

22 Ways On How To Start A Persuasive Speech

If you want to convince your audience to take action, you better know how to start a persuasive speech, or else you will loose right at the start. The first 10 to 20 seconds of your presentation is the time when you have the most attention. Use this time wisely with awesome presentation openers.
Time to Overthink your Presentation Openers
If you don’t capture your audience’s attention right away you’ve probably lost it forever. Chances are that after the first 60 seconds (at the latest) people’s thoughts will drift off to thoughts like: “What am I gonna have for lunch today?”, “Has my daughter done her homework?”, “Where did I put my phone?”
You get the point: you need to hook up your audience from the moment you enter the stage or stand up to give a short talk. Time to think about a presentation opener that will blow them away.
Start before you say the first word
Don’t think of your presentation opener only as the actual words you’re gonna say. Your opener starts before you even open your mouth: it’s the way you enter the stage, the way you smile at the audience, the way you’re dressed, your voice and body language. So prepare yourself, stand tall, smile, be enthusiastic!
Don’t start by introducing yourself
In case you’re asking yourself whether you should introduce yourself first: the answer is no . At least not in the traditional way. Chances are your audience already knows who you are; either they are working with you, they read your name on the speakers list or heard you being introduced by a moderator. Remember that your presentation should always be about the audience – not about you. Don’t waste the critical first seconds introducing yourself.
Hi, my name is Bob, I have 22 years working experience in the field of Presentation Coachings and am currently writing a book on Powerpoint and today I will talk about the history of stuttering. I have worked with many people in this field and I have learnt that (…) blablablabla
Wanna know a guaranteed way of boring your audience to death the moment you open your mouth? This is it. Have you ever heard Steve Jobs open his presentation with “Hi my name is Steve”? Chances are you haven’t. Not only because the world knew who he is anyways – also, because it’s just a bad opener. Why? People wanna know what’s in for them. They are far less interested in you as you might think.
You are not as interesting as you think
Your presentation should be about your audience and what they can take away from it. So if you have to introduce yourself: do it in the context of your presentation and do it only after you’ve hooked the audience up.
How to start a persuasive speech or presentation? Hook them up!
So coming to the point: You need to capture your audience’s attention right away. How can you do this? Here are our favorite tactics:
Surprise/ Shock: Shocking or surprising your audience with statistics or facts is a great way of getting their attention. As said before: give them the most interesting piece of information right away. You can still explain it later.
$3 Mio (Pause) This is the value of sales we have forgone last year ” is a much better opener than “Today we’re going to discuss last year’s sales figures”. “ The world’s richest 1 percent is now wealthier than the rest of humanity combined ” will shock people rather than “Today we’re gonna talk about income inequality.
Story: We all love stories and engaging people with a surprising or funny anecdote is one of the best ways to get your point across. Take Steve Job’s famous commencement speech at Stanford as an example:
I am honored to be with you today at your commencement from one of the finest universities in the world. I never graduated from college. Truth be told, this is the closest I’ve ever gotten to a college graduation. Today I want to tell you three stories from my life. That’s it. No big deal. Just three stories. The first story is about connecting the dots. (…)
It’s surprising, confusing and it makes people curious. He’s taking his audience on a journey.
Humor: Make the audience laugh and they’ll love you. Humor is one of the best presentation openers ever (if used correctly). There are few things that make us connect to another person as easily as by laughing together. But be careful: make sure your joke fits the context.
Rhetorical Question
Engage your audience right away by asking them questions. Look at the first paragraph of Simon Sinek’s Ted Talk :
How do you explain when things don’t go as we assume? Or better, how do you explain when others are able to achieve things that seem to defy all of the assumptions? For example: Why is Apple so innovative? Year after year, after year, they’re more innovative than all their competition. And yet, they’re just a computer company. They’re just like everyone else. They have the same access to the same talent,the same agencies, the same consultants, the same media . Then why is it that they seem to have something different? Why is it that Martin Luther King led the Civil Rights Movement? He wasn’t the only man who suffered in pre-civil rights America, and he certainly wasn’t the only great orator of the day. Why him?
It’s a 20 second introduction just consisting of questions and one of the presentation openers that grab your attention right away.
Video/ Graphics: If it’s a product presentation why don’t you simply show them the product? This is what they came for. Or show them a short video. This is a great way if you’re battling stage fright. It hooks up the audience for you while you get the chance to concentrate on your next steps.
There are countless ways of opening your presentation. Choose a presentation opener that makes sense for your topic and practice it a few times. Try it next time you’re addressing your audience and you’ll see the results.
Download a list of 22 ingenious presentation openers NOW

You might also like

PRESENTER.WORLD
is a global movement to help YOU become a great presenter that makes great things happen. A movement for ambitious doers, presenters, speakers & storytellers of all levels and those who want to become a badass in sharing their message. AND the Experts helping YOU to get there!
Together we save the world from boring presentations!
How we can help
PRESENTER.WORLD Free Stuff PRESENTER.WORLD Academy PRESENTER.WORLD Coaching PRESENTER.WORLD Agency
Latest Posts
Join the movement

Free Facebook Group

This site uses cookies. By continuing to browse the site, you are agreeing to our use of cookies.
How to Write and Structure a Persuasive Speech
- Homework Tips
- Learning Styles & Skills
- Study Methods
- Time Management
- Private School
- College Admissions
- College Life
- Graduate School
- Business School
- Distance Learning
- M.Ed., Education Administration, University of Georgia
- B.A., History, Armstrong State University
The purpose of a persuasive speech is to convince your audience to agree with an idea or opinion that you present. First, you'll need to choose a side on a controversial topic, then you will write a speech to explain your position, and convince the audience to agree with you.
You can produce an effective persuasive speech if you structure your argument as a solution to a problem. Your first job as a speaker is to convince your audience that a particular problem is important to them, and then you must convince them that you have the solution to make things better.
Note: You don't have to address a real problem. Any need can work as the problem. For example, you could consider the lack of a pet, the need to wash one's hands, or the need to pick a particular sport to play as the "problem."
As an example, let's imagine that you have chosen "Getting Up Early" as your persuasion topic. Your goal will be to persuade classmates to get themselves out of bed an hour earlier every morning. In this instance, the problem could be summed up as "morning chaos."
A standard speech format has an introduction with a great hook statement, three main points, and a summary. Your persuasive speech will be a tailored version of this format.
Before you write the text of your speech, you should sketch an outline that includes your hook statement and three main points.
Writing the Text
The introduction of your speech must be compelling because your audience will make up their minds within a few minutes whether or not they are interested in your topic.
Before you write the full body you should come up with a greeting. Your greeting can be as simple as "Good morning everyone. My name is Frank."
After your greeting, you will offer a hook to capture attention. A hook sentence for the "morning chaos" speech could be a question:
- How many times have you been late for school?
- Does your day begin with shouts and arguments?
- Have you ever missed the bus?
Or your hook could be a statistic or surprising statement:
- More than 50 percent of high school students skip breakfast because they just don't have time to eat.
- Tardy kids drop out of school more often than punctual kids.
Once you have the attention of your audience, follow through to define the topic/problem and introduce your solution. Here's an example of what you might have so far:
Good afternoon, class. Some of you know me, but some of you may not. My name is Frank Godfrey, and I have a question for you. Does your day begin with shouts and arguments? Do you go to school in a bad mood because you've been yelled at, or because you argued with your parent? The chaos you experience in the morning can bring you down and affect your performance at school.
Add the solution:
You can improve your mood and your school performance by adding more time to your morning schedule. You can accomplish this by setting your alarm clock to go off one hour earlier.
Your next task will be to write the body, which will contain the three main points you've come up with to argue your position. Each point will be followed by supporting evidence or anecdotes, and each body paragraph will need to end with a transition statement that leads to the next segment. Here is a sample of three main statements:
- Bad moods caused by morning chaos will affect your workday performance.
- If you skip breakfast to buy time, you're making a harmful health decision.
- (Ending on a cheerful note) You'll enjoy a boost to your self-esteem when you reduce the morning chaos.
After you write three body paragraphs with strong transition statements that make your speech flow, you are ready to work on your summary.
Your summary will re-emphasize your argument and restate your points in slightly different language. This can be a little tricky. You don't want to sound repetitive but will need to repeat what you have said. Find a way to reword the same main points.
Finally, you must make sure to write a clear final sentence or passage to keep yourself from stammering at the end or fading off in an awkward moment. A few examples of graceful exits:
- We all like to sleep. It's hard to get up some mornings, but rest assured that the reward is well worth the effort.
- If you follow these guidelines and make the effort to get up a little bit earlier every day, you'll reap rewards in your home life and on your report card.
Tips for Writing Your Speech
- Don't be confrontational in your argument. You don't need to put down the other side; just convince your audience that your position is correct by using positive assertions.
- Use simple statistics. Don't overwhelm your audience with confusing numbers.
- Don't complicate your speech by going outside the standard "three points" format. While it might seem simplistic, it is a tried and true method for presenting to an audience who is listening as opposed to reading.
- 100 Persuasive Speech Topics for Students
- 100 Persuasive Essay Topics
- 50 Argumentative Essay Topics
- Examples of Great Introductory Paragraphs
- How to Write a Persuasive Essay
- 5 Tips on How to Write a Speech Essay
- Tips on How to Write an Argumentative Essay
- How To Write an Essay
- Writing an Opinion Essay
- 5 Steps to Writing a Position Paper
- How to Structure an Essay
- What Is Expository Writing?
- Ethos, Logos, Pathos for Persuasion
- Definition and Examples of Analysis in Composition
- Audience Analysis in Speech and Composition
- How to Write a Good Thesis Statement
BOSTON, JUNE 25-26 PUBLIC SPEAKING CLASS IS ALMOST FULL! RESERVE YOUR SPOT NOW

- Public Speaking Classes
- Corporate Presentation Training
- Online Public Speaking Course
- Northeast Region
- Midwest Region
- Southeast Region
- Central Region
- Western Region
- Presentation Skills
- 101 Public Speaking Tips
- Fear of Public Speaking
Persuasive Speech: How to Write an Effective Persuasive Speech

Most often, it actually causes the other person to want to play “Devil’s advocate” and argue with you. In this article, we are going to show you a simple way to win people to your way of thinking without raising resentment. If you use this technique, your audience will actually WANT to agree with you! The process starts with putting yourself in the shoes of your listener and looking at things from their point of view.
Background About How to Write a Persuasive Speech. Facts Aren’t Very Persuasive.

Most people think that a single fact is good, additional facts are better, and too many facts are just right. So, the more facts you can use to prove your point, the better chance you have of convincing the other person that you are right. The HUGE error in this logic, though, is that if you prove that you are right, you are also proving that the other person is wrong. People don’t like it when someone proves that they are wrong. So, we prove our point, the other person is likely to feel resentment. When resentment builds, it leads to anger. Once anger enters the equation, logic goes right out the window.
In addition, when people use a “fact” or “Statistic” to prove a point, the audience has a natural reaction to take a contrary side of the argument. For instance, if I started a statement with, “I can prove to you beyond a doubt that…” before I even finish the statement, there is a good chance that you are already trying to think of a single instance where the statement is NOT true. This is a natural response. As a result, the thing that we need to realize about being persuasive is that the best way to persuade another person is to make the person want to agree with us. We do this by showing the audience how they can get what they want if they do what we want.
You may also like How to Design and Deliver a Memorable Speech .
A Simple 3-Step Process to Create a Persuasive Presentation

The process below is a good way to do both.
Step One: Start Your Persuasive Speech with an Example or Story
When you write an effective persuasive speech, stories are vital. Stories and examples have a powerful way to capture an audience’s attention and set them at ease. They get the audience interested in the presentation. Stories also help your audience see the concepts you are trying to explain in a visual way and make an emotional connection. The more details that you put into your story, the more vivid the images being created in the minds of your audience members.
This concept isn’t mystical or anything. It is science. When we communicate effectively with another person, the purpose is to help the listener picture a concept in his/her mind that is similar to the concept in the speaker’s mind. The old adage is that a “picture is worth 1000 words.” Well, an example or a story is a series of moving pictures. So, a well-told story is worth thousands of words (facts).
By the way, there are a few additional benefits of telling a story. Stories help you reduce nervousness, make better eye contact, and make for a strong opening. For additional details, see Storytelling in Speeches .
I’ll give you an example.
Factual Argument: Seatbelts Save Lives

- 53% of all motor vehicle fatalities from last years were people who weren’t wearing seatbelts.
- People not wearing seatbelts are 30 times more likely to be ejected from the vehicle.
- In a single year, crash deaths and injuries cost us over $70 billion dollars.
These are actual statistics. However, when you read each bullet point, you are likely to be a little skeptical. For instance, when you see the 53% statistic, you might have had the same reaction that I did. You might be thinking something like, “Isn’t that right at half? Doesn’t that mean that the other half WERE wearing seatbelts?” When you see the “30 times more likely” statistic, you might be thinking, “That sounds a little exaggerated. What are the actual numbers?” Looking at the last statistic, we’d likely want to know exactly how the reporter came to that conclusion.
As you can see, if you are a believer that seatbelts save lives, you will likely take the numbers at face value. If you don’t like seatbelts, you will likely nitpick the finer points of each statistic. The facts will not likely persuade you.
Example Argument: Seatbelts Save Lives

When I came to, I tried to open my door. The accident sealed it shut. The windshield was gone. So I took my seatbelt off and scrambled out the hole. The driver of the truck was a bloody mess. His leg was pinned under the steering wheel.
The firefighters came a few minutes later, and it took them over 30 minutes to cut the metal from around his body to free him.
A Sheriff’s Deputy saw a cut on my face and asked if I had been in the accident. I pointed to my truck. His eyes became like saucers. “You were in that vehicle?”
I nodded. He rushed me to an ambulance. I had actually ruptured my colon, and I had to have surgery. I was down for a month or so, but I survived. In fact, I survived with very few long-term challenges from the accident.
The guy who hit me wasn’t so lucky. He wasn’t wearing a seatbelt. The initial impact of the accident was his head on the steering wheel and then the windshield. He had to have a number of facial surgeries. The only reason he remained in the truck was his pinned leg. For me, the accident was a temporary trauma. For him, it was a life-long tragedy.
The Emotional Difference is the Key
As you can see, there are major differences between the two techniques. The story gives lots of memorable details along with an emotion that captures the audience. If you read both examples, let me ask you a couple of questions. Without looking back up higher on the page, how long did it take the firefighters to cut the other driver from the car? How many CDs did I have? There is a good chance that these two pieces of data came to you really quickly. You likely remembered this data, even though, the data wasn’t exactly important to the story.
However, if I asked you how much money was lost last year as a result of traffic accidents, you might struggle to remember that statistic. The CDs and the firefighters were a part of a compelling story that made you pay attention. The money lost to accidents was just a statistic thrown at you to try to prove that a point was true.
The main benefit of using a story, though, is that when we give statistics (without a story to back them up,) the audience becomes argumentative. However, when we tell a story, the audience can’t argue with us. The audience can’t come to me after I told that story and say, “It didn’t take 30 minutes to cut the guy out of the car. He didn’t have to have a bunch of reconstructive surgeries. The Deputy didn’t say those things to you! The audience can’t argue with the details of the story, because they weren’t there.
Step 2: After the Story, Now, Give Your Advice
When most people write a persuasive presentation, they start with their opinion. Again, this makes the listener want to play Devil’s advocate. By starting with the example, we give the listener a simple way to agree with us. They can agree that the story that we told was true. So, now, finish the story with your point or your opinion. “So, in my opinion, if you wear a seatbelt, you’re more likely to avoid serious injury in a severe crash.”
By the way, this technique is not new. It has been around for thousands of years. Aesop was a Greek slave over 500 years before Christ. His stories were passed down verbally for hundreds of years before anyone ever wrote them down in a collection. Today, when you read an Aesop fable, you will get 30 seconds to two minutes of the story first. Then, at the conclusion, almost as a post-script, you will get the advice. Most often, this advice comes in the form of, “The moral of the story is…” You want to do the same in your persuasive presentations. Spend most of the time on the details of the story. Then, spend just a few seconds in the end with your morale.
Step 3: End with the Benefit to the Audience

So, the moral of the story is to wear your seatbelt. If you do that, you will avoid being cut out of your car and endless reconstructive surgeries .
Now, instead of leaving your audience wanting to argue with you, they are more likely to be thinking, “Man, I don’t want to be cut out of my car or have a bunch of facial surgeries.”
The process is very simple. However, it is also very powerful.
How to Write a Successful Persuasive Speech Using the “Breadcrumb” Approach
Once you understand the concept above, you can create very powerful persuasive speeches by linking a series of these persuasive stories together. I call this the breadcrumb strategy. Basically, you use each story as a way to move the audience closer to the ultimate conclusion that you want them to draw. Each story gains a little more agreement.
So, first, just give a simple story about an easy to agree with concept. You will gain agreement fairly easily and begin to also create an emotional appeal. Next, use an additional story to gain additional agreement. If you use this process three to five times, you are more likely to get the audience to agree with your final conclusion. If this is a formal presentation, just make your main points into the persuasive statements and use stories to reinforce the points.
Here are a few persuasive speech examples using this approach.
An Example of a Persuasive Public Speaking Using Breadcrumbs
Marijuana Legalization is Causing Huge Problems in Our Biggest Cities Homelessness is Out of Control in First States to Legalize Marijuana Last year, my family and I took a mini-vacation to Colorado Springs. I had spent a summer in Colorado when I was in college, so I wanted my family to experience the great time that I had had there as a youth. We were only there for four days, but we noticed something dramatic had happened. There were homeless people everywhere. Keep in mind, this wasn’t Denver, this was Colorado City. The picturesque landscape was clouded by ripped sleeping bags on street corners, and trash spread everywhere. We were downtown, and my wife and daughter wanted to do some shopping. My son and I found a comic book store across the street to browse in. As we came out, we almost bumped into a dirty man in torn close. He smiled at us, walked a few feet away from the door, and lit up a joint. He sat on the corner smoking it. As my son and I walked the 1/4 mile back to the store where we left my wife and daughter, we stepped over and walked around over a dozen homeless people camped out right in the middle of the town. This was not the Colorado that I remembered. From what I’ve heard, it has gotten even worse in the last year. So, if you don’t want to dramatically increase your homelessness population, don’t make marijuana legal in your state. DUI Instances and Traffic Accidents Have Increased in Marijuana States I was at the airport waiting for a flight last week, and the guy next to me offered me his newspaper. I haven’t read a newspaper in years, but he seemed so nice that I accepted. It was a copy of the USA Today, and it was open to an article about the rise in unintended consequences from legalizing marijuana. Safety officials and police in Colorado, Nevada, Washington, and Oregon, the first four state to legalize recreational marijuana, have reported a 6% increase in traffic accidents in the last few years. Although the increase (6%) doesn’t seem very dramatic, it was notable because the rate of accidents had been decreasing in each of the states for decades prior to the law change. Assuming that only one of the two parties involved in these new accidents was under the influence, that means that people who aren’t smoking marijuana are being negatively affected by the legalization. So, if you don’t want to increase your chances of being involved in a DUI incident, don’t legalize marijuana. (Notice how I just used an article as my evidence, but to make it more memorable, I told the story about how I came across the article. It is also easier to deliver this type of data because you are just relating what you remember about the data, not trying to be an expert on the data itself.) Marijuana is Still Largely Unregulated Just before my dad went into hospice care, he was in a lot of pain. He would take a prescription painkiller before bed to sleep. One night, my mom called frantically. Dad was in a catatonic state and wasn’t responsive. I rushed over. The hospital found that Dad had an unusually high amount of painkillers in his bloodstream. His regular doctor had been on vacation, and the fill-in doctor had prescribed a much higher dosage of the painkiller by accident. His original prescription was 2.5 mg, and the new prescription was 10 mg. Since dad was in a lot of pain most nights, he almost always took two tablets. He was also on dialysis, so his kidneys weren’t filtering out the excess narcotic each day. He had actually taken 20 MG (instead of 5 MG) on Friday night and another 20 mg on Saturday. Ordinarily, he would have had, at max, 15 mg of the narcotic in his system. Because of the mistake, though, he had 60 MGs. My point is that the narcotics that my dad was prescribed were highly regulated medicines under a doctor’s care, and a mistake was still made that almost killed him. With marijuana, there is really no way of knowing how much narcotic is in each dosage. So, mistakes like this are much more likely. So, in conclusion, legalizing marijuana can increase homelessness, increase the number of impaired drivers, and cause accidental overdoses.
If you use this breadcrumb approach, you are more likely to get at least some agreement. Even if the person disagrees with your conclusion, they are still likely to at least see your side. So, the person may say something like, I still disagree with you, but I totally see your point. That is still a step in the right direction.
For Real-World Practice in How to Design Persuasive Presentations Join Us for a Class
Our instructors are experts at helping presenters design persuasive speeches. We offer the Fearless Presentations ® classes in cities all over the world about every three to four months. In addition to helping you reduce nervousness, your instructor will also show you secrets to creating a great speech. For details about any of the classes, go to our Presentation Skills Class web page.
For additional details, see Persuasive Speech Outline Example .

Podcasts , presentation skills
View More Posts By Category: Free Public Speaking Tips | leadership tips | Online Courses | Past Fearless Presentations ® Classes | Podcasts | presentation skills | Uncategorized
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- Communication Skills
- Public Speaking
- Speechwriting
How to Write a Persuasive Speech
Last Updated: December 10, 2023 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Patrick Muñoz . Patrick is an internationally recognized Voice & Speech Coach, focusing on public speaking, vocal power, accent and dialects, accent reduction, voiceover, acting and speech therapy. He has worked with clients such as Penelope Cruz, Eva Longoria, and Roselyn Sanchez. He was voted LA's Favorite Voice and Dialect Coach by BACKSTAGE, is the voice and speech coach for Disney and Turner Classic Movies, and is a member of Voice and Speech Trainers Association. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 1,530,121 times.
A persuasive speech is a speech intended to convince the audience to do something. Whether you want to get people to vote, stop littering, or change their minds about an important issue, persuasive speeches are an effective way to sway an audience. There are many elements that go into a successful persuasive speech. But, with some preparation and practice, you can deliver a powerful speech.
Preparing to Write

- Especially if your topic is a controversial one, it's a good idea to know the arguments on all sides of the issue. [1] X Research source Whatever argument you are making, you'll be more persuasive if you can address the views of the opposing side.
- Spend some time reading books or articles about your topic. You can go to the library and ask a librarian for help finding books, or just go online and find some articles. Make sure to use reliable sources, like major news organizations, or academic books or articles.
- Opinion-oriented sources, like editorials, talk radio, or partisan cable news, can be valuable for finding out what other people think about your topic. But, don't rely on them as your only source of information. They can be very biased. If you use them at all, make sure to read a variety of viewpoints on the matter, not just one side.

- For example, if your topic is recycling, it's important to know a lot about recycling. But, your speech will need to reflect exactly what you hope the audience will do. Are you trying to get people to vote in favor of a citywide recycling program? Or are you trying to convince them to sort out their glass and cans and put them in a separate bin? These will be different speeches, so having the goal spelled out early will help you craft your message.

- An audience that knows little about your topic will need more background information and simpler language. An audience made up of experts on the topic would likely find such a simple speech boring.
- Likewise, an audience that already supports your view on a topic will be easier to persuade to take some action. You won't need to convince them you are right, but only that they need to do something. By contrast, an audience that does not agree with you will need persuasion to even consider your point of view.
- For example, imagine you want to convince your audience to support a city-wide recycling program. If they already think recycling is important, you only need to convince them of the value of this specific program. But, if they don't care about recycling or oppose it, you will need to first convince them that recycling is worthwhile.

- Ethos. These are appeals to the audience's ethics or morals. For example: "Recycling is the right thing to do. Wasting our limited resources steals from future generations, which is immoral."
- Pathos. These are appeals to the audience's emotions. For example: "Think of the animals that lose their homes every day because of trees being chopped down. If we recycled more, we could save these beautiful forests."
- Logos. These are appeals to the audiences logic or intellect. For example: "We know that there is a limited supply of natural resources. We can make this supply last longer by recycling."
- You can rely on any one or some combination.

- The number of points you can make to support your position will be determined by how much time you have to speak.
- As a rule of thumb, three to four supporting points is usually a good number. [2] X Research source
- For example, in the speech about recycling, your three main points might be: 1. Recycling saves resources, 2. Recycling reduces the amount of garbage, and 3. Recycling is cost-effective.
Writing your Speech

- An attention grabber. This could be a statement (or sometimes a visual) that gets your audience's attention. It can be a good idea to be a little startling or dramatic at the opening of your speech. For example, you might start with information (or pictures) showing how a nearby landfill is nearly full to capacity.
- A link to the audience. This is a means of showing that you have something in common with the audience. Show that you have a similar background or share an emotional connection of some kind. This will really depend on knowing your audience. For example, if you are a parent, speaking to other parents, you might emphasize the concern for your own children's future. If you share a common interest or ideological position with your audience, you can emphasize that.
- Your credentials. This is a means of showing that you are knowledgeable or an authority on the topic of the speech. Highlight the research you've done on your topic. If you have any personal or professional experience with the topic, be sure to emphasize that, too. In the recycling example, you might say "I've invested many hours studying the recycling issue and the types of programs available in other cities."
- Your goal. Explain to the audience what you hope the speech will accomplish. For example: "I hope by the end of my talk that you will agree that we need a city wide recycling program."
- A road map. Finally, tell the audience what the main points of the speech will be. For example, "I believe we must start a recycling program for these three reasons...."

- Arrange these points logically. Don't jump from one point to the next, and then back again. Instead, complete an argument, then move on to another that flows logically from it. [4] X Research source
- Use credible sources from your research to back the points you are making. Even if your point is more emotional (pathos), introducing some factual information will make your argument stronger. For example "Each year, 40,000 acres of beautiful forests are destroyed to make paper, according to a study from the American Recycling Institute."
- Use real life examples that the audience can relate to. Even an argument based on facts and logic (logos) should relate to the audience's lives and interests. For example: "In these hard economic times, I know many of you are afraid that a recycling program will mean a costly increase in taxes. But, the city of Springfield started a program like this one three years ago. So far they've seen an increase in revenue as a result of the program. Many residents have seen a decrease in their taxes as a result."

- Make sure that you describe opposing views fairly and objectively. Consider whether someone who actually holds that view would approve of the way you are describing their position. If you aren't sure, find someone who thinks that way and ask!
- For example, you would not want to say: "opponents of recycling just don't care if we waste our precious resources, or our money." That's not a fair description of their opinion.
- Instead, you might say: "opponents of recycling are concerned that the cost might be much higher than just using new materials," and then go on to offer an argument about why recycling might be the more cost-effective option.

- Don't just restate, verbatim, what you've already said. Instead, use this as an opportunity to reinforce the way your main points support your call to action. For example: "To sum up, I've shown you (points a, b, and c). These three undeniable facts point to a city-wide recycling program as the most sensible and ethical step we can take in helping create a more sustainable future. Please, join me in voting 'yes' on this program in November."
Delivering your Speech

- Try practicing in front of a mirror, so that you can see how you are delivering the speech. This can help you notice your facial expressions and body language. These can help or hinder your ability to get your message across.
- For example, you might notice you are slouching, or that that you fidget with your collar. These actions suggest to an audience that you aren't confident.
- Better still, record yourself with a video camera and watch the tape afterwards. This can help you see (and hear) where your delivery needs improvement. [5] X Research source It has the benefit of providing audio, and also won't distract you as much as a mirror when you're speaking.
- Once you've practiced on your own a few times, try giving the speech to a small group of friends or family members. Ask for their feedback on your message and delivery.

- Generally speaking, this will mean dressing professionally. But, the degree of formality will vary. A speech to a film club to convince them to show your film won't require the same degree of formality as speaking to the executives of a movie distribution company. For the executives, you would want to wear a suit. For the film club, that might be overdoing it.

- Be friendly and make eye contact with the audience.
- Move around, where appropriate, but don't fidget or pick at your clothes or hair.
- Don't read the speech. It's okay to use a few notes to keep yourself on track, but your speech should be mostly memorized.
- Roll with the punches. If you make a mistake, don't let it derail your whole speech. This might be an opportunity to use a little humor. Then, move on.

- For example, if you want them to contact the mayor, demanding a recycling program, don't just ask them to do it. Give them stamped, addressed envelopes to send a letter, or cards with the mayor's phone number and email address. If you do this, many more people are likely to follow through.
Patrick Muñoz
Speak from your heart and connect with your audience. Look them in the eyes and really talk to them. Make sure you're comfortable delivering your speech and that you use a warm, confident tone.
Sample Template

Community Q&A
- Look around at the audience, making eye contact, especially during pauses in your speech. If you're feeling nervous about this, pick out a single person in the audience and pretend you are speaking only to them. After a little while, pick someone else, and repeat. [6] X Research source Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Speak forward, projecting your voice toward the audience with confidence. Do not speak down toward the floor. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Try to cite sources for statistics and use credible, non-biased sources. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
Tips from our Readers
- If you have a nervous laugh, be careful to control it during your speech. Otherwise, your audience will likely think what you have to say isn't important.

- Avoid being confrontational, when possible. Don't be sarcastic or mocking when discussing viewpoints other than your own. This can be alienating to your audience, even those who may agree with you. Thanks Helpful 55 Not Helpful 17
- Don't be pompous or arrogant during your speech. Be humble, and be open to questions, suggestions, and feedback. Thanks Helpful 1 Not Helpful 1
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://grammar.yourdictionary.com/style-and-usage/steps-for-writing-a-persuasive-speech.html
- ↑ http://www.best-speech-topics.com/writing-a-persuasive-speech.html
- ↑ https://www.speechanddebate.org/wp-content/uploads/Tips-for-Writing-a-Persuasive-Speech.pdf
- ↑ https://www.comm.pitt.edu/structuring-speech
- ↑ https://www.leonardoenglish.com/blog/recording-yourself-in-english
- ↑ https://www.zenbusiness.com/blog/eyecontact/
About This Article

To write a persuasive speech, start with a strong opening that will make your reader want to pay attention, including an attention grabber, your credentials, the essay's goal, and a road map for the essay. Next, offer persuasive evidence or reasons why the reader should support your viewpoint. Arrange these points logically, use credible sources, and employ some real life examples. Additionally, address counter-arguments to show that you’re looking at the topic from all sides. Finally, conclude by clearly letting the audience know how to put your ideas into action. To learn how to involve your audience when you deliver your speech, keep reading. Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Evan Murphree
Feb 8, 2022
Did this article help you?

Dianka Pradhan
Jun 28, 2019
Brittany Grech
Mar 27, 2017
Mavis Agyeiwaa Kyei
Oct 27, 2020
Jun 5, 2017

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter

Improve your practice.
Enhance your soft skills with a range of award-winning courses.
Persuasive Speech Outline, with Examples
March 17, 2021 - Gini Beqiri
A persuasive speech is a speech that is given with the intention of convincing the audience to believe or do something. This could be virtually anything – voting, organ donation, recycling, and so on.
A successful persuasive speech effectively convinces the audience to your point of view, providing you come across as trustworthy and knowledgeable about the topic you’re discussing.
So, how do you start convincing a group of strangers to share your opinion? And how do you connect with them enough to earn their trust?
Topics for your persuasive speech
We’ve made a list of persuasive speech topics you could use next time you’re asked to give one. The topics are thought-provoking and things which many people have an opinion on.
When using any of our persuasive speech ideas, make sure you have a solid knowledge about the topic you’re speaking about – and make sure you discuss counter arguments too.
Here are a few ideas to get you started:
- All school children should wear a uniform
- Facebook is making people more socially anxious
- It should be illegal to drive over the age of 80
- Lying isn’t always wrong
- The case for organ donation
Read our full list of 75 persuasive speech topics and ideas .

Preparation: Consider your audience
As with any speech, preparation is crucial. Before you put pen to paper, think about what you want to achieve with your speech. This will help organise your thoughts as you realistically can only cover 2-4 main points before your audience get bored .
It’s also useful to think about who your audience are at this point. If they are unlikely to know much about your topic then you’ll need to factor in context of your topic when planning the structure and length of your speech. You should also consider their:
- Cultural or religious backgrounds
- Shared concerns, attitudes and problems
- Shared interests, beliefs and hopes
- Baseline attitude – are they hostile, neutral, or open to change?
The factors above will all determine the approach you take to writing your speech. For example, if your topic is about childhood obesity, you could begin with a story about your own children or a shared concern every parent has. This would suit an audience who are more likely to be parents than young professionals who have only just left college.
Remember the 3 main approaches to persuade others
There are three main approaches used to persuade others:
The ethos approach appeals to the audience’s ethics and morals, such as what is the ‘right thing’ to do for humanity, saving the environment, etc.
Pathos persuasion is when you appeal to the audience’s emotions, such as when you tell a story that makes them the main character in a difficult situation.
The logos approach to giving a persuasive speech is when you appeal to the audience’s logic – ie. your speech is essentially more driven by facts and logic. The benefit of this technique is that your point of view becomes virtually indisputable because you make the audience feel that only your view is the logical one.
- Ethos, Pathos, Logos: 3 Pillars of Public Speaking and Persuasion
Ideas for your persuasive speech outline
1. structure of your persuasive speech.
The opening and closing of speech are the most important. Consider these carefully when thinking about your persuasive speech outline. A strong opening ensures you have the audience’s attention from the start and gives them a positive first impression of you.
You’ll want to start with a strong opening such as an attention grabbing statement, statistic of fact. These are usually dramatic or shocking, such as:
Sadly, in the next 18 minutes when I do our chat, four Americans that are alive will be dead from the food that they eat – Jamie Oliver
Another good way of starting a persuasive speech is to include your audience in the picture you’re trying to paint. By making them part of the story, you’re embedding an emotional connection between them and your speech.
You could do this in a more toned-down way by talking about something you know that your audience has in common with you. It’s also helpful at this point to include your credentials in a persuasive speech to gain your audience’s trust.

Obama would spend hours with his team working on the opening and closing statements of his speech.
2. Stating your argument
You should pick between 2 and 4 themes to discuss during your speech so that you have enough time to explain your viewpoint and convince your audience to the same way of thinking.
It’s important that each of your points transitions seamlessly into the next one so that your speech has a logical flow. Work on your connecting sentences between each of your themes so that your speech is easy to listen to.
Your argument should be backed up by objective research and not purely your subjective opinion. Use examples, analogies, and stories so that the audience can relate more easily to your topic, and therefore are more likely to be persuaded to your point of view.
3. Addressing counter-arguments
Any balanced theory or thought addresses and disputes counter-arguments made against it. By addressing these, you’ll strengthen your persuasive speech by refuting your audience’s objections and you’ll show that you are knowledgeable to other thoughts on the topic.
When describing an opposing point of view, don’t explain it in a bias way – explain it in the same way someone who holds that view would describe it. That way, you won’t irritate members of your audience who disagree with you and you’ll show that you’ve reached your point of view through reasoned judgement. Simply identify any counter-argument and pose explanations against them.
- Complete Guide to Debating
4. Closing your speech
Your closing line of your speech is your last chance to convince your audience about what you’re saying. It’s also most likely to be the sentence they remember most about your entire speech so make sure it’s a good one!
The most effective persuasive speeches end with a call to action . For example, if you’ve been speaking about organ donation, your call to action might be asking the audience to register as donors.
Practice answering AI questions on your speech and get feedback on your performance .
If audience members ask you questions, make sure you listen carefully and respectfully to the full question. Don’t interject in the middle of a question or become defensive.
You should show that you have carefully considered their viewpoint and refute it in an objective way (if you have opposing opinions). Ensure you remain patient, friendly and polite at all times.
Example 1: Persuasive speech outline
This example is from the Kentucky Community and Technical College.
Specific purpose
To persuade my audience to start walking in order to improve their health.
Central idea
Regular walking can improve both your mental and physical health.
Introduction
Let’s be honest, we lead an easy life: automatic dishwashers, riding lawnmowers, T.V. remote controls, automatic garage door openers, power screwdrivers, bread machines, electric pencil sharpeners, etc., etc. etc. We live in a time-saving, energy-saving, convenient society. It’s a wonderful life. Or is it?
Continue reading
Example 2: Persuasive speech
Tips for delivering your persuasive speech
- Practice, practice, and practice some more . Record yourself speaking and listen for any nervous habits you have such as a nervous laugh, excessive use of filler words, or speaking too quickly.
- Show confident body language . Stand with your legs hip width apart with your shoulders centrally aligned. Ground your feet to the floor and place your hands beside your body so that hand gestures come freely. Your audience won’t be convinced about your argument if you don’t sound confident in it. Find out more about confident body language here .
- Don’t memorise your speech word-for-word or read off a script. If you memorise your persuasive speech, you’ll sound less authentic and panic if you lose your place. Similarly, if you read off a script you won’t sound genuine and you won’t be able to connect with the audience by making eye contact . In turn, you’ll come across as less trustworthy and knowledgeable. You could simply remember your key points instead, or learn your opening and closing sentences.
- Remember to use facial expressions when storytelling – they make you more relatable. By sharing a personal story you’ll more likely be speaking your truth which will help you build a connection with the audience too. Facial expressions help bring your story to life and transport the audience into your situation.
- Keep your speech as concise as possible . When practicing the delivery, see if you can edit it to have the same meaning but in a more succinct way. This will keep the audience engaged.
The best persuasive speech ideas are those that spark a level of controversy. However, a public speech is not the time to express an opinion that is considered outside the norm. If in doubt, play it safe and stick to topics that divide opinions about 50-50.
Bear in mind who your audience are and plan your persuasive speech outline accordingly, with researched evidence to support your argument. It’s important to consider counter-arguments to show that you are knowledgeable about the topic as a whole and not bias towards your own line of thought.
- Games, topic printables & more
- The 4 main speech types
- Example speeches
- Commemorative
- Declamation
- Demonstration
- Informative
- Introduction
- Student Council
- Speech topics
- Poems to read aloud
- How to write a speech
- Using props/visual aids
- Acute anxiety help
- Breathing exercises
- Letting go - free e-course
- Using self-hypnosis
- Delivery overview
- 4 modes of delivery
- How to make cue cards
- How to read a speech
- 9 vocal aspects
- Vocal variety
- Diction/articulation
- Pronunciation
- Speaking rate
- How to use pauses
- Eye contact
- Body language
- Voice image
- Voice health
- Public speaking activities and games
- About me/contact
- How to write a persuasive speech
Writing a persuasive speech
By: Susan Dugdale | Last modified: 04-24-2023
Getting started with a 7 point action plan
To help you through the process of writing a persuasive speech from beginning to end, here's a 7 step checklist.
To get the most from it move through it sequentially - point by point. You'll find links to topic suggestion pages, explanations about how to structure your speech and the importance of audience analysis with examples and more.
In my experience, a successful persuasive speech can't be flicked out in five minutes! There may be brilliantly competent speakers who can do it if they know their subject, and their audience inside out. However the rest of us, me included, have to put the time in to achieve what we want to. ☺
Quick links to get around this page easily
Checklist for writing a persuasive speech
1. Selecting a persuasive speech topic
If you've already got a speech topic move on to setting a goal . For those who don't, read on.
A major part of the challenge of writing a persuasive speech can be choosing what to speak about.
If you're preparing the speech as part of a class exercise or for a public speaking club like Toastmasters you have seemingly unlimited choice. And that can be bewildering! The possibilities are vast. How do you narrow them down?
The answer is to choose something that you genuinely care about, fits the occasion AND that you know your audience will be interested in.
Speech topic suggestions to explore

- 100 Persuasive speech ideas
- 50 Good persuasive speech topics
- 105 Fun persuasive speech topics
- 309 'Easy' persuasive speech topics
- 310 Persuasive speech topics for college
- 108 Feminist persuasive speech topics
Return to Top
2. Setting a goal
The goal of writing a persuasive speech is to change or move the audience toward accepting your position on the topic. An essential part of that is knowing exactly what it is you want to achieve.
There are degrees of change. Do you want a little, or a lot?
Most wanted response or MWR
What you decide is called your most wanted response or MWR.
A realistic MWR is reached through analysis of your audience in relation to your topic.
Example: My topic is "obesity in children".
Audience - who are they.
I am speaking to mothers whose children all attend the same kindergarten.
The staff are concerned about the number of children who are over weight for their age.
The children mostly come from homes where both parents work.

Current food habits as reported by kindergarten staff
Food is bought already made up for a variety of reasons including time saving, convenience, and a lack of knowledge about how to prepare it any other way.
'Treat' food (sweets, cake etc.) is also used to pacify and/or to reinforce good behavior.
Fussy or picky eating is allowed principally because the effort and time required to change already established patterns is difficult to find.
The problem is compounded by lack of exercise.
Most Wanted Response (MWR) options
In setting the goal (MWR) for the speech I need to decide what approach will achieve the best results.
Do I want to influence the mothers to open their minds to the idea that allowing a child to establish habitual unhealthy eating patterns is detrimental to their children's growth and development?
Or do I want them to stop using treat and pre-prepared foods immediately and only offer home cooked healthy options instead?
The first approach is softly-softly. The second is direct or hard hitting.
3. Audience analysis
Who is your audience.
How you persuade, and your MWR (goal) is most effectively established when you understand who you are talking to.
In relation to the topic you're going to speak about are they:
- Hostile - actively don't want to hear what you have to say for many reasons which may include prejudice, fear, ignorance, inertia, cultural difference, differing values/beliefs ...
- Neutral - no decided opinion or beliefs and therefore no investment toward maintaining the current state or moving toward a new one. This is the middle ground.
- Motivated - actively seeking to change. These people are already aware of the 'problem' and are looking for solutions. They want to hear what you have to tell them and are likely to be ready to be convinced of the rightness of your solution.
What else do you need to know?
Aside from their anticipated baseline attitude, (hostile, neutral, motivated), toward your speech topic, what else would be useful to know about your audience?
Find out their:
- General Age
- Shared fears, concerns or problems
- Cultural background(s)
- Shared interests, beliefs, values, goals, hopes, desires
- What obstacles there are to adopting the change you desire
The more you can find out, the more you can tailor writing a persuasive speech (including tone and language choice), and your MWR to fit.
For instance, going back to the obesity in children example above, we could decide, given what we've found out about the audience, the hard-hitting approach would generate too many obstacles to overcome.
Therefore we will be writing a persuasive speech with a non-threatening MWR that has mothers accepting a pamphlet on children's healthy snack choices to take home.
4. Keep it local
Where possible draw your examples from local material. The reason is we are more likely to care or respond when we actively know who or what is involved firsthand. We identify, and the more we identify, the more invested we are in finding a solution. The situation becomes real to us and we care.
5. Evidence and empathy
An essential part of putting together a good persuasive speech is finding credible evidence to support your argument.
Seek out reputable, reliable, quotable sources to back the points you make. Without them your speech will fail its purpose.
Persuasion is a synthesis of emotional as well as intellectual appeal.
Emotional content will be dismissed unless it is properly backed. Conversely purely intellectual content will be dismissed if it lacks empathy or feeling. You need both - in equal measure.
6. Balance and obstacles
Seek out and address the opposition's arguments, or obstacles in the path of adopting your course of action, fairly and respectfully. Find the elements you share. Openly acknowledge and be clear about them. This builds credibility and trust and as a result your points of departure are more likely to be listened to.
7. Choosing a structural pattern
Once you've decided your topic and its angle, done your audience analysis, fixed what you want to achieve (MWR), researched for evidence, and addressed the obstacles, you're finally ready to begin writing.
What pattern or model will you use?

There is more than one.
Have a look at each of the four below to see which best suits your topic, speech purpose and audience.
1) Monroe's Motivated Sequence

This is a tried and tested model developed in the 1930's by Allan H Monroe. Monroe's Motivated Sequence follows the normal mind-flow or thought sequence someone goes through when someone else is persuading them to do something.
It's a pattern used over and over again by the professional persuaders: marketers, advertisers, politicians ...
Monroe's Motivated Sequence in action
You can find out more about the five steps involved in writing a persuasive speech using Monroe's Motivated Sequence here. There's an explanation with examples of each step, and a printable blank outline template to download.
There's also an example persuasive speech to read that uses the method.
2) Problem/Solution
This is a two step pattern. The first part outlines/explains the problem and the second provides the solution which includes meeting the obstacles and giving evidence.
3) Comparison
In this pattern the method is to compare an item/object/idea/action against another similar item/object/idea/action and establish why the item/object/idea/action you are supporting is superior.
Example: Why a SBI website is better than a Wordpress site if you want to build an online business
- Reason One Wordpress primarily is a blogging platform and blogging is not a business model
- Reason Two Wordpress does not supply fully integrated step-by-step instructions to build a sustainable e-business
- Reason Three Wordpress does not provide its users with constant and fully tested upgrades/updating
With each comparison point compelling, relevant evidence is provided and obstacles are met.
(If you're curious check out the SBI v Wordpress comparison. There are many more than three reasons why SBI is the preferred online business platform! Wordpress or SBI? And these days you can actually have both through SBI.)
4) Using the negative to persuade
In this model the reasons why you are against the opposition of your chosen topic are highlighted.
Example: The topic is Teenage Binge Drinking and the angle is to persuade parents to take more control
- Leads to anti-social behavior - for example, mindless vandalism, drunk-driving, and unprotected sex
- Impacts on growing brains - an overview of current research
- Has implications for developing addictions - alcoholism, nicotine ...
Each negative reason is backed with evidence. One piles on top the other creating an urgency to solve the problem. Your positive solution coming at the end of the speech clinches the argument.
More speech resources
For more about the processes involved in writing a successful speech check these pages:
- Using storytelling effectively

For more about delivering your persuasive speech persuasively please don't overlook these pages. They are gold! Writing is a only part of the process. How you deliver completes it.
- How to rehearse
- Using vocal variety
- Return to the top of the page
speaking out loud
Subscribe for FREE weekly alerts about what's new For more see speaking out loud

Top 10 popular pages
- Welcome speech
- Demonstration speech topics
- Impromptu speech topic cards
- Thank you quotes
- Impromptu public speaking topics
- Farewell speeches
- Phrases for welcome speeches
- Student council speeches
- Free sample eulogies
From fear to fun in 28 ways
A complete one stop resource to scuttle fear in the best of all possible ways - with laughter.

Useful pages
- Search this site
- About me & Contact
- Blogging Aloud
- Free e-course
- Privacy policy
©Copyright 2006-24 www.write-out-loud.com
Designed and built by Clickstream Designs
Persuasive Speeches — Types, Topics, and Examples
What is a persuasive speech.
In a persuasive speech, the speaker aims to convince the audience to accept a particular perspective on a person, place, object, idea, etc. The speaker strives to cause the audience to accept the point of view presented in the speech.
The success of a persuasive speech often relies on the speaker’s use of ethos, pathos, and logos.

Ethos is the speaker’s credibility. Audiences are more likely to accept an argument if they find the speaker trustworthy. To establish credibility during a persuasive speech, speakers can do the following:
Use familiar language.
Select examples that connect to the specific audience.
Utilize credible and well-known sources.
Logically structure the speech in an audience-friendly way.
Use appropriate eye contact, volume, pacing, and inflection.
Pathos appeals to the audience’s emotions. Speakers who create an emotional bond with their audience are typically more convincing. Tapping into the audience’s emotions can be accomplished through the following:
Select evidence that can elicit an emotional response.
Use emotionally-charged words. (The city has a problem … vs. The city has a disease …)
Incorporate analogies and metaphors that connect to a specific emotion to draw a parallel between the reference and topic.
Utilize vivid imagery and sensory words, allowing the audience to visualize the information.
Employ an appropriate tone, inflection, and pace to reflect the emotion.
Logos appeals to the audience’s logic by offering supporting evidence. Speakers can improve their logical appeal in the following ways:
Use comprehensive evidence the audience can understand.
Confirm the evidence logically supports the argument’s claims and stems from credible sources.
Ensure that evidence is specific and avoid any vague or questionable information.
Types of persuasive speeches
The three main types of persuasive speeches are factual, value, and policy.

A factual persuasive speech focuses solely on factual information to prove the existence or absence of something through substantial proof. This is the only type of persuasive speech that exclusively uses objective information rather than subjective. As such, the argument does not rely on the speaker’s interpretation of the information. Essentially, a factual persuasive speech includes historical controversy, a question of current existence, or a prediction:
Historical controversy concerns whether an event happened or whether an object actually existed.
Questions of current existence involve the knowledge that something is currently happening.
Predictions incorporate the analysis of patterns to convince the audience that an event will happen again.
A value persuasive speech concerns the morality of a certain topic. Speakers incorporate facts within these speeches; however, the speaker’s interpretation of those facts creates the argument. These speeches are highly subjective, so the argument cannot be proven to be absolutely true or false.
A policy persuasive speech centers around the speaker’s support or rejection of a public policy, rule, or law. Much like a value speech, speakers provide evidence supporting their viewpoint; however, they provide subjective conclusions based on the facts they provide.
How to write a persuasive speech
Incorporate the following steps when writing a persuasive speech:
Step 1 – Identify the type of persuasive speech (factual, value, or policy) that will help accomplish the goal of the presentation.
Step 2 – Select a good persuasive speech topic to accomplish the goal and choose a position .

Step 3 – Locate credible and reliable sources and identify evidence in support of the topic/position. Revisit Step 2 if there is a lack of relevant resources.
Step 4 – Identify the audience and understand their baseline attitude about the topic.
Step 5 – When constructing an introduction , keep the following questions in mind:
What’s the topic of the speech?
What’s the occasion?
Who’s the audience?
What’s the purpose of the speech?
Step 6 – Utilize the evidence within the previously identified sources to construct the body of the speech. Keeping the audience in mind, determine which pieces of evidence can best help develop the argument. Discuss each point in detail, allowing the audience to understand how the facts support the perspective.
Step 7 – Addressing counterarguments can help speakers build their credibility, as it highlights their breadth of knowledge.
Step 8 – Conclude the speech with an overview of the central purpose and how the main ideas identified in the body support the overall argument.

Persuasive speech outline
One of the best ways to prepare a great persuasive speech is by using an outline. When structuring an outline, include an introduction, body, and conclusion:
Introduction
Attention Grabbers
Ask a question that allows the audience to respond in a non-verbal way; ask a rhetorical question that makes the audience think of the topic without requiring a response.
Incorporate a well-known quote that introduces the topic. Using the words of a celebrated individual gives credibility and authority to the information in the speech.
Offer a startling statement or information about the topic, typically done using data or statistics.
Provide a brief anecdote or story that relates to the topic.
Starting a speech with a humorous statement often makes the audience more comfortable with the speaker.
Provide information on how the selected topic may impact the audience .
Include any background information pertinent to the topic that the audience needs to know to understand the speech in its entirety.
Give the thesis statement in connection to the main topic and identify the main ideas that will help accomplish the central purpose.
Identify evidence
Summarize its meaning
Explain how it helps prove the support/main claim
Evidence 3 (Continue as needed)
Support 3 (Continue as needed)
Restate thesis
Review main supports
Concluding statement
Give the audience a call to action to do something specific.
Identify the overall importan ce of the topic and position.
Persuasive speech topics
The following table identifies some common or interesting persuasive speech topics for high school and college students:
| Benefits of healthy foods | Animal testing | Affirmative action |
| Cell phone use while driving | Arts in education | Credit cards |
| Climate change | Capital punishment/death penalty | Fossil fuels |
| Extinction of the dinosaurs | Community service | Fracking |
| Extraterrestrial life | Fast food & obesity | Global warming |
| Gun violence | Human cloning | Gun control |
| Increase in poverty | Influence of social media | Mental health/health care |
| Moon landing | Paying college athletes | Minimum wage |
| Pandemics | Screen time for young children | Renewable energy |
| Voting rights | Violent video games | School choice/private vs. public schools vs. homeschooling |
| World hunger | Zoos & exotic animals | School uniforms |
Persuasive speech examples
The following list identifies some of history’s most famous persuasive speeches:
John F. Kennedy’s Inaugural Address: “Ask Not What Your Country Can Do for You”
Lyndon B. Johnson: “We Shall Overcome”
Marc Antony: “Friends, Romans, Countrymen…” in William Shakespeare’s Julius Caesar
Ronald Reagan: “Tear Down this Wall”
Sojourner Truth: “Ain’t I a Woman?”
How to Start a Speech: The Best (and Worst) Speech Openers
Subscribe to our weekly newsletter.
One of the hardest things about public speaking is knowing how to start a speech. Your opening line is your first impression. It’s how you capture attention. It’s how you captivate the audience. So how do you make sure you nail it every time?
The best way to know how to open a speech is to look at what has worked in the past. When we examined the top speeches of all time and the most popular TED talks of all time, we found some interesting speaking patterns.
Time has identified the top 10 greatest speeches of all time. They are:
Opening Lines of the Top 10 Greatest Speeches of All Time
#1: Socrates – “Apology”

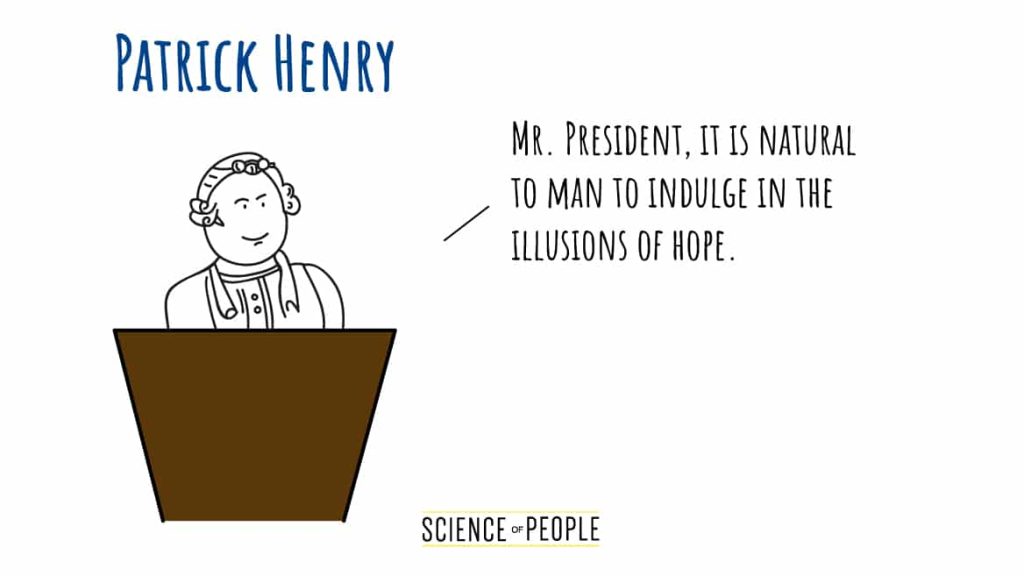
#2: Patrick Henry – “Give Me Liberty or Give Me Death”
#3: Frederick Douglass – “The Hypocrisy of American Slavery”

#4: Abraham Lincoln – “Gettysburg Address”
Opening Line: “Fourscore and seven years ago our fathers brought forth on this continent a new nation, conceived in liberty and dedicated to the proposition that all men are created equal.”

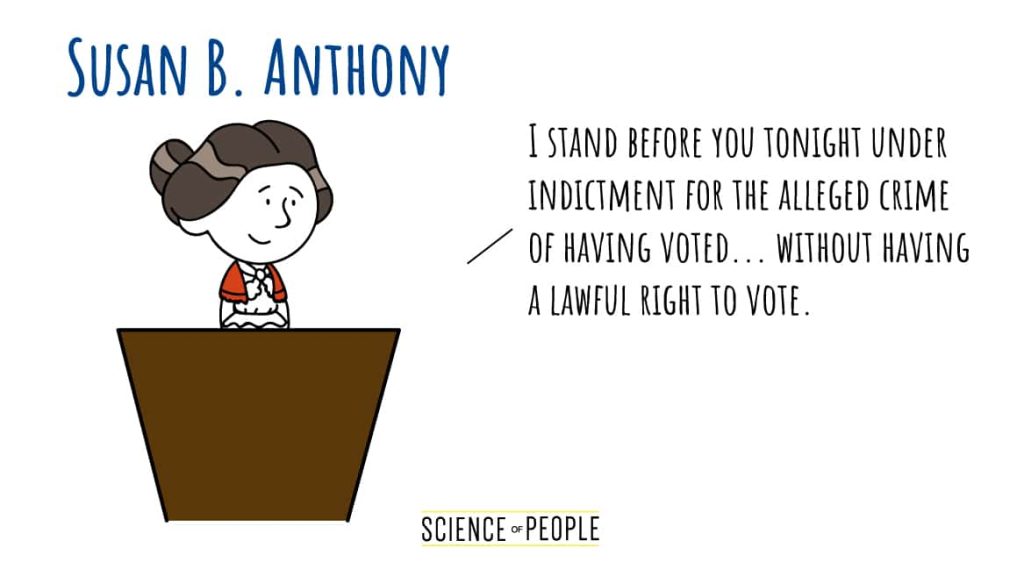
#5: Susan B. Anthony – “Women’s Rights to the Suffrage”
#6: Winston Churchill – “Blood, Toil, Tears, and Sweat”

#7: John F. Kennedy – “Inaugural Address”
Opening Line: “We observe today not a victory of party, but a celebration of freedom — symbolizing an end, as well as a beginning — signifying renewal, as well as change.”

#8: Martin Luther King, Jr. – “I Have a Dream”

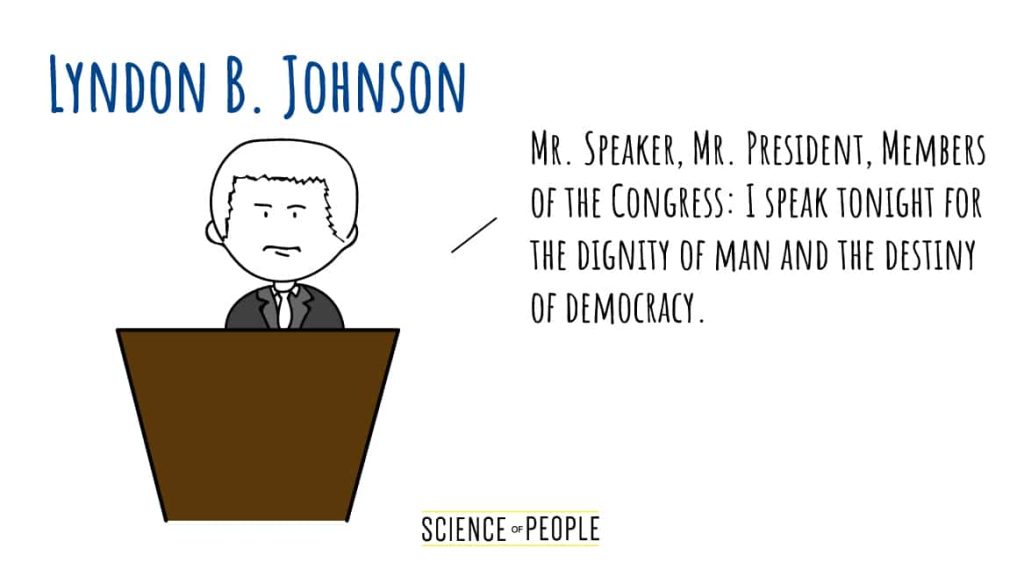
#9: Lyndon B. Johnson – “The American Promise”
#10: Ronald Reagan – “Remarks at the Brandenburg Gate”

How do all of these historical greats start their speeches? Is there a difference between these and some of the more modern top TED talks?
Before we dive in, let’s recap with some critical do’s and don’ts when opening a speech:
Opening Lines of the Top 10 TED Talks of All Time
Here are the opening lines to the top 10 Ted Talks of all time according to view count:
#1: Sir Ken Robinson – “Do schools kill creativity?” Opening Line: “Good morning. How are you? It’s been great, hasn’t it? I’ve been blown away by the whole thing. In fact, I’m leaving.”
#2: Amy Cuddy – “Your Body Language May Shape Who You Are” Opening Line: “So I want to start by offering you a free, no-tech life hack, and all it requires of you is this: that you change your posture for two minutes.”
#3: Simon Sinek – “How Great Leaders Inspire Action”
#4: Brene Brown – “The Power of Vulnerability” Opening Line: “So, I’ll start with this: a couple years ago, an event planner called me because I was going to do a speaking event.”
#5: Mary Roach – “10 Things You Didn’t Know About Orgasm” Opening Line: “All right. I’m going to show you a couple of images from a very diverting paper in The Journal of Ultrasound in Medicine.”
#6: Julian Treasure – “How to Speak so that People Want to Listen” Opening Line: “The human voice: It’s the instrument we all play.”
#7: Jill Bolte Taylor – “My Stroke of Insight” Opening Line: “I grew up to study the brain because I have a brother who has been diagnosed with a brain disorder: schizophrenia.”
#8: James Veitch – “This is What Happens When You Reply to Spam Email” Opening Line: “A few years ago, I got one of those spam emails.”
#9: Cameron Russell – “Looks Aren’t Everything; Believe Me, I’m a Model” Opening Line: “Hi. My name is Cameron Russell, and for the last little while, I’ve been a model.”
#10: Dan Pink – “The Puzzle of Motivation” Opening Line: “I need to make a confession at the outset here.”
What can we learn from these opening lines? There are some patterns that can help us. First, let’s start with what you shouldn’t do. Have you ever made one of these cardinal speaking sins?
Never Start a Presentation with…
Anything technical! This is a big mistake people make when they have not done a tech check ahead of time or are feeling nervous. Never start with these openers:
- Is this microphone working?
- Can you hear me?
- Wow, these lights are bright!
Your nervousness. Many people think it is vulnerable to start with how nervous they are about speaking — you can mention this later, but it should not be the first thing. Why? People will then only be looking for signs of your nervousness. Don’t start with:
- I’m so nervous right now!
- Wow there are so many people here.
- I’m not a great public speaker.
A lackluster or non-believable nicety. It’s great to be grateful to the person who introduced you, but it’s not a great way to include the audience. It’s ok to thank the audience for being there—but do it at the end (not as your opening line). These are all too boring:
- Thanks for having me.
- Thanks for that intro.
- Nice to be here.
Boring, shmoring! I have an exception here if you can make it funny. Ken Robinson started with a nicety and then turned it into a joke. He said, “ “Good morning. How are you? It’s been great, hasn’t it? I’ve been blown away by the whole thing. In fact, I’m leaving.”
More Public Speaking Resources
Get even more public speaking tips with our related resources:
- 10 Presentation Ideas that will Radically Improve Your Presentation Skills
- 6 Public Speaking Apps to try Before Your Next Presentation
- My Top 5 Favorite Public Speakers
- 15 Science-Based Public Speaking Tips To Become a Master Speaker
- How to Give Captivating Presentations
- How to Give an Awesome Toast
How to Start a Presentation
A story. The absolute best way to start a presentation is with a story. There is nothing better to capture the imagination and attention of an audience. Try to use these speaking openers as fill-in-the-blanks for your speech.
- I’m here for a reason. And it’s an interesting story…
- The best thing that ever happened to me was…
- Once upon a time…
In his talk, “The lies our culture tells us about what matters,” David Brooks started off with a great opening line AND a story. He said, “So, we all have bad seasons in life. And I had one in 2013. My marriage had just ended, and I was humiliated by that failed commitment.” Makes you want to watch right…
And if you need help on storytelling basics, be sure to check out some of my top 5 favorite speakers .
A BIG idea. Sometimes you want to share your big idea right up front. This can be helpful because it is intriguing and gets people clued in right away. All TED speakers try to integrate their big idea early.
- You’re here for a reason. It’s…
- The single most important thing I want to share with you today is…
- Today, I want to share a big idea…
I love how Stacy Smith starts off her talk with her big idea framed in an interesting way. She said, “Today, I want to tell you about a pressing social issue. Now, it’s not nuclear arms, it’s not immigration, and it’s not malaria. I’m here to talk about movies.”
Special Note: Be very careful to NOT deliver your one-liner by re-reading your title slide. You also want to position it as exciting and intriguing. For example, don’t say, “Today I am going to talk about body language.” Instead say, “Today I am going to teach you the single most important thing you can do to improve your charisma… and it starts with your body.”
A quirky one-liner. If you can use humor — do it! Humor or curiosity is a great way to start a speech on a high. You can get creative with these! Think of an interesting fact about you, your audience or your topic that can lead you into your content.
- One thing most people don’t know about me is…
- A teacher, a mother and a duck walk into a bar…
- I want to tell you something surprising.
When I gave my TEDx London Talk I started off with a quirky one-liner that immediately got a few laughs. It was “Hi, I’m Vanessa and I am a recovering awkward person.” It worked so well it is also the first line of my book, Captivate .
II love the way Eve Ensler opens her speech with an interesting one-liner: “For a long time, there was me, and my body.”
This is a great tip from Conor Neill. He says that it is great to start with a question that the audience is asking themselves or would be very curious to know the answer to. This might be phrasing a pain point or worry for your audience.
- Do you ever worry about…?
- Have you ever wondered…?
- You might have always thought…
See Cono Neill’s examples here:
Did you know…? Any interesting factoid or curiosity is bound to intrigue your audience. This is great if it leads into your content or a story. I like to start with did you know… Here are some that I use. You will have to fill in the blank for your audience:
- Did you know that it takes less than a second to make a first impression ?
- Did you know that your nonverbal communication is 12.5 times more powerful than your words ?
- Did you know that we are lied to 200 times a day ?
Jamie Oliver does this amazingly in his TED Talk. He starts with this mind-blowing fact, “Sadly, in the next 18 minutes when I do our chat, four Americans that are alive will be dead through the food that they eat.”
Hopefully these opening lines will give you some ideas to use to open your speech.
How to End a Speech: My Favorite Closers
Do you know how to end on a high? Leave a lasting impression in your presentation? Science tells us that the first and last parts of your presentations are the most important. Get our FREE download to get our closer guide.
Popular Guides
20 thoughts on “how to start a speech: the best (and worst) speech openers”.
Love your material
didnt help me but still good stuff
Thank you Vanessa. I’ve been a public speaker for 25 years and I’m impressed with your content here. Thank you. Looking forward to a deep dive into more of your material. With gratitude.
Found these examples super informative. Can’t wait to mix match the examples to see which one will work best for my presentation!
I am preparing to make a presentation on Public Speaking and came across your article. This is very instructive and timely too.Many thanks.
Comments are closed.
How to Deal with Difficult People at Work
Do you have a difficult boss? Colleague? Client? Learn how to transform your difficult relationship. I’ll show you my science-based approach to building a strong, productive relationship with even the most difficult people.
Related Articles
Science of People offers over 1000+ articles on people skills and nonverbal behavior.
Get our latest insights and advice delivered to your inbox.
It’s a privilege to be in your inbox. We promise only to send the good stuff.
- Personal Development
- Sales Training
- Business Training
- Time Management
- Leadership Training
- Book Writing
- Public Speaking
- Live Speaker Training With Brian
- See Brian Speak
- Coaching Programs
- Become a Coach
- Personal Success
- Sales Success
- Business Success
- Leadership Success
- How to Start a Speech: The Best Ways to Capture Your Audience
You’ve heard the saying, “First impressions are lasting; you never get a second chance to create a good first impression” — right?
The same is true when talking about how to start a speech…
The truth is, when you start your speech, you must focus everything on making a positive first impression on your audience members (especially if you are doing the presentation virtually ). Capturing the audience’s attention from the very beginning is crucial to prevent them from being distracted, losing interest, or forming negative opinions.
The introduction is the formal greeting for speeches, so let’s be sure to get this right to hook the audience. Understanding the importance of speech openings can significantly impact making a strong first impression. Planning and delivering the first words with confidence and relevance is essential, as they set the tone for the entire presentation and ensure you deliver a professional start, free from hesitation or irrelevance.
Here are 15 different ways to start a speech as well as 2 extra BONUS tips at the end.
1) Thank the Organizers and Audience
You can start by thanking the audience for coming and thanking the organization for inviting you to speak.
Refer to the person who introduced you or to one or more of the senior people in the organization in the audience.
This compliments them, makes them feel proud and happy about your presence, and connects you to the audience like an electrical plug in a socket.
2) Start With a Positive Statement
A presentation tip at the start is to tell the audience members how much they will like and enjoy what you have to say.
For example, you might say:
“You’re really going to enjoy the time we spend together this evening. I’m going to share with you some of the most important ideas that have ever been discovered in this area.”
Remember that speaking is an art, so be an artist and take complete control of your performance,
3) Compliment the Audience
You can begin by complimenting the audience members sincerely and with great respect.
Smile as if you are really glad to see them as if they are all old friends of yours that you have not seen for quite a while.
You can tell them that it is a great honor for you to be here, that they are some of the most important people in this business or industry, and that you are looking forward to sharing some key ideas with them.
You could say something like:
“It is an honor to be here with you today. You are the elite, the top 10 percent of people in this industry. Only the very best people in any field will take the time and make the sacrifice to come so far for a conference like this.”
4) Start Your Speech With the First Sentence Referring to Current Events
Use a current event front-page news story to transition into your subject and to illustrate or prove your point. You can bring a copy of the newspaper and hold it up as you refer to it in your introduction.
This visual image of you holding the paper and reciting or reading a key point rivets the audience’s attention and causes more people to lean forward to hear what you have to say.
5) Refer to a Historical Event
For many years, I studied military history…
Especially the lives and campaigns of the great generals and the decisive battles they won. One of my favorites was Alexander the Great. Standing in the symbolic shadow of such historical figures can provide a powerful and engaging start to any speech, especially when drawing parallels to contemporary challenges.
One day, I was asked to give a talk on leadership principles to a roomful of managers for a Fortune 500 company.
I decided that the campaign of Alexander the Great against Darius of Persia would make an excellent story that would illustrate the leadership qualities of one of the great commanders in history.
I opened my talk with these words:
“Once upon a time there was a young man named Alex who grew up in a poor country. But Alex was a little bit ambitious. From an early age, he decided that he wanted to conquer the entire known world. But there was a small problem.
Most of the known world was under the control of a huge multinational called the Persian Empire, headed by King Darius II. To fulfill his ambition, Alex was going to have to take the market share away from the market leader, who was very determined to hold on to it.
This is the same situation that exists between you and your major competitors in the market today. You are going to have to use all your leadership skills to win the great marketing battles of the future.”
6) Refer to a Well Known Person
You can start by quoting a well-known person or publication that recently made an interesting or important statement.
One of the subjects I touch upon regularly is the importance of continual personal development.
I will say something like:
“In the twenty-first century, knowledge and know-how are the keys to success. As basketball coach Pat Riley said, ‘If you are not getting better, you are getting worse.’”
7) Refer to a Recent Conversation
Start by telling a story about a recent conversation with someone in attendance.
For instance, I might say:
“A few minutes ago, I was talking with Tom Robinson in the lobby. He told me that this is one of the very best times to be working in this industry, and I agree.”
8) Make a Shocking Statement With a Startling Fact
You can start your talk by making a shocking statement of some kind.
For example, you might say something like:
“Here’s a startling fact: According to a recent study, there will be more change, more competition, and more opportunities in this industry in the next year than ever before. And 72 percent of the people in this room will be doing something different within two years if they do not rapidly adapt to these changes.”
Click here If you want to learn more techniques to wow your audience.
9) Quote From Recent Research
You can start by quoting a relevant, recent research report.
One example is:
“According to a story in a recent issue of Businessweek, there were almost 11 million millionaires in America in 2018, most of them self-made.”
10) Start Your Speech With a Strong Opening By Giving Them Hope
The French philosopher Gustav Le Bon once wrote, “The only religion of mankind is, and always has been hope.”
When you speak effectively, you give people hope of some kind.
Remember, the ultimate purpose of public speaking, is to inspire people to do things that they would not have done in the absence of your comments.
Everything you say should relate to the actions you want people to take and the reasons that they should take those actions.
11) Be Entertaining
Bill Gove used to walk onto the stage after his introduction if he had just finished talking to someone on the side and was breaking off to give his talk to the group.
The audience got the feeling that his entire talk was one continuous conversation, devoid of meaningless filler words .
Bill would often go to the edge of the stage and then drop his voice in a conspiratorial way, open his arms, and beckon the audience members to come a little closer.
He would say, “Come here, let me tell you something,” and then he would wave them forward as though he was about to tell a secret to the entire room.
The amazing thing was that everyone in the room would lean forward to hear this “secret” that he was about to share. People would all suddenly realize what they were doing and break out in laughter. It was a wonderful device to get the audience into the palm of his hands.
12) Ask a Question
You can open by making a positive statement and then pose a rhetorical question to engage your audience and set the stage for your presentation.
Try something like this:
“This is a great time to be alive and in business in America. But let me ask you, what does it truly mean to be self-employed in today’s economy?”
Raise your hand to indicate what you want people to do. I have used this line, and after a moment of thought, I then say to someone who looks intrigued in the front, “How many people here feel truly self-employed?”
Invariably, someone will say, “We all do!”
I then compliment and affirm the answer: “You’re right! We are all self-employed, from the time we take our first jobs to the day that we retire; we all work for ourselves, no matter who signs our paychecks.”
Similarly, a 17-year-old science fair winner effectively engaged their audience with a question at the beginning of their TED Talk, showcasing the power of this technique.
13) Open With a Problem
You can start with a problem that must be solved. If it is a problem that almost everyone has in common, you will immediately have the audience’s complete and undivided attention.
For example, you could say:
“Fully 63 percent of baby boomers are moving toward retirement without enough money put aside to provide for themselves for as long as they are going to live. We must address this problem and take action immediately to ensure that each person who retires will be able to live comfortably for the rest of his or her natural life.”
Introducing a new idea at this point can be a powerful way to engage your audience further, by promising a solution that is both innovative and beneficial.
14) Make a Strong Statement, Then Ask a Question
You can start by making a strong and powerful statement and then ask a question. You then follow with an answer and ask another question. This gets people immediately involved and listening to your every word.
Here’s an example:
“Twenty percent of the people in our society make 80 percent of the money. Are you a member of the top 20 percent? If not, would you like to join the top 20 percent or even the top 10 percent? Well, in the next few minutes, I am going to give you some ideas to help you become some of the highest-paid people in our society. Would that be a good goal for our time together today?”
15) Tell a Personal Story
You can start your talk with a personal story. Some of the most powerful words to capture the complete attention of the audience and make a personal connection are, “Once upon a time…”
From infancy and early childhood, people love stories of any kind. When you start off a presentation with a personal anecdote using the words, “Once upon a time…” you tell the audience that a relatable story is coming. People immediately settle down, become quiet, and lean forward, eager to hear how your experience might mirror their own or offer them new insights.
When I conduct full-day seminars and I want to bring people back to their seats after a break, I will say loudly, “Once upon a time there was a man, right here in this city…”
As soon as I say these words, people hurry back to their seats and begin to listen attentively, connecting with the story on a personal level.
Incorporating a personal story is very effective.
In fact, it’s probably one of the best public speaking tips I’ve learned to this day.
Bonus Tip: Tell Them About Yourself
Very often, I will start a serious speech or presentation to a business, sales, or entrepreneurial group by saying:
“I started off without graduating from high school. My family had no money. Everything I accomplished in life I had to do on my own with very little help from anyone else.”
It is amazing how many people come up to me after a talk that began with those words and tells me that was their experience as well.
They tell me that they could immediately identify with me because they too had started with poor grades and limited funds, as most people do. As a result, they were open to the rest of my talk, even a full-day seminar, and felt that everything I said was more valid and authentic than if I had been a person who started off with a successful background.
Building a bridge like this is very helpful in bringing the audience onto your side.
Bonus Tip: Get Them Talking to One Another
You can ask people to turn to the person next to them to discuss a particular point.
For instance, you could say:
“Tell the person next to you what you would like to learn from this seminar.”
Whatever you ask your audience members to do, within reason, they will do it for you. Your commands and your thought leadership will easily influence them, as long as you ask them with confidence.
By following any one of these tips for starting your speech, you are sure to grab your audience’s attention every time. How do you start a speech? Let me know in the comments.
« Previous Post How to Develop Self-Discipline to Succeed Next Post » 15 Simple Ways to Be Successful in Life
About Brian Tracy — Brian is recognized as the top sales training and personal success authority in the world today. He has authored more than 60 books and has produced more than 500 audio and video learning programs on sales, management, business success and personal development, including worldwide bestseller The Psychology of Achievement. Brian's goal is to help you achieve your personal and business goals faster and easier than you ever imagined. You can follow him on Twitter , Facebook , Pinterest , Linkedin and Youtube .
- Most Recent
- Goal Setting for Success & Developing SMART Habits
- 15 Simple Ways to Be Successful in Life
- How to Develop Self-Discipline to Succeed
- The Art of Business Success: A Blueprint for Entrepreneurs
- Free Webinar: How To Write a Book and Become a Published Author
- Free Video Series: 3-Part Sales Mastery Training Series
- Free Assessment: The Confidence Factor
- Free Assessment: Discovering Your Talents
Browse Categories
- Financial Success
Follow Brian & Join the Discussion
- Free Resources
- Best Sellers
- Knowledge Base
- Shipping & Returns
- Privacy Policy
- About Brian
- Brian Recommends
Your Privacy is Guaranteed. We will never give, lease or sell your personal information. Period!
© Copyright 2001-2024 Brian Tracy International. All Rights Reserved.
International Study Centre
- Student life
- Accommodation
- Durham University
- Virtual events
- International Foundation Year
- Pre-Masters
- English Language Preparation
- Prepare for Success
- Enhanced Induction
- Entry requirements
- Fees, accommodation and living costs
- Visa information
- Preparing to study
- Ask a question
How to write a persuasive speech
- Link copied!

Being able to write and deliver a persuasive speech is not only a skill that will help you at university – but something that will help you in both your career and your personal life. Whether you’re giving a graded speech for a class, explaining something as part of your job, or defending something you’re passionate about, delivering a persuasive speech will only help you to succeed. Follow our tips for how to develop your skills in persuasive speech writing.
What is a persuasive speech?
To persuade someone is to change their point of view and have them agree with you. In a university setting, this may be for a graded presentation or a debate. Although given verbally, your first step will be to write the speech before you deliver it – this will ensure you are fully prepared, have time to think about what you want to say, and ensure everything is properly researched. You don’t want to get caught out saying something that is untrue.
Persuasive speech topics
The first thing you need to do when writing a persuasive speech is to choose your topic. If you’re giving a speech as part of your university degree, this may have been provided to you as part of the assignment. If one hasn’t been provided, but the speech is for a specific class , try to think about the topics covered in your previous lessons or suggested reading from the teacher. Use the knowledge you’ve already gained in the class and show your teacher just how much you’ve paid attention.
Passion is key
If there are no guidelines on choosing your persuasive speech topic, then you have more choice when making your decision. This is a great opportunity to talk about something you’re truly passionate about. If your audience sees you are genuinely interested in your topic, they will see your speech as more authentic and credible. How can you persuade someone to side with you if it doesn’t seem like you believe in what you’re saying yourself?
Persuasive speech examples
If you’re still struggling to think of a topic, here are some examples that might help. When choosing from the below examples, it is still important to select a topic that interests you. Some good examples of persuasive speech topics for university students include:
- Is eating meat unethical?
- Should the minimum wage be increased?
- Should cities offer free bike sharing programmes?
- Can money buy happiness?
- Should we abolish daylight savings time?
- Are art and music programmes an essential part of schooling?
- Should more people use public transportation?
- Should teenagers be allowed to purchase violent video games?
- Should we donate unused food from supermarkets?
- Should we keep animals in zoos?
Now that you’ve picked your topic, you can start writing your speech. The first thing you need to know is your opinion. Are you for or against your topic? Once you’ve decided which side of the argument you want to defend, you can begin writing your persuasive speech.
Research, research, research
All university assignments begin with research, and persuasive speeches are no different. You can research however suits you best, utilising library resources, books you own, and the internet. It may even help to research both sides of the argument, including the opposing opinion to your own, to get a better understanding of your chosen topic.
Persuasive speech structure
Start your persuasive speech with a strong introduction, grabbing the attention of your audience. This can be emotional, shocking, or funny – as long as it is powerful. After you have your audience’s attention, you should clearly introduce the topic of your speech.
You now need to distil your research into a few key arguments. These should be the most powerful and persuasive arguments from your research, the ones that you believe will convince your listeners to agree with your point of view. Choose between two to four key arguments to keep your audience interested.
When giving a persuasive speech, it is important to acknowledge and address any counter arguments from the opposition. Not only does this show that you have done your research, but it addresses any concerns or doubts your audience may have.
Lastly, you should finish your persuasive speech with a strong closing argument. You may choose to save your strongest argument for this point, or reinforce a previous point you made. Either way, your closing argument should be the thing your audience remembers the most.
Giving a persuasive speech as an international student
If you’re studying at a UK university and English isn’t your first language, you may worry about writing a persuasive speech as part of your degree programme. The best way to prepare in this scenario is to make sure you have a strong understanding of the English language. At Durham University International Study Centre, you can take a pathway programme designed to develop all the skills you need to succeed as an international students. These programmes include a core English module programme designed to develop your language skills to a university level.
You can also develop your English language skills outside of the classroom. Choosing to live in student accommodation gives you even more opportunities to speak English in a less formal setting. And who knows? You can even practise delivering a persuasive speech by convincing your flatmates what to cook for dinner tonight.
Frequently asked questions
What is an example of persuasive speech .
A persuasive speech is any time you are having to choose a side of an argument and present it to another person. Persuasive speeches are used in many different areas of life. This could be in a school or university setting, in a job, or in a social setting.
What are some good persuasive speech topics for university?
When choosing a persuasive speech topic for university, always choose a topic or cause you’re interested in and passionate about. If you want to convince other people to agree with your stance, you must be seen to believe in it yourself.
How do you start a persuasive speech?
The best persuasive speeches always start with an impactful opening that grabs the audience’s attention. If you hope to persuade someone to agree with you, they need to listen to your whole argument. A strong opening ensures the audience is listening to you from the very start.
6 Tips for Writing a Persuasive Speech (On Any Topic)

B y far, the best way to learn how to write speeches is to read the great ones, from Pericles’ Funeral Oration, to Dr. King’s Mountaintop speech, to Faulkner’s Nobel acceptance address. But if you’re looking for some quick tips, here are a few things to bear in mind next time you’re asked to give a speech:
1. Write like you talk. There is no First Law of Speechwriting, but if there were, it would probably be something like this: a speech is meant to be spoken, not read. That simple (and obvious) fact has a few important (and less obvious) implications. Use short words. Write short sentences. Avoid awkward constructions that might cause a speaker to stumble. Tip: Read the speech aloud as you’re writing. If you do it enough, you’ll start hearing the words when you type them.
2. Tell a story . I once wrote speeches for a governor whose aide told me: speechwriting is about slinging soundbites together. That approach is a recipe for writing neither good speeches nor good soundbites. Whenever we sat down to discuss a speech for the first time, President Obama would ask us: What’s the story we’re trying to tell? Like any good story, a speech has its own narrative arc. For the President, it’s usually a slow warm-up, a substantive middle, and an inspirational end. That’s his style. Tell your story in whatever way feels natural. Tip: A good story can be a lot more powerful than the most compelling facts and statistics.
3. Structure matters . It’s usually harder to figure out the right structure for a speech – the order of the points to make – than the words themselves. The order of those points matters because an argument that’s clear and logical is more likely to be persuasive. There is a reason that some of America’s greatest speechwriters – from Lincoln to JFK’s speechwriter Ted Sorensen to President Obama himself – studied the law, a profession that values the ability to make a logical argument. Tip: Lists (like this one) are one way to impose a structure on a speech.
4. Be concise. It is said that Woodrow Wilson once gave the following reply to a speaking request: “If you’d like me to speak for five minutes, I’ll need a month to prepare. If you’d like me to speak for 20 minutes, I’ll need two weeks. But if you’d like me to speak for an hour, I’m ready right now.” As Wilson knew, it’s harder to be concise than verbose. But the best way to make a point is concisely, as Churchill did when he announced during a wartime address: “The news from France is very bad.” Next time you think you can’t afford to cut that paragraph you love, remember: the Gettysburg Address, perhaps the greatest speech in American history, is fewer than 300 words. Tip: Challenge yourself to cut as many words as possible from each sentence without losing the line’s meaning.
5. Be authentic. If you’ve ever given a speech, you’ve probably been told, “Just speak from the heart.” It’s not very helpful writing advice, but that doesn’t mean it’s wrong. Once, when we were writing President Obama’s 2008 Democratic Convention address, we got stuck on a certain section of the speech. The President advised us: Think about the moment we’re in, think about what the country is going through, and write something that feels true. It was a helpful reminder to stop focusing on polls and soundbites and simply say something we believed in as simply as we could. Tip: Sharing a personal story can help you find your voice and build a connection with the audience.
6. Don’t just speak – say something. When Michelangelo was tasked with painting the Sistine Chapel, he considered it a thankless job. He would have much rather spent his time sculpting than painting. But he used the occasion to paint perhaps the most revered fresco in history. So, the next time you’re asked to speak, don’t just write a speech, write a great one. A speech’s greatness has as much to do with its values as anything else. No one remembers the speeches of segregationists, though there were no doubt eloquent preachers spewing hate in the days of Jim Crow. No one remembers Hitler’s speeches, though few would dispute his oratorical prowess. Of course, Hitler, like the segregationists, lost. But it’s also because hope will always be more compelling than hate. It’s no accident that the best-known, best-loved speech in history – the Sermon on the Mount – is an articulation of humanity’s highest ideals. Tip: Before sitting down to write, get inspired by reading great speeches from collections like William Safire’s “Lend Me Your Ears.”
Adam Frankel is VP, External Affairs at Andela . Previously, he was Special Assistant and Senior Speechwriter to President Barack Obama.
More Must-Reads from TIME
- Melinda French Gates Is Going It Alone
- How to Buy Groceries Without Breaking the Bank
- Lai Ching-te Is Standing His Ground
- How to Cool Your Body Down Fast
- Forget Having It All . Let’s Try Having Enough
- 4 Signs Your Body Needs a Break
- The 15 Best Movies to Watch on a Plane
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Contact us at [email protected]
What are your chances of acceptance?
Calculate for all schools, your chance of acceptance.
Your chancing factors
Extracurriculars.
112 Persuasive Speech Topics That Are Actually Engaging
What’s covered:, how to pick an awesome persuasive speech topic, 112 engaging persuasive speech topics, tips for preparing your persuasive speech.
Writing a stellar persuasive speech requires a carefully crafted argument that will resonate with your audience to sway them to your side. This feat can be challenging to accomplish, but an engaging, thought-provoking speech topic is an excellent place to start.
When it comes time to select a topic for your persuasive speech, you may feel overwhelmed by all the options to choose from—or your brain may be drawing a completely blank slate. If you’re having trouble thinking of the perfect topic, don’t worry. We’re here to help!
In this post, we’re sharing how to choose the perfect persuasive speech topic and tips to prepare for your speech. Plus, you’ll find 112 persuasive speech topics that you can take directly from us or use as creative inspiration for your own ideas!
Choose Something You’re Passionate About
It’s much easier to write, research, and deliver a speech about a cause you care about. Even if it’s challenging to find a topic that completely sparks your interest, try to choose a topic that aligns with your passions.
However, keep in mind that not everyone has the same interests as you. Try to choose a general topic to grab the attention of the majority of your audience, but one that’s specific enough to keep them engaged.
For example, suppose you’re giving a persuasive speech about book censorship. In that case, it’s probably too niche to talk about why “To Kill a Mockingbird” shouldn’t be censored (even if it’s your favorite book), and it’s too broad to talk about media censorship in general.

Steer Clear of Cliches
Have you already heard a persuasive speech topic presented dozens of times? If so, it’s probably not an excellent choice for your speech—even if it’s an issue you’re incredibly passionate about.
Although polarizing topics like abortion and climate control are important to discuss, they aren’t great persuasive speech topics. Most people have already formed an opinion on these topics, which will either cause them to tune out or have a negative impression of your speech.
Instead, choose topics that are fresh, unique, and new. If your audience has never heard your idea presented before, they will be more open to your argument and engaged in your speech.
Have a Clear Side of Opposition
For a persuasive speech to be engaging, there must be a clear side of opposition. To help determine the arguability of your topic, ask yourself: “If I presented my viewpoint on this topic to a group of peers, would someone disagree with me?” If the answer is yes, then you’ve chosen a great topic!
Now that we’ve laid the groundwork for what it takes to choose a great persuasive speech topic, here are over one hundred options for you to choose from.
- Should high school athletes get tested for steroids?
- Should schools be required to have physical education courses?
- Should sports grades in school depend on things like athletic ability?
- What sport should be added to or removed from the Olympics?
- Should college athletes be able to make money off of their merchandise?
- Should sports teams be able to recruit young athletes without a college degree?
- Should we consider video gamers as professional athletes?
- Is cheerleading considered a sport?
- Should parents allow their kids to play contact sports?
- Should professional female athletes be paid the same as professional male athletes?
- Should college be free at the undergraduate level?
- Is the traditional college experience obsolete?
- Should you choose a major based on your interests or your potential salary?
- Should high school students have to meet a required number of service hours before graduating?
- Should teachers earn more or less based on how their students perform on standardized tests?
- Are private high schools more effective than public high schools?
- Should there be a minimum number of attendance days required to graduate?
- Are GPAs harmful or helpful?
- Should schools be required to teach about standardized testing?
- Should Greek Life be banned in the United States?
- Should schools offer science classes explicitly about mental health?
- Should students be able to bring their cell phones to school?
- Should all public restrooms be all-gender?
- Should undocumented immigrants have the same employment and education opportunities as citizens?
- Should everyone be paid a living wage regardless of their employment status?
- Should supremacist groups be able to hold public events?
- Should guns be allowed in public places?
- Should the national drinking age be lowered?
- Should prisoners be allowed to vote?
- Should the government raise or lower the retirement age?
- Should the government be able to control the population?
- Is the death penalty ethical?
Environment
- Should stores charge customers for plastic bags?
- Should breeding animals (dogs, cats, etc.) be illegal?
- Is it okay to have exotic animals as pets?
- Should people be fined for not recycling?
- Should compost bins become mandatory for restaurants?
- Should electric vehicles have their own transportation infrastructure?
- Would heavier fining policies reduce corporations’ emissions?
- Should hunting be encouraged or illegal?
- Should reusable diapers replace disposable diapers?
Science & Technology
- Is paper media more reliable than digital news sources?
- Should automated/self-driving cars be legalized?
- Should schools be required to provide laptops to all students?
- Should software companies be able to have pre-downloaded programs and applications on devices?
- Should drones be allowed in military warfare?
- Should scientists invest more or less money into cancer research?
- Should cloning be illegal?
- Should societies colonize other planets?
- Should there be legal oversight over the development of technology?
Social Media
- Should there be an age limit on social media?
- Should cyberbullying have the same repercussions as in-person bullying?
- Are online relationships as valuable as in-person relationships?
- Does “cancel culture” have a positive or negative impact on societies?
- Are social media platforms reliable information or news sources?
- Should social media be censored?
- Does social media create an unrealistic standard of beauty?
- Is regular social media usage damaging to real-life interactions?
- Is social media distorting democracy?
- How many branches of government should there be?
- Who is the best/worst president of all time?
- How long should judges serve in the U.S. Supreme Court?
- Should a more significant portion of the U.S. budget be contributed towards education?
- Should the government invest in rapid transcontinental transportation infrastructure?
- Should airport screening be more or less stringent?
- Should the electoral college be dismantled?
- Should the U.S. have open borders?
- Should the government spend more or less money on space exploration?
- Should students sing Christmas carols, say the pledge of allegiance, or perform other tangentially religious activities?
- Should nuns and priests become genderless roles?
- Should schools and other public buildings have prayer rooms?
- Should animal sacrifice be legal if it occurs in a religious context?
- Should countries be allowed to impose a national religion on their citizens?
- Should the church be separated from the state?
- Does freedom of religion positively or negatively affect societies?
Parenting & Family
- Is it better to have children at a younger or older age?
- Is it better for children to go to daycare or stay home with their parents?
- Does birth order affect personality?
- Should parents or the school system teach their kids about sex?
- Are family traditions important?
- Should parents smoke or drink around young children?
- Should “spanking” children be illegal?
- Should parents use swear words in front of their children?
- Should parents allow their children to play violent video games?
Entertainment
- Should all actors be paid the same regardless of gender or ethnicity?
- Should all award shows be based on popular vote?
- Who should be responsible for paying taxes on prize money, the game show staff or the contestants?
- Should movies and television shows have ethnicity and gender quotas?
- Should newspapers and magazines move to a completely online format?
- Should streaming services like Netflix and Hulu be free for students?
- Is the movie rating system still effective?
- Should celebrities have more privacy rights?
Arts & Humanities
- Are libraries becoming obsolete?
- Should all schools have mandatory art or music courses in their curriculum?
- Should offensive language be censored from classic literary works?
- Is it ethical for museums to keep indigenous artifacts?
- Should digital designs be considered an art form?
- Should abstract art be considered an art form?
- Is music therapy effective?
- Should tattoos be regarded as “professional dress” for work?
- Should schools place greater emphasis on the arts programs?
- Should euthanasia be allowed in hospitals and other clinical settings?
- Should the government support and implement universal healthcare?
- Would obesity rates lower if the government intervened to make healthy foods more affordable?
- Should teenagers be given access to birth control pills without parental consent?
- Should food allergies be considered a disease?
- Should health insurance cover homeopathic medicine?
- Is using painkillers healthy?
- Should genetically modified foods be banned?
- Should there be a tax on unhealthy foods?
- Should tobacco products be banned from the country?
- Should the birth control pill be free for everyone?
If you need more help brainstorming topics, especially those that are personalized to your interests, you can use CollegeVine’s free AI tutor, Ivy . Ivy can help you come up with original persuasive speech ideas, and she can also help with the rest of your homework, from math to languages.
Do Your Research
A great persuasive speech is supported with plenty of well-researched facts and evidence. So before you begin the writing process, research both sides of the topic you’re presenting in-depth to gain a well-rounded perspective of the topic.
Understand Your Audience
It’s critical to understand your audience to deliver a great persuasive speech. After all, you are trying to convince them that your viewpoint is correct. Before writing your speech, consider the facts and information that your audience may already know, and think about the beliefs and concerns they may have about your topic. Then, address these concerns in your speech, and be mindful to include fresh, new information.
Have Someone Read Your Speech
Once you have finished writing your speech, have someone read it to check for areas of strength and improvement. You can use CollegeVine’s free essay review tool to get feedback on your speech from a peer!
Practice Makes Perfect
After completing your final draft, the key to success is to practice. Present your speech out loud in front of a mirror, your family, friends, and basically, anyone who will listen. Not only will the feedback of others help you to make your speech better, but you’ll become more confident in your presentation skills and may even be able to commit your speech to memory.
Hopefully, these ideas have inspired you to write a powerful, unique persuasive speech. With the perfect topic, plenty of practice, and a boost of self-confidence, we know you’ll impress your audience with a remarkable speech!
Related CollegeVine Blog Posts


27 Persuasive Speech Topics to Captivate Your Audience
- The Speaker Lab
- June 13, 2024
Table of Contents
If you’ve ever written a persuasive speech, chances are you’ve struggled to choose a persuasive speech topic . It makes sense, right? You want to speak on something relevant yet unique, timely but timeless. Sometimes it feels like every good idea is already taken or too controversial. Or maybe the topic you’re considering seems too bland and won’t stir the pot enough. CEOs, entrepreneurs, authors—everyone with something important to say faces this challenge.
Well, fear not. We’ve got some fresh ideas for persuasive speech topics coming right up. These aren’t your high school debate prompts; they’re designed for individuals ready to make waves across industries and impact audiences. So if you’re on a mission to reshape perceptions and create genuine transformation, stick around.
Understanding the Power of Persuasion
Before we dive into these topics, let’s get one thing straight: understanding persuasion in speech is like having a superpower. But what makes some speeches stick with us forever? Persuasive speaking works its charm by tapping into our emotions and reasoning. It’s that perfect blend of ethos, pathos, and logos that the Greek philosopher Aristotle talked about centuries ago.
- Ethos: This is all about credibility. If the audience trusts the speaker (you), they’re more likely to be on board with your message.
- Pathos: Here’s where emotions come into play. The right emotional appeal can make an audience start to see things your way.
- Logos: Logic seals the deal. A well-reasoned argument backed by solid facts? Hard to argue against that.
This trio works together to create a kind of spellbinding effect that doesn’t just persuade, but also sticks with your audience long after the talk has ended. With these three rhetorical appeals in hand, you can do more than convince; you can transform thinking and ignite action because your persuasive speech topic resonates on a deeply personal level for each listener.
Find Out Exactly How Much You Could Make As a Paid Speaker
Use The Official Speaker Fee Calculator to tell you what you should charge for your first (or next) speaking gig — virtual or in-person!
Choosing Persuasive Speech Topics That Resonate With Your Audience
Tailoring your topic to your audience isn’t just important; it’s everything when it comes to persuasion. After all, if you don’t know who you’re talking to, how will you grab their attention? Imagine chatting about quantum physics with a room full of poets or discussing poetry at a tech conference. See the mismatch? Choosing the right persuasive speech topic means finding one that resonates deeply with your listeners’ lives and experiences.
To analyze your audience effectively, you’re going to want to do a little digging ahead of time.
- Dig into Demographics: Age, occupation, education level—these aren’t just numbers and titles; they’re clues into what might spark interest.
- Catch the Cultural Cues: What cultural backgrounds are present in your audience? Understanding their cultural fabric can influence what makes them laugh, what they hold sacred, and even the subjects that might be touchy.
- Tune into their Concerns: What keeps them up at night? Whether it’s climate change or personal finance, aligning your speech here can keep your audience engaged.
In essence, knowing your audience means respecting them enough to make sure they walk away feeling heard and understood rather than preached at or overlooked. And guess what? When folks feel respected and valued, they listen more closely.
Exploring Persuasive Speech Topics
Whether you’re a seasoned speaker or just starting out on your public speaking journey, choosing persuasive speech topics that resonate with audiences can feel difficult. However, knowing who’s sitting in your audience can make that decision a lot easier. Analyzing your audience ensures that your message hits home and sparks interest and debate. Consider some of the categories below as you brainstorm your speech topic.
- Current Events and Social Issues: Hot off the press. These topics are fresh, relevant, and have everyone talking already. You’re halfway there.
- Ethical Dilemmas and Moral Questions: Moral dilemmas offer rich soil for persuasion because they invite listeners to explore their values.
- Technology and Innovation: Tech shapes our future every day. Discuss its impacts or ethical considerations for endless engagement.
- Health and Wellness: This area touches everyone’s life at some point. From diet fads to healthcare policies—if it affects well-being, people want to hear about it.
- Educational Reform and Policy Changes: Schools shape societies’ futures; thus discussions around education reforms carry weight for many listeners looking toward tomorrow’s promise.
Your chosen topic doesn’t need to be grandiose or controversial. Sometimes simplicity speaks volumes more than we give it credit for. When crafting your persuasive speech, the goal is simply to choose a topic that both informs and transforms perspectives.
Current Events and Social Issues
Diving into the realm of current events and societal debates has the power to transform a decent speech into one that lingers in memory. Why? By engaging with present-day events and societal dilemmas, we are moved, provoked, and occasionally our perspectives on life are profoundly altered.
So, let’s dive right in. Here are some persuasive speech topics that are not just timely but packed with potential to spark debate, drive change, or at least get people thinking.
- Climate Change: It’s been talked about for years, but with wildfires raging and ice caps melting it’s a more critical topic than ever. How can we not only stop but reverse the damage?
- Social Justice Movements: From Black Lives Matter to Stop Asian Hate, these movements have stirred conversations worldwide. In what ways are governments expected to step up and guarantee fairness among their citizens? How can each person pitch in meaningfully to support these vital movements?
- The Tech Takeover: Technology is shaping our future, but at what cost? Let’s talk digital privacy rights or AI ethics.
- Mental Health Awareness: With a global pandemic throwing life as we know it out of balance, mental health has taken center stage. How do we build societies that support mental wellness?
Right now, we’re smack in the middle of events that will fill history books for generations to come. Each of these topics isn’t just relevant; they’re urgent. But remember this: while diving deep into any of them could make for powerful persuasive speeches, always aim for empathy over controversy.
Ethical Dilemmas and Moral Questions
We live in an era teeming with issues ripe for debate—climate change action versus economic growth challenges; genetic engineering marvels against ethical quandaries; digital age freedoms wrestling with security needs—the list goes on. Persuasive essay topics that deal with ethical dilemmas and moral questions can be great ways to challenge your audience—and even yourself. Take a look:
- Government Surveillance: Is it a necessary protection or an invasion of privacy?
- Vaccine Mandates: Is it a public health safety net or a personal freedom infringement?
- Data Privacy vs. Technological Advancement: Where do we draw the line?
- Artificial Intelligence: Should machines have rights like humans do?
Good persuasive speeches do more than wade through facts. They spark engaging dialogues, challenge people’s beliefs, and maybe even alter their viewpoints. Exploring persuasive speech topics about ethics and morality forces us to dig deeper and frequently nudges us beyond the boundaries of our comfort zones. But here’s the kicker: they also make your speech unforgettable.
Technology and Innovation
Technology’s relentless pace has us all on our toes, wondering what’s next. As a result, it gives us plenty of persuasive speech topics to consider.
- AI Ethics: Artifical intelligence can be a force for good, but it can also have negative outcomes, like the loss of jobs. Should it be regulated? If so, how?
- Data Privacy: What responsibility do corporations have to consumers when it comes to data privacy? This would be a great topic to explore data and privacy rights.
- Gene Editing: Thanks to technology like CRISPR, it’s now possible to edit genetic code. But is it ethical to edit the genes of humans, either born or unborn? How far is too far?
- Elon’s Mars Mission: Is exploring other planets our human duty or a waste of resources?
With technology moving faster than legislation can keep up, posing these questions is vital. Without scrutiny, technology can quickly become a dangerous tool, so it’s important to spend time exploring its implications. Whether you’re prepping for your next persuasive speech or simply want to stay informed, digging into these topics is a great way to keep your audience engaged and informed.
Health and Wellness
When it comes to persuasive speech topics, health-related issues pack a punch like no other because, well, who isn’t interested in living their best life? In addition, it’s a topic that everyone can easily relate to because our well-being is something that we all think about. As far the specific issue you choose, you’ll want to look back on the research you did on your audience. Are they fitness buffs looking for the next challenge or parents concerned about family nutrition? Tailor your topic accordingly.
- Effects of the Pandemic: Dive into how global pandemics reshape public health policies.
- Mental Health: In what capacity is mental health affected by technology? Is social media a concern? If so, what steps should parents take to protect themselves and their children in an increasingly digital world?
- Artificial Intelligence: Chat about wearable tech transforming personal wellness or AI’s role in advancing healthcare solutions.
- Educational Reform & Policy Changes: Debate the necessity of nutritional education in schools or argue for more accessible healthcare services.
Health is a great topic for persuasive speeches because if there’s one thing we can all agree on, it’s wanting good health—not just for us but generations to come.
Free Download: 6 Proven Steps to Book More Paid Speaking Gigs in 2024
Download our 18-page guide and start booking more paid speaking gigs today!
Education Reform and Policy Changes
Schooling serves as the cornerstone for nurturing groundbreaking advancements, fostering fairness, and upholding democratic values. However, these days, many are calling for education reform . These voices challenge us to question norms, imagine new possibilities, and rally for collective action. Of course, not everyone sees eye-to-eye on what needs changing in our schools or how to do it. So before you pick one of the topics below, again, make sure you understand who you’re talking to. That’s step one towards making an impact.
- Standardized Testing: How necessary is it and who really benefits from it?
- Educational Funding: What is causing funding inequities between rich and poor districts? How might this be addressed? What solutions have been tried and have they worked?
- School Curriculum: How should schools implement inclusive curriculums reflecting diverse histories and experiences?
Before change can occur, questions must be asked. By posing questions about the state of education in the U.S., you can challenge what people really know about the system in place. And who knows? You just might surprise yourself by what you find.
Exploring persuasive speech topics is the first step towards delivering a memorable speech. When you understand the power behind every word and meet your audience’s expectations, you can craft messages that resonate.
Potential topics range from current events to technology and innovation. Even ethical dilemmas can turn into a great persuasive speech when handled carefully. Similarly, speaking on health and wellness turns personal goals into universal concerns that are sure to grip your audience. Last but not least, educational reform provides plenty of room for conversation, as it’s sure to affect generations to come.
These aren’t just topics, though. When you stand before an audience next time around, remember: you’re not just delivering a speech—you’re igniting change one word at a time.
- Last Updated: June 12, 2024

Explore Related Resources
Learn How You Could Get Your First (Or Next) Paid Speaking Gig In 90 Days or Less
We receive thousands of applications every day, but we only work with the top 5% of speakers .
Book a call with our team to get started — you’ll learn why the vast majority of our students get a paid speaking gig within 90 days of finishing our program .
If you’re ready to control your schedule, grow your income, and make an impact in the world – it’s time to take the first step. Book a FREE consulting call and let’s get you Booked and Paid to Speak ® .
About The Speaker Lab
We teach speakers how to consistently get booked and paid to speak. Since 2015, we’ve helped thousands of speakers find clarity, confidence, and a clear path to make an impact.
Get Started
Let's connect.
Copyright ©2023 The Speaker Lab. All rights reserved.
Module 10: Persuasive Speaking
Structure of a persuasive speech, learning objectives.
Identify characteristic structures of a persuasive speech.
In many ways, a persuasive speech is structured like an informative speech. It has an introduction with an attention-getter and a clear thesis statement. It also has a body where the speaker presents their main points and it ends with a conclusion that sums up the main point of the speech.
The biggest difference is that the primary purpose of an informative speech is to explain whereas the primary purpose of a persuasive speech is to advocate the audience adopt a point of view or take a course of action. A persuasive speech, in other words, is an argument supported by well-thought-out reasons and relevant, appropriate, and credible supporting evidence.
We can classify persuasive speeches into three broad categories:
- The widely used pesticide Atrazine is extremely harmful to amphibians.
- All house-cats should be kept indoors to protect the songbird population.
- Offshore tax havens, while legal, are immoral and unpatriotic .
The organizational pattern we select and the type of supporting material we use should support the overall argument we are making.
The informative speech organizational patterns we covered earlier can work for a persuasive speech as well. In addition, the following organization patterns are especially suited to persuasive speeches (these are covered in more detail in Module 6: Organizing and Outlining Your Speech):
- Causal : Also known as cause-effect, the causal pattern describes some cause and then identifies what effects resulted from the cause. This can be a useful pattern to use when you are speaking about the positive or negative consequences of taking a particular action.
- Problem-solution : With this organizational pattern, you provide two main points. The first main point focuses on a problem that exists and the second details your proposed solution to the problem. This is an especially good organization pattern for speeches arguing for policy changes.
- Problem-cause-solution: This is a variation of the problem-solution organizational pattern. A three-step organizational pattern where the speaker starts by explaining the problem, then explains the causes of the problem, and lastly proposes a solution to the problem.
- Comparative advantage : A speaker compares two or more things or ideas and explains why one of the things or ideas has more advantages or is better than the other.
- Monroe’s motivated sequence : An organizational pattern that is a more elaborate variation of the problem-cause-solution pattern. We’ll go into more depth on Monroe’s motivated sequence on the next page.
- Structure of a Persuasive Speech. Authored by : Mike Randolph with Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution

50 Speech Closing Lines (& How to Create Your Own) | The Ultimate Guide
Hrideep barot.
- Public Speaking , Speech Writing

While speech openings are definitely one of the most important components of a speech, something that is equally as important is the way you conclude your speech.
There are few worse ways to end your speech than with a terse ‘thank you’–no elaboration or addition whatsoever.
Speech endings are just as crucial to the success of your speech as speech openings, and you must spend just as much time picking the perfect ending as you do to determine your best possible speech opening.
The words you speak at the beginning and end of your speech are words that your audience will pay the most attention to, and remember longer than any other part of your speech.
Speech endings can put even the most experienced speaker in flux, and increase their anxiousness manifold as they sit there attempting to figure out the perfect way to end your speech.
If you’re someone who’s in flux about your speech ending too, don’t worry. We’ve got some amazing ways to conclude your speech with a bang!
1. Circling Back To The Beginning
The idea behind circling back to the beginning of your speech is to reinforce the idea of your speech being a complete whole. By circling back to the beginning and connecting it to your ending, you let the audience understand that the idea of your speech is complete & standalone.
Circling back to the beginning of your speech also acts as an excellent way of reinforcing the central idea of your speech in the audience’s mind, and makes it more likely that they will remember it after the speech ends.
Need more inspiration for speech opening lines? Check out our article on 15 Powerful Speech Opening Lines & Tips To Create Your Own.
How To Circle Back To The Beginning
The easiest way to do this is to set up your beginning for the conclusion of your speech. That is, if you’re saying something like, say, a story or joke in the beginning, then you can leave your audience in a cliffhanger until the ending arrives.
Another great way to circle back to the beginning is by simply restating something you said at the start. The added knowledge from attending the rest of your speech will help the audience see this piece of information in a new–and better–light.
1. Will Stephen
Ending Line: “I’d like you to think about what you heard in the beginning, and I want you to think about what you hear now. Because it was nothing & it’s still nothing.”
2. Canwen Xu
Speech Ending: My name is Canwen, my favorite color is purple and I play the piano but not so much the violin…
Think of a memorable moment from your life, and chances are you’ll realize that it involved a feeling of happiness–something that we can associate with smiling or laughter. And what better way to generate laughter than by incorporating the age-old strategy of good humor.
The happy and lighthearted feeling you associate with good memories is the kind of emotional reaction you want to create in your audience too. That’s what will make your speech stick in their memory.
Done incorrectly, humor can be a disaster. Done right, however, it can entirely transform a speech.
Humor doesn’t only mean slapstick comedy (although there’s nothing wrong with slapstick, either). Humor can come in many forms, including puns, jokes, a funny story…the list is endless.
How To Incorporate Humor In Your Speech Ending
The simplest way to incorporate humor into your speech ending is by telling a plain old joke–something that’s relevant to your topic, of course.
You can also tell them a short, funny anecdote–may be an unexpected conclusion to a story you set up in the beginning.
Another way would be by employing the power of repetition. You can do this by associating something funny with a word, and then repeating the word throughout your speech. During the end, simply say the word or phrase one last time, and it’s likely you’ll leave off your audience with a good chuckle.
1. Woody Roseland
Ending Line: “Why are balloons so expensive? Inflation.”
2. Andras Arato
Ending Line: “There are three rules to becoming famous. Unfortunately, nobody knows what they are.”
3. Hasan Minhaj
Ending Line: “And you want to know the scariest part? Pretty soon every country on the earth is going to have its own TLC show.”
4. Sophie Scott
Speech Ending: In other words, when it comes to laughter, you and me baby, ain’t nothing but mammals.
5. Tim Urban
Speech Ending: We need to stay away from the Instant Gratification Monkey. That’s a job for all of us. And because there’s not that many boxes on there. It’s a job that should probably start today. Well, maybe not today, but, you know, sometime soon.
6. Hasan Minhaj
Speech Ending: Showing my legs on TV is probably the scariest thing I’ve ever done. And keep in mind last week I went after the Prince of Saudi Arabia.
3. Question
The idea behind posing a question at the end of your speech is to get the wheels in your audience’s minds turning and to get them thinking of your speech long after it has ended. A question, if posed correctly, will make your audience re-think about crucial aspects of your speech, and is a great way to prompt discussion after your speech has ended.
How To Add Questions To Your Speech Ending
The best type of questions to add to your speech ending is rhetorical questions. That’s because, unlike a literal question, a rhetorical question will get the audience thinking and make them delve deeper into the topic at hand.
Make sure your question is central to the idea of your speech, and not something frivolous or extra. After all, the point of a question is to reinforce the central idea of your topic.
1. Lexie Alford
Speech Ending: Ask yourself: How uncomfortable are you willing to become in order to reach your fullest potential?
2. Apollo Robbins
Speech Ending: If you could control somebody’s attention, what would you do with it?
Quotes are concise, catchy phrases or sentences that are generally easy to remember and repeat.
Quotes are an age-old way to start–and conclude–a speech. And for good reason.
Quotes can reinforce your own ideas by providing a second voice to back them up. They can also provoke an audience’s mind & get them thinking. So, if you add your quote to the end of your speech, the audience will most likely be thinking about it for long after you have finished speaking.
How To Use Quotes In Your Speech Ending
While adding quotes to your speech ending, make sure that it’s relevant to your topic. Preferably, you want to pick a quote that summarizes your entire idea in a concise & memorable manner.
Make sure that your quote isn’t too long or complicated. Your audience should be able to repeat it as well as feel its impact themselves. They shouldn’t be puzzling over the semantics of your quote, but its intended meaning.
1. Edouard Jacqmin
Speech Ending: “Life is either a daring adventure or nothing at all.”
2. Chris Crowe
Speech Ending: “It’s more certain than death and taxes.”
3. Olivia Remes
Speech Ending: I’d like to leave you with a quote by Martin Luther King: “You don’ have to see the whole staircase. Just take the first step.”
4. Tomislav Perko
Speech Ending: Like that famous quote says, “In twenty years from now on, you’ll be more disappointed by the things you didn’t do than by the things you did do.
5. Diana Nyad
Speech Ending: To paraphrase the poet, Mary Oliver, she says, “So, what is it? What is it you’re doing with this one wild and precious life of yours?”
5. Piece Of Advice
The point of giving a piece of advice at the end of your speech is not to pull your audience down or to make them feel bad/inferior about themselves. Rather, the advice is added to motivate your audience to take steps to do something–something related to the topic at hand.
The key point to remember is that your advice is included to help your audience, not to discourage them.
How To Add Piece Of Advice To Your Speech Ending
To truly make your audience follow the advice you’re sharing, you must make sure it resonates with them. To do so, you need to inject emotions into your advice, and to present it in such a manner that your audience’s emotions are aroused when they hear it.
Your advice shouldn’t be something extra-complicated or seemingly impossible to achieve. This will act as a counter-agent. Remember that you want your audience to follow your advice, not to chuck it away as something impossible.
Our article, 15 Powerful Speech Ending Lines And Tips To Create Your Own , is another great repository for some inspiration.
1. Ricardo Lieuw On
Speech Ending: “Learn something new, or a new way of approaching something old because there are a few skills are valuable as the art of learning.”
2. Tomas Chamorro-Premuzic
Speech Ending: “If we want to improve the competence level of our leaders, then we should first improve our own competence for judging and selecting leaders.”
3. Sharique Samsudheen
Speech Ending: “Some people love money, some people hate money, some people crave money, some people even kill for money. But what they miss is they just need to learn how to manage money well, and that will give them financial freedom.”
4. Kate Simonds
Speech Ending: Teens, you need to believe in your voices and adults, you need to listen.
5. Melissa Butler
Speech Ending: When you go home today, see yourself in the mirror, see all of you, look at all your greatness that you embody, accept it, love it and finally, when you leave the house tomorrow, try to extend that same love and acceptance to someone who doesn’t look like you.
6. Iskra Lawrence
Speech Ending: Speak to your body in a loving way. It’s the only one you got, it’s your home, and it deserves your respect. If you see anyone tearing themselves down, build them back up And watch your life positively grow when you give up the pursuit of perfection.
6. Contemplative Remark
As the name itself suggests, contemplative remarks are intended to make your audience contemplate or mull over something. The ‘something’ in question should be the idea central to your speech, or a key takeaway that you want them to return home with.
The idea is to get your audience thinking and to keep them thinking for a long, long time.
How To Add A Contemplative Remark To Your Speech Ending
To add a contemplative remark to your speech ending, you first need to figure out your key takeaway or main theme. Then, you want to arrange that as a question, and propose it to your audience at the end of your speech.
Remember that your question shouldn’t be something too wordy or complicated to understand. As with the quotes, you don’t want your audience stuck on the semantics. Rather, you want them to focus on the matter at hand.
1. Lisa Penney
Speech Ending: “So I invite you to pay more attention to your thoughts & consider the legacy you leave behind.”
2. Grant Sanderson
Speech Ending: “Some of the most useful math that you can find or teach has its origin in someone who was just looking for a good story.”
3. Greta Thunberg
Speech Ending: “We will not let you get away with this. Right here, right now is where we draw the line. The world is waking up & change is coming whether you like it or not.”
4. Bill Eckstrom
Speech Ending: Now, think about this: it’s not the complexity-triggering individuals or events you should fear the most, but it’s your own willingness to accept or seek discomfort that will dictate the growth of not just you, but our entire world.
5. Robert Hoge
Speech Ending: Choose to accept your face, choose to appreciate your face, don’t look away from the mirror so quickly; understand all the love, and the life, and the pain that is the part of your face, that is the art of your face. Tomorrow when you wake up, what will your choice be?
7. Personal Anecdote
Personal anecdotes, as the name suggests, are anecdotes that are personal to the speaker or instances from their life. Personal anecdotes are a great way to incorporate the magical powers of storytelling in your speech, as well as to make a personal connection with the audience. Using personal anecdotes, you can hit two birds with one stone!
How To Add Personal Anecdotes To Your Speech Ending
To add personal anecdotes to your speech ending, you need to filter through your life experiences to find out ones that directly relate to your topic at hand. You don’t want to include an anecdote, no matter how compelling it is, if it doesn’t relate to your topic.
Remember to not keep your anecdote too long. Your audience will most likely lose their attention if you do so.
1. Sheila Humphries
Speech Ending: “Why do you go work for these people?” My answer to them was, “If I could help one child make it in this world, it’ll be worth it all.”
8. Call To Action
A call-to-action is one of the absolute best ways to conclude a speech with a bang. A well-written speech should aim to alter the audience’s mind or belief system in some way and to make them take an action in that direction. One crucial way to assure your audience does this is by using a call to action.
How To Add A Call To Action To Your Speech Ending
A call to action comes right before the ending of your speech to provide your audience with a clear idea or set of instructions about what they’re supposed to do after your talk ends.
A call to action should provide a roadmap to the audience for their future steps, and to outline clearly what those future steps are going to be.
1. Armin Hamrah
Speech Ending: “So tonight, after you finish your Math homework & before you lay your head down on that fluffy pillow, bring a piece of paper and pen by your bedside…”
2. Graham Shaw
Speech Ending: “So I invite you to get your drawings out there & spread the word that when we draw, we remember more!”
3. Andy Puddicombe
Speech Ending: You don’t have to burn any incense, and you definitely don’t have to sit on the floor. All you need to do is to take out 10 minutes out a day to step back, familiarize yourself with the present moment so that you get to experience a greater sense of focus, calm, and clarity in your life.
4. Amy Cuddy
Speech Ending: Before you go into the next stressful evaluative situation, for two minutes, try doing this in the elevator…
5. Jia Jiang
Speech Ending: When you are facing the next obstacle or the next failure, consider the possibilities. Don’t run! If you just embrace them, they might become your gifts as well.
9. Motivational Remark
As the name clearly explains, a motivational remark motivates your audience to carry out a plan of action. It ruffles the audience’s mind and emotions and has a powerful impact on the steps that your audience will take after you’ve finished speaking.
How To Add A Motivational Remark To Your Speech Ending
The key to a good motivational remark is to inspire your audience. Your motivational remark should act as a ray of hope to your audience and positively inspire them to take a desired course of action.
Your motivational remark should not be negative in any way. You don’t want to guilt or coerce your audience into doing something or feeling a certain way. You want to leave them on a positive note to move forward with their life.
1. Khanh Vy Tran
Speech Ending: “No matter what you’re going through right now & no matter what the future holds for you, please don’t change yourself. Love yourself, accept yourself & then transform yourself.”
2. Mithila Palkar
Speech Ending: “Get a job, leave a job, dance, sing, fall in love. Carve your own niche. But most importantly: learn to love your own randomness.”
3. Andrew Tarvin
Speech Ending: “Anyone can learn to be funnier. And it all starts with a choice. A choice to try to find ways to use humor. A choice to be like my grandmother, to look at the world around you and say WTF–wow, that’s fun.”
4. Laura Vanderkam
Speech Ending: There is time. Even if we are busy, we have time for what matters. And when we focus on what matters, we can build the lives we want in the time we’ve got.
5. Julian Treasure
Speech Ending: Let’s get listening taught in schools, and transform the world in one generation into a conscious listening world, a world of connection, a world of understanding, and a world of peace.
6. Mariana Atencio
Speech Ending: Let’s celebrate those imperfections that make us special. I hope that it teaches you that nobody has a claim on the word ‘normal’. We are all different. We are all quirky and unique and that is what makes us wonderfully human.
10. Challenge
Much like a call to action, the aim of proposing a challenge at the end of your speech is to instigate your audience to take some desired course of action. A challenge should make an appeal to your audience’s emotion, and motivate them to meet it.
How To Add A Challenge To Your Speech Ending
To apply a challenge effectively to your speech ending, you need to make sure that it’s something relevant to your topic. Your challenge should drive the central topic of your speech forward, and make your audience engage in real-life steps to apply your idea in the real world.
While its always a good idea to set a high bar for your challenge, make sure its an achievable one too.
1. Jamak Golshani
Speech Ending: “I challenge you to open your heart to new possibilities, choose a career path that excites you & one that’s aligned to who you truly are.”
2. Ashley Clift-Jennings
Speech Ending: So, my challenge to you today is, “Do you know, would you even know how to recognize your soulmate?” If you are going out in the world right now, would you know what you are looking for?
11. Metaphor
Metaphors are commonly used as a short phrase that draws a comparison between two ideas in a non-literal sense. People use metaphors quite commonly in daily life to explain ideas that might be too difficult or confusing to understand otherwise. Metaphors are also great tools to be used in speech, as they can present your main idea in a simple and memorable way.
How To Add Metaphors To Your Speech Ending
To add a metaphor to your speech ending, you need to first decide on the main idea or takeaway of your speech. Your metaphor should then be organized in such a way that it simplifies your main idea and makes it easier for your audience to understand & remember it.
The key is to not make your metaphor overly complicated or difficult to retain and share. Remember that you’re trying to simplify your idea for the audience–not make them even more confused.
1. Ramona J. Smith
Speech Ending: “Stay in that ring. And even after you take a few hits, use what you learned from those previous fights, and at the end of the round, you’ll still remain standing.”
2. Shi Heng YI
Speech Ending: “If any of you chooses to climb that path to clarity, I will be very happy to meet you at the peak.”
3. Zifang “Sherrie” Su
Speech Ending: “Are you turning your back on your fear? Our life is like this stage, but what scares are now may bring you the most beautiful thing. Give it a chance.”
12. Storytelling
The idea behind using stories to end your speech is to leave your audience with a good memory to take away with them.
Stories are catchy, resonating & memorable ways to end any speech.
Human beings can easily relate to stories. This is because most people have grown up listening to stories of some kind or another, and thus a good story tends to evoke fond feelings in us.
How To Incorporate Stories In Your Speech Ending
A great way to incorporate stories in your speech ending is by setting up a story in the beginning and then concluding it during the end of your speech.
Another great way would be to tell a short & funny anecdote related to a personal experience or simply something related to the topic at hand.
However, remember that it’s the ending of your speech. Your audience is most likely at the end of their attention span. So, keep your story short & sweet.
1. Sameer Al Jaberi
Speech Ending: “I can still see that day when I came back from my honeymoon…”
2. Josephine Lee
Speech Ending: “At the end of dinner, Jenna turned to me and said…”
Facts are another excellent speech ending, and they are used quite often as openings as well. The point of adding a fact as your speech ending is to add shock value to your speech, and to get your audience thinking & discussing the fact even after your speech has ended.
How To Add Facts To Your Speech Ending
The key to adding facts to your speech ending is to pick a fact that thrusts forward your main idea in the most concise form possible. Your fact should also be something that adds shock value to the speech, and it should ideally be something that the audience hasn’t heard before.
Make sure that your fact is relevant to the topic at hand. No matter how interesting, a fact that doesn’t relate to your topic is going to be redundant.
1. David JP Phillips
Speech Ending: 3500 years ago, we started transfering knowledge from generation to generation through text. 28 years ago, PowerPoint was born. Which one do you think our brain is mostly adapted to?
14. Rhethoric Remark
Rhetoric remarks are another excellent way to get the wheels of your audience’s minds turning. Rhetoric remarks make your audience think of an imagined scenario, and to delve deeper into your topic. Rhetoric remarks or questioned don’t necessarily need to have a ‘right’ or one-shot answer, which means you can be as creative with them as possible!
How To Add Rhethoric Remarks To Your Speech Ending
Since rhetorical questions don’t need to have a definite answer, you have much freedom in determining the type of question or statement you wish to make. However, as with all other speech endings, a rhetorical question shouldn’t be asked just for the sake of it.
A rhetorical question should make your audience think about your topic in a new or more creative manner. It should get them thinking about the topic and maybe see it from an angle that they hadn’t before.
Rhetorical questions shouldn’t be too confusing. Use simple language & make sure it’s something that the audience can easily comprehend.
1. Mona Patel
Speech Ending: Pick your problem, ask “What if?” Come up with ideas. Bring them down. Then execute on them. Maybe you’re thinking, “What if we can’t?” I say to you, “What if we don’t?”
2. Lizzie Velasquez
Speech Ending: I want you to leave here and ask yourself what defines you. But remember: Brave starts here.
Another great way to end your speech with a literal bang is by using music! After all, if there’s something that can impact the human mind with just as much force as a few well-placed words, it’s the correct music.
How To Add Music To Your Speech Ending
To add music to your speech ending, you must make sure that the music has something to do with your speech theme. Remember that you’re not playing music in your concert. The piece of music that you choose must be relevant to your topic & work to have a contribution in your overall speech.
1. Tom Thum
Speech Ending: *ends the TED Talk with beat boxing*
16. Reitirate The Title
The title of your speech is its most important component. That’s why you need to pay careful attention to how you pick it, as it is something that your viewers will most likely remember the longest about your speech.
Your title will also act as a guiding hand towards how your audience forms an initial idea about your speech and is what they will associate your entire speech with.
By repeating your title at the end of your speech, you increase the chances that your audience will remember it–and your speech–for a long time.
How To Retierate The Title In Your Speech Ending
Your title is something that your audience associates your entire speech with. However, you don’t want to simply add the title in your speech end for the sake of adding it. Instead, make it flow naturally into your speech ending. This will make it seem less forced, and will also increase the chances of your audience remembering your entire speech ending and not just the title of your speech.
1. Ruairi Robertson
Speech Ending: I feel we can all contribute to this fight worth fighting for our own health, but more importantly, our future generations’ health by restoring the relationship between microbe and man. There is SOME FOOD FOR THOUGHT!
Need more inspiration for speech closing lines? Check out our article on 10 Of The Best Things To Say In Closing Remarks.
Level up your public speaking in 15 minutes!
Get the exclusive Masterclass video delivered to your inbox to see immediate speaking results.
You have successfully joined our subscriber list.
To sum up, speech endings are just as imperative to the success of your speech as speech openings, and you must spend just as much time picking the perfect ending as you do to determine your best possible speech opening. The words you speak at the beginning and end of your speech are words that your audience will pay the most attention to, and remember longer than any other part of your speech.
Still looking for inspiration? Check out this video we made on closing remarks:
Enroll in our transformative 1:1 Coaching Program
Schedule a call with our expert communication coach to know if this program would be the right fit for you

Crisis Leadership 101: Cultivating Empathy While Exercising Authority

Lost Voice? Here’s How to Recover Sore Throat and Speak Again

7 Keys to Emcee Like a Pro: Unlock Your Hosting Potential

- [email protected]
- +91 98203 57888
Get our latest tips and tricks in your inbox always
Copyright © 2023 Frantically Speaking All rights reserved

What Is Public Speaking? Why Is It Important? (Definition + Tips)
What is public speaking? In this article, you'll learn what speaking in public is about and the importance of public speaking in business.

If you’ve been asked to give a public speech, you may wonder: what is public speaking and why is public speaking important? Those questions are quite logical if you’ve never thought much about public speaking before.
Public speaking is important in business, education, and the public arena. There are many benefits to speaking in public, whether you’re an individual or a business.
In this article, we’ll define public speaking for you. We’ll discuss the importance of public speaking in general. We’ll also cover the importance of public speaking in business. Plus, we’ll share some resources to help you become a better public speaker. This includes some public speaking examples.
Also, if you want to pursue speaking in public yourself, download our free eBook: The Complete Guide to Making Great Presentations . It’ll help you master the complete presentation process.
What Is Public Speaking & Why It’s Important (Quickstart Video)
If you’re reading this, you’re probably asking the question “ what is public speaking “? You may even be faced with the prospect of creating a public speech yourself.
Or maybe you just want to know “ why is public speaking important “? Whatever your situation, we’ve got you covered with this short video that gives a public speaking definition and provides you with some tips to make a better public speech.
To learn even more about public speaking and why it’s important, study the written tutorial below.
A Public Speaking Definition
So what exactly is public speaking? Basically, it’s a presentation that’s given live before an audience. Public speeches can cover a wide variety of different topics. The goal of the speech may be to educate, entertain, or influence the listeners. Often, visual aids in the form of an electronic slideshow are used to supplement the speech. This makes it more interesting to the listeners.

A quality public communication definition should explain how it’s different from an online presentation, which is why we’ll cover it here. Here’s a description of some of the differences:
- A public speaking presentation is different from an online presentation because an online presentation is available any time. A public speech is typically limited to a specific time or place.
- Online presentations often use slideshows or pre-recorded videos of a speaker. (This includes recordings of a live public speaking presentation).
Because speaking in public is done before a live audience, you need to consider some special factors. We’ll touch on those shortly.
Now that you’ve got an understanding of the meaning of public speaking, let’s take a quick look at the history of (and the importance of) public speaking.
A History of Public Speaking
What is the history of public speaking? And why is public speaking important?

There’s a good chance that there’s been public speech, in one form or another, as long as there’ve been people. But most public speaking experts involved with public speaking in business communication trace the origins of modern public speaking back to ancient Greece and Rome.
Of course, those societies didn’t have slideshows, but they did have a need for speaking in public. As a result, they developed public speaking methods that are still studied today.
The ancient Greeks used public speech primarily to praise or persuade others. At one point, all Greek citizens had the right to suggest or oppose laws during their assemblies. This resulted in a need for skilled public speakers. Speaking in public became a desirable skill and was taught. Public speaking in the time of the Greeks was called rhetoric. Later, when Rome came to power, speaking in public was used during the Roman senate sessions. The Romans adopted the public speaking rhetoric methods of the Greeks. In fact, most public speaking teachers of the time were Greek.
The Latin style of public speaking was popular in the U.S. and Europe until the mid-20th century . After World War II, a less formal and more conversational speaking style of speaking became popular. Also, electronic tools became available to enhance public presentations.
Towards the end of the 20th century, electronic tools migrated to the computer. They evolved into the computer software tools, like PowerPoint , that we know and use today.
Don’t be fooled, though. Even though today’s public speeches are less formal, they still need to be well organized. More on that later. Now, let’s take a look at the importance of public speaking.
The Importance of Public Speaking
If you ask most people, they’ll probably say they don’t like public speech. They may even admit to being afraid of it since fear of public speaking is very common. Or they may just be shy or introverted. For those reasons, many people avoid speaking in public if they can. If you’re one of those people who avoid speaking in public, you’re missing out.
You may be wondering, “What is public communication and how can it benefit me?” Over the years, public speaking in communication has played a major role in education, government, and business. Words have the power to inform, persuade, educate, and even entertain. And the spoken word can be even more powerful than the written word in the hands of the right speaker.
Whether you’re a small business owner or a student, you’ll benefit from improving your public speaking skills. Some benefits of speaking in public include:
- improves confidence
- better research skills
- stronger deductive skills
- ability to advocate for causes
Speaking in public is especially important for businesses to market their offers. This allows them to get their message in front of potential customers. Salespeople and executives are often expected to have good public speaking skills. To learn more about some of the benefits of speaking in public, review this article .
Next, let’s explore the methods you can use to become better at speaking in public.
How to Become Better at Public Speaking (5 Quick Tips)
Okay, so now you understand the benefits of public speaking. You might be a little more interested in the topic. Still, you might think it’s not for you. Maybe you gave a speech once and it didn’t go well. Maybe you’re afraid of speaking in public. Or maybe you think you don’t have a natural ability for giving speeches.
The truth is that speaking in public is a skill. And you can learn any skill. While some people may have more natural speaking ability than others, anyone can learn to be a better public speaker. It just takes some know-how and some effort.
To help you become better at giving public speeches, we’ll take a look at these five areas:
- writing the speech
- overcoming a fear of speaking
- practicing the speech
- preparing your presentation slide designs
- giving the speech
We’ll start with writing the speech.
1. Write an Effective Speech
The first thing you’ll want to do is work on writing a well-organized, engaging speech. Even a great speaking voice or a great deal of charisma isn’t enough if your material isn’t any good.
Specifically, it’s crucial to research your audience beforehand so that you can target your speech directly to them as much as possible. Become familiar with their wants and needs, as well as any problems you can solve for them. This will drive the actual topic that you actually select for your speech, as well as how you research it.
The more research you do, the easier writing your speech will be.
2. Overcome the Fear of Speaking
Fear of public speaking is very real and can hold you back if you let it. If you don’t feel confident when giving your speech, your listeners may pick up on that. This can make your presentation less effective.
Fortunately, there are some techniques to help manage the fear of speaking in public. They also help you become more confident.
First, let’s tackle fear of public speaking. If you’ve already written an effective speech, then you’ve already taken an important first step. The more familiar you are with your speech, the less worried you’ll be on presentation day.
Besides knowing your topic well, be sure to practice, practice, practice! And remember that if you do make any mistakes on presentation day, it’ll be less obvious to your audience than you think.
Next, let’s work on improving your confidence.
3. Practice the Speech
Even if you’re not afraid of speaking in public, practice helps you give a more effective speech. If you’re in a rush, you may be tempted to skip practicing your speech to save time. While skipping practice may seem like a good idea, it’s really not.
Practicing your speech improves your public presentation skills. It also increases your familiarity with the presentation. As a result, your speech will go smoothly. You can go over this handy checklist to help you practice your speech.
4. Prepare Your Presentation Slide Designs
Your slide design needs to be on point. You’ll want to make sure it looks professional and is easy to read. Luckily, you can find plenty of modern and professional presentation templates on Envato Elements.
You’ll also want to download The Complete Guide to Making Great Presentations eBook now. Download it for FREE with a subscription to the Tuts+ Business Newsletter. Learn how to get your ideas formed into a powerful presentation that’ll move your audience.
Don’t forget to make good use of tools like PowerPoint , Google Slides , or Keynote . The right template for your slide deck can make a huge difference in your presentation.
5. Give the Speech
You’ve written a good speech. You feel more confident about giving a speech in public, and you’ve practiced. You’re ready to actually give the speech. There are some tips and tricks you can use on the day of your speech to make it go more smoothly, though.
Remember, you’re giving a presentation before a live audience at a specific place and time. So, you’ve got some concerns about the speaking venue that those who give online presentations don’t have to worry about.
Some common concerns for public speakers include:
- Will the audience be able to hear me?
- Does the venue have the equipment I need?
- Are there enough seats for all my listeners?
Public Speaking Examples
Public speaking examples are great for learning or improving a new skill. That applies to speaking in public as well. If you get the chance to listen to some top-rated public speakers, you should do it. You can observe how other speakers go about giving their speech. In the process, you’ll improve your own speaking skills.
One great source of recorded public speeches is Ted Talks , which is a series of short presentations on a wide variety of topics. Ted Talks are known for attracting world-class and celebrity speakers. You can find my favorite Ted Talks in this article .
The Best Source for Simple PowerPoint Templates (With Unlimited Use)
Envato Elements is the perfect place to find modern PowerPoint templates . For a single monthly fee, access unlimited downloads of PowerPoint themes, photos, fonts, and other resources to use in your next presentation.
Elements gives you the best bang for your buck. And thanks to the unlimited downloads, you can try out a variety of slide designs as you build out your public speaking PowerPoint presentation.

PowerPoint templates from Envato Elements have plenty of features to help you create a stunning presentation, such as:
- bold text and title slides to capture audience attention
- rich image placeholders to show off photos and videos
- many infographic elements and charts to visualize data
- plenty of customization options to make the template your own
Thanks to these templates, you’ll be able to create a modern, standout presentation to go with your public speech.
5 Modern PowerPoint Templates From Envato Elements
1. minimalism clean powerpoint presentation.

Try this template if you’re looking for a clean and simple PowerPoint slide design. The template features a versatile layout. Use it for any type of presentation or topic. It includes 50+ unique slide designs, tons of customization options, and vector elements. The template was designed in widescreen format.
2. Kaspa PowerPoint Presentation

The Kaspa PowerPoint template has a modern and trendy design. It’s best suited for presentations that need a lot of photos to share information. The template can be customized completely. It comes with slide animations and transitions. The template also includes vector icons.
3. Guava PowerPoint

The Guava PowerPoint has a dramatic, yet elegant design. You’ll notice dark image overlays and elegant typography that makes your message stand out. The template comes with 50+ unique designs, image placeholders, and master slides. It was designed in widescreen resolution.
4. Dauna Minimalist PowerPoint

The Dauna template is another minimalist PowerPoint design. It works well for any type of business presentation. You’ll find 30 unique slides and two color variations. The template comes with image placeholders and plenty of customization options.
5. Pastelize Colorful Business PowerPoint Presentation

If you’re looking for a colorful and bold PowerPoint, the Pastelize template is the perfect choice. The template includes many slide designs, three color variations and color themes, and image placeholders.
Make Great Presentations ( Free PDF eBook Download )
We also have the perfect complement to this tutorial, which will walk you through the complete presentation process. Learn how to write your presentation, design it like a pro, and prepare it to present powerfully.

Download our new eBook: The Complete Guide to Making Great Presentations . It’s available for free with a subscription to the Tuts+ Business Newsletter.
What Is Public Speaking? Now You Know! Time to Get Work on Your Next Speech
So what is public communication in terms of what it can do for you, your career, or your business?
In a nutshell, a world of potential! In this article, we defined public speaking and why it’s so important in your business. Hopefully, the public speaking meaning we explored will help dispel any fear you may have.
We discussed a thorough public communication definition so that you can be adequately prepared for your next speech. Besides the public speaking definition, you learned a bit about the history of public speaking and how it evolved to modern standards today.
We also shared some helpful tools to help you learn how to give a public speech and provided you with a source for good public speaking examples that you can learn from.
You should now be ready to grow as a public speaker. Be sure to check out the sleek PowerPoint templates on Envato Elements as you prepare for your next speech. You’ll find a ton of inspiration for your next presentation!
So go ahead. Write that public speech and give it. You’ll be glad you did!
Related Articles

- Newsletters
- Account Activating this button will toggle the display of additional content Account Sign out
Amy Coney Barrett Sounds Fed Up with Clarence Thomas’ Sloppy Originalism
This is part of Opinionpalooza , Slate’s coverage of the major decisions from the Supreme Court this June. Alongside Amicus , we kicked things off this year by explaining How Originalism Ate the Law . The best way to support our work is by joining Slate Plus . (If you are already a member, consider a donation or merch !)
A minor dispute over a trademark registration erupted into a heated battle over originalism at the Supreme Court last week, splintering the justices into warring camps over the value and practicality of history in constitutional analysis. No surprise there—as the term accelerates toward a contentious finale, the tensions roiling major cases are bound to spill over into littler ones. What’s remarkable is who seized on this squabble over intellectual property to launch a scathing salvo against the conservative majority’s “laser-like focus” on “supposed history and tradition”: Justice Amy Coney Barrett, a conservative who presented as a true believer in originalism when joining the Supreme Court four years ago. Barrett’s latest opinion exudes disenchantment with the methodology, at least as it’s used by this court; it also suggests she has buyer’s remorse about signing on to Bruen , a significant expansion of the Second Amendment that’s arguably the most radical and unworkable “originalist” opinion she’s joined so far.
We will know soon enough. Last week’s squabble reads like shadowboxing over a much bigger decision to come: U.S. v. Rahimi , a follow-up to the Bruen decision. Rahimi gives the court an opportunity to walk back the most disastrous and lethal aspects of its Second Amendment extremism. Barrett now seems like she may be eager to take it.
Vidal v. Elster , last Thursday’s decision, is not the kind of case that usually makes headlines. Steve Elster is a labor lawyer who wanted to trademark the phrase “Trump too small,” inspired by Sen. Marco Rubio’s crude debate joke about Donald Trump’s hands in 2016. The Patent and Trademark Office, however, refused to register the trademark, citing a law that bars trademarks made up of a name “identifying a particular living individual except by his written consent.” (Needless to say, the former president did not give his consent.) Elster sued, alleging a violation of the First Amendment. He pointed out that the Supreme Court has held that two similar provisions of federal law violate free speech, one that bars disparaging trademarks and another that bars “ immoral or scandalous ” trademarks. So, he argued, the prohibition against trademarks that use other people’s names—the so-called names clause—should also be declared unconstitutional.
The Supreme Court unanimously ruled against Elster, upholding the statute. But the justices fractured badly on the reason why, dividing more or less into a 5–4 split. Writing for the five men, Justice Clarence Thomas relied exclusively upon history (or his version of it) to resolve the case. Typically, he explained, laws that discriminate on the basis of content—that is, their “topic,” “idea,” or “message”—are subject to heightened scrutiny under the First Amendment. And by targeting trademarks that reference other people, the “names clause” is a “content-based regulation of speech.” But Thomas then declared that the law is not constitutionally suspect because it aligns with the “history and tradition” of the nation “since the founding.” Trademark restrictions “have always turned on a mark’s content” yet “have always coexisted with the First Amendment,” so they represent an exception to the usual constitutional limitations. Embarking upon a grand journey from the 1700s through today, Thomas presented a smattering of comparable laws from the past to demonstrate this “historical rule.” In short, he concluded, it has always been done, so it always may be done. Case closed.
In a separate opinion, Barrett agreed with Thomas’ bottom line but sharply disagreed with pretty much everything