Two Variables, p. 269
Section 5.7 Graphing a System of Linear Inequalities, p. 275 Writing a System of Linear Inequalities, p. 276
Question 1. Why do the equations in Exercise 35 on page 266 contain absolute value expressions? Answer:
Question 2. Why is it important to be precise when answering part (a) of Exercise 39 on page 272? Answer:
Question 3. Describe the overall step-by-step process you used to solve Exercise 35 on page 279. Answer:
Performance Task Prize Patrol

Solving Systems of Linear Equations Chapter Review
5.1 Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Graphing (pp. 235–240)
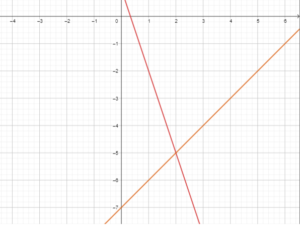
5.2 Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Substitution (pp. 241–246)
Solve the system of linear equations by substitution. Check your solution. Question 4. 3x + y = -9 y = 5x + 7 Answer: Given equations 3x + y = -9 y = 5x + 7
3x + y = -9 -5x + y = 7 8x = -16 x = -16/8 x = -2 3x + y = -9 3(-2) + y = -9 -6 + y = -9 y = -9 + 6 y = -3 3x + y = -9 3(-2) + (-3) = -9 -6 – 3 = -9 -9 = -9 LHS = RHS
Question 5. x + 4y = 6 x – y = 1 Answer: x + 4y = 6 x – y = 1 5y = 5 y = 1 x – y = 1 x – 1 = 1 x = 1 + 1 x = 2 x – y = 1 2 – 1 = 1 1 = 1
Question 6. 2x + 3y = 4 y + 3x = 6 Answer: 2x + 3y = 4 y + 3x = 6
2x + 3y = 4 y + 3x = 6 —- × 3 ⇒ 3y + 9x = 18
2x + 3y = 4 9x + 3y = 18 -7x = -14 x = 2 2x + 3y = 4 2(2) + 3y = 4 4 + 3y = 4 3y = 0 y = 0 2x + 3y = 4 2(2) + 3(0) = 4 4 + 0 = 4 4 = 4 LHS = RHS
Question 7. You spend $20 total on tubes of paint and disposable brushes for an art project. Tubes of paint cost $4.00 each and paintbrushes cost $0.50 each. You purchase twice as many brushes as tubes of paint. How many brushes and tubes of paint do you purchase? Answer: Given, You spend $20 total on tubes of paint and disposable brushes for an art project. Tubes of paint cost $4.00 each and paintbrushes cost $0.50 each. Let x be the total number of paint tubes y be the number of paintbrushes 4x + 0.5y = 20 y = 2x 4x + 0.5(2x) = 20 5x = 20 x = 4 4x + 0.5y = 20 4(4) + 0.5y = 20 16 + 0.5y = 20 0.5y = 4 y = 8 The number of paintbrushes purchased is 4 and the number of tubes of paint purchased is 8.
5.3 Solving Systems of Linear Equations by Elimination (pp. 247 – 252)
Solve the system of linear equations by elimination. Check your solution. Question 8. 9x – 2y = 34 5x + 2y = -6 Answer: 9x – 2y = 34 5x + 2y = -6 14x = 28 x = 28/14 x = 2 5x + 2y = -6 5(2) + 2y = -6 10 + 2y = -6 2y = -6 – 10 2y = -16 y = -8 Check: 5x + 2y = -6 5(2) + 2(-8) = -6 10 – 16 = -6 -6 = -6 LHS = RHS
Question 9. x + 6y = 28 2x – 3y = -19 Answer: x + 6y = 28 2x – 3y = -19 — × 2
x + 6y = 28 4x – 6y = -38 5x = -10 x = -2 -2 + 6y = 28 6y = 28 + 2 6y = 30 y = 5 Check: x + 6y = 28 -2 + 6(5) = 28 -2 + 30 = 28 28 = 28 LHS = RHS
Question 10. 8x – 7y = -3 6x – 5y = -1 Answer: 8x – 7y = -3 —- × 5 ⇒ 40x – 35y = -15 6x – 5y = -1 —- × 7 ⇒ 42x – 35y = -4
40x – 35y = -15 42x – 35y = -4 -2x = 11 x = -11/2 6x – 5y = -1 6(-11/2) – 5y = -1 3(-11) -5y = -1 -33 – 5y = -1 -5y = -1 + 33 -5y = 32 y = -32/5
5.4 Solving Special Systems of Linear Equations (pp. 253–258)
Solve the system of linear equations. Question 11. x = y + 2 -3x + 3y = 6 Answer: x = y + 2 ⇒ x – y = 2 -3x + 3y = 6 ⇒ -x + y = 2 x – y = 2 -x + y = 2 0 = 2 LHS ≠ RHS
Question 12. 3x – 6y = -9 -5x + 10y = 10 Answer: 3x – 6y = -9 ⇒ x – 2y = -3 -5x + 10y = 10 ⇒ -x + 2y = 2
x – 2y = -3 -x + 2y = 2 0 = -1 LHS ≠ RHS
Question 13. -4x + 4y = 32 3x + 24 = 3y Answer: -4x + 4y = 32 ⇒ -x + y = 8 3x + 24 = 3y ⇒ x -y = – 8
-x + y = 8 x -y = – 8 0 = 0 LHS = RHS
5.5 Solving Equations by Graphing (pp. 261–26
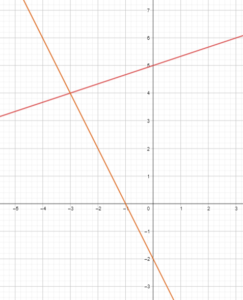
5.6 Graphing Linear Inequalities in Two Variables (pp. 267–272)
Solving Systems of Linear Equations Chapter Test
Solve the system of linear equations using any method. Explain why you chose the method.
Question 1. 8x + 3y = -9 -8x + y = 29 Answer: 8x + 3y = -9 -8x + y = 29 2y = 20 y = 20/2 y = 10 -8x + y = 29 -8x + 10 = 29 -8x = 19 x = -19/8
Question 2. \(\frac{1}{2}\)x + y = -6 y = \(\frac{3}{5}\)x + 5 Answer: \(\frac{1}{2}\)x + y = -6 y = \(\frac{3}{5}\)x + 5
\(\frac{1}{2}\)x + y = -6 \(\frac{3}{5}\)x – y = -5 \(\frac{1}{2}\)x + \(\frac{3}{5}\)x = -11 5x + 15x = -110 x + 3x = -22 4x = -22 x = -11/2 y = \(\frac{3}{5}\)x + 5 y = \(\frac{3}{5}\)(-11/2) + 5 y = \(\frac{-33}{10}\) + 5 y = -3.3 + 5 y = 1.7
Question 3. y = 4x + 4 -8x + 2y = 8 Answer: y = 4x + 4 -8x + 2y = 8 ⇒ -4x + y = 4
4x – y = -4 -4x + y = 4 0 = 0
Question 4. x = y – 11 x – 3y = 1 Answer: x = y – 11 ⇒ x – y = -11 x – 3y = 1
x – y = -11 x – 3y = 1 2y = -12 y = -6 x – y = -11 x + 6 = -11 x = -11 – 6 x = -17
Question 5. 6x – 4y = 9 9x – 6y = 15 Answer: 6x – 4y = 9 9x – 6y = 15 ⇒ 3x – 2y = 5— × 2
6x – 4y = 9 6x – 4y = 10 0 = -1 LHS ≠ RHS
Question 6. y = 5x – 7 -4x + y = -1 Answer: y = 5x – 7 ⇒ 5x – y = 7 -4x + y = -1 ⇒ -4x + y = -1
5x – y = 7 -4x + y = -1 x = 6 5(6) – y = 7 30 – y = 7 30 – 7 = y y = 23
Question 7. Write a system of linear inequalities so the points (1, 2) and (4, -3) are solutions of the system, but the point (-2, 8) is not a solution of the system. Answer: (1, 2) and (4, -3) m = -3-2/(4-1) m = -5/3 y – y1 = m(x – x1) y – 2 = -5/3(x – 1) y – 2 = -5/3x + 5/3 y = -5/3x + 11/3 y = -5/3(-2) + 11/3 8 > 1/3 y ≤ -5/3x + 11/3
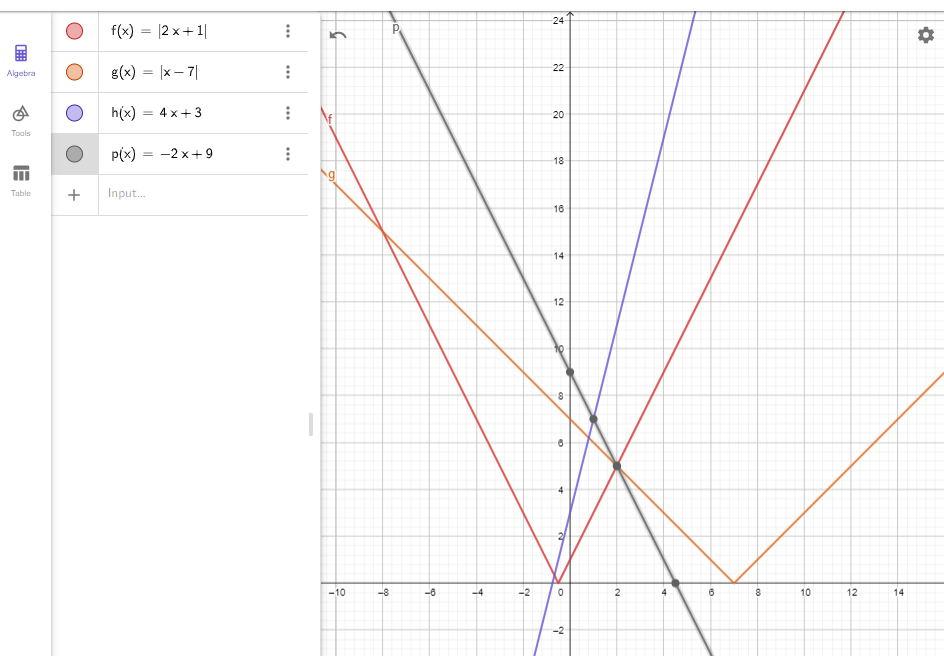
b. Let x be the cost of 1 gallon of gasoline and y be the cost of 1 quarts of oil 8x + 2y = 38.40 10x + 2y = 45.50 Thus there is not enough information to determine the cost of 1 gallon of gasoline and 1 quart of oil.
c. 10x + 2y = 45.50 8x + 2y = 38.40 Solve both equations 10x + 2y – (8x + 2y) = 45.50 – 38.40 10x + 2y – 8x – 2y = 7.1 2x = 7.1 x = 3.55 10 × 3.55 + 2y = 45.50 35.50 + 2y = 45.50 2y = 45.50 – 35.50 2y = 10 y = 5
Question 13. Describe the advantages and disadvantages of solving a system of linear equations by graphing. Answer: Advantages: 1. We can determine the solutions easily from the graph. 2. It is easy to graph the equation by writing it in intercept form. Disadvantages: 1. The graph is difficult to draw if we are dealing with equations having radicals.

Question 15. Compare the slopes and y-intercepts of the graphs of the equations in the linear system 8x + 4y = 12 and 3y = -6x – 15 to determine whether the system has one solution, no solution, or infinitely many solutions. Explain. Answer: 8x + 4y = 12 and 3y = -6x – 15 y = -2x + 3 3y = -6x – 15 y = -2x – 5 So, both equations have a slope of -2. But one has a y-intercept of 3 and the other has a y-intercept of -5. They are parallel so they will never intersect. So, the system has no solutions.
Solving Systems of Linear Equations Cumulative Assessment

Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
CPM Educational Program
Expert textbook solutions.
Browse your textbook to find expert solutions, hints, and answers for all exercises. The solutions are always presented as a clear and concise, step-by-step explanation with included theory and helpful figures, graphs, and diagrams. Mathleaks covers the most commonly adopted textbooks with more than 250000 expert solutions.
Mathleaks Solver
With Mathleaks, you’re not tied to your textbook for solutions. Instead, scan and solve exercises with our math solver, which instantly reads the problem by using the camera on your smartphone or tablet. Access the solver through the Mathleaks app or on our website. The Mathleaks solver works for Pre-Algebra, Algebra 1, and Algebra 2.
Mathleaks Community
Get access to the world's most popular math community with Mathleaks. You can connect with other students all over the US who are studying with the same textbook or in the same math course.
Study math more efficiently using Mathleaks for CPM Educational Program textbooks.
- Core Connections Integrated I, 2013
- Core Connections Algebra 1, 2013
- Core Connections Geometry, 2013
- Core Connections Algebra 2, 2013
- Core Connections Integrated I, 2014
- Core Connections Integrated II, 2015
- Core Connections: Course 1
- Core Connections: Course 2
- Core Connections: Course 3
- Core Connections Integrated III, 2015
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Unit 1: Algebra foundations
Unit 2: solving equations & inequalities, unit 3: working with units, unit 4: linear equations & graphs, unit 5: forms of linear equations, unit 6: systems of equations, unit 7: inequalities (systems & graphs), unit 8: functions, unit 9: sequences, unit 10: absolute value & piecewise functions, unit 11: exponents & radicals, unit 12: exponential growth & decay, unit 13: quadratics: multiplying & factoring, unit 14: quadratic functions & equations, unit 15: irrational numbers, unit 16: creativity in algebra.

- High Schools
Every Child, By Name and Face to Graduation
Page Navigation
- Math Department Homepage
- Math Department Staff Directory
- Algebra 2 Honors
- Calc I (Math 181)
- AP Statistics
- Credit Recovery Alg 1
- Formal Geometry
- Intro Precalculus
- Math 126 Dual Credit
- Math 126/127 (Precalc with Trig)
- Precollege Math
- Prob/Stat/Discrete Math
- MATH 124 Dual Credit
- Back to DRHS Homepage
- Dual Credit Application Information
Algebra 1 DRHS
Click here for youtube channel video lessons, alg 1 syllabus 2024-2025, free printatle graph paper, contact your teacher:.
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
DESMOS GRAPHING CALCULATOR
Desmos scientific calculator, algebra 1 textbook login .
If you're signing in from off-campus, you will need to click the link below to enter washoe\your student id number in the user name field. For example if your student ID number is 1234567... enter washoe\1234567
To view the textbook, click on the green "Envision Algebra 1 Common Core 2018" button on the main page and then "Interactive Student Edition," which is the first button.
To watch the video tutorials for each lesson, click on the green "Envision Algebra 1 Common Core 2018" icon under programs. From there, click on the chapter and lesson and the video tutorials can be viewed by clicking "Virtual Nerd.
Alg 1 Class Notes
Ch 1 notes blank, ch 1 notes filled out, ch 2 notes blank, ch 2 notes filled out, ch 3 notes filled out, ch 4 notes filled out, ch 5 notes filled out, ch 6 notes filled out, ch 7 notes filled out, chapter 8 notes blank, algebra 1 handouts and keys, ch 1 homework and practice test, ch 2 homework and practice test, ch 3 homework and practice test, ch 4 hw + practice test, ch 5 hw + practice test.
- Questions or Feedback? |
- Web Community Manager Privacy Policy (Updated) |
IMAGES
COMMENTS
Use Mathleaks to get learning-focused solutions and answers to Algebra 1 math, either 8th grade Algebra 1 or 9th grade Algebra 1, for the most commonly used textbooks from publishers such as Houghton Mifflin Harcourt, Big Ideas Learning, CPM, McGraw Hill, and Pearson. Getting helpful and educational math answers and solutions to high school Algebra 1 exercises could be the key to understanding ...
Find step-by-step solutions and answers to Algebra 1 Common Core - 9780133185485, as well as thousands of textbooks so you can move forward with confidence.
©Glencoe/McGraw-Hill iv Glencoe Algebra 1 Teacher's Guide to Using the Chapter 5 Resource Masters The Fast FileChapter Resource system allows you to conveniently file the resources you use most often. The Chapter 5 Resource Mastersincludes the core materials needed for Chapter 5. These materials include worksheets, extensions, and assessment options.
If you are searching for instant help on the concepts of Algebra 1 Ch 5 Solving Systems of Linear Equations then this is the one-stop destination for all your needs. Make the most out of the BIM Book Algebra 1 Chapter 5 Solving Systems of Linear Equations Solutions Key provided and clarify your doubts on the same.
Chapter 5 Resource Masters. The Chapter 5 Resource Mastersincludes the core materials needed for Chapter 5. These materials include worksheets, extensions, and assessment options. The answers for these pages appear at the back of this booklet.
With Mathleaks, you'll have instant access to expert solutions and answers to all of the CPM math questions you may have from the CPM Educational Program publications such as Pre-Algebra, Algebra 1, Algebra 2, and Geometry. Mathleaks offers the ultimate homework help and much of the content is free to use.
Textbook solutions for BIG IDEAS MATH Algebra 1: Common Core Student Edition 2015… 1st Edition HOUGHTON MIFFLIN HARCOURT and others in this series. View step-by-step homework solutions for your homework. Ask our subject experts for help answering any of your homework questions!
Now, with expert-verified solutions from Big Ideas Math: Algebra 1 1st Edition, you'll learn how to solve your toughest homework problems. Our resource for Big Ideas Math: Algebra 1 includes answers to chapter exercises, as well as detailed information to walk you through the process step by step.
Find step-by-step solutions and answers to Holt Algebra 1: Student Edition - 9780030358272, as well as thousands of textbooks so you can move forward with confidence.
a. Sample answer: 25; 5; 100; 0; 10; negative numbers b. Sample answer: 10; 9; 600; 4; 0; numbers greater than or equal to 150 c. Sample answer: 10; 7; 300; 2; 1; numbers greater than 170 Add or subtract the same number to or from each side of the inequality to create an equivalent inequality.
Algebra 1 Workbook - Chapter 5 Algebra 1 Workbook - Chapter 5 Algebra 1 Workbook - Chapter 5 Algebra 1 Workbook - Chapter 5 14. 16. 10. 12. Lesson 5.3 Practice Level B 2. 6.
Click a link below to access the Algebra 1 worksheet for a specific section. CHAPTER 1 WORKSHEETS. 1-1 Variables and Expressions ( SOLUTIONS) 1-2 Order of Operations and Evaluating Expressions ( SOLUTIONS) 1-3 Real Numbers and the Number Line ( SOLUTIONS) 1-4 Properties of Real Numbers ( SOLUTIONS)
The Algebra 1 course, often taught in the 9th grade, covers Linear equations, inequalities, functions, and graphs; Systems of equations and inequalities; Extension of the concept of a function; Exponential models; and Quadratic equations, functions, and graphs. Khan Academy's Algebra 1 course is built to deliver a comprehensive, illuminating, engaging, and Common Core aligned experience!
Find step-by-step solutions and answers to Holt Algebra 1 Homework and Practice Workbook - 9780030466373, as well as thousands of textbooks so you can move forward with confidence.
5.1 Extra Practice In Exercises 1-3, tell whether the ordered pair is a solution of the system of linear equations.
Textbook solutions for High School Math 2012 Common-core Algebra 1 Practice And… 1st Edition Prentice Hall and others in this series. View step-by-step homework solutions for your homework. Ask our subject experts for help answering any of your homework questions!
Access Prentice Hall Math Algebra 1 Student Edition 1st Edition Chapter 5 solutions now. Our solutions are written by Chegg experts so you can be assured of the highest quality!
To watch the video tutorials for each lesson, click on the green "Envision Algebra 1 Common Core 2018" icon under programs. From there, click on the chapter and lesson and the video tutorials can be viewed by clicking "Virtual Nerd.
Find step-by-step solutions and answers to Big Ideas Math Algebra 1: A Common Core Curriculum - 9781608408382, as well as thousands of textbooks so you can move forward with confidence.
In this class there is a distinction between Practice Problems and Homework Problems. Practice Problems are found in the workbook, and students check their answers with the solutions provided. Homework assignments and tests are printed from the website, completed, and turned in for a grade.
Free math problem solver answers your algebra homework questions with step-by-step explanations.
Find step-by-step solutions and answers to Glencoe Algebra 1 - 9780079039897, as well as thousands of textbooks so you can move forward with confidence.
Arts and Humanitie... Philosophy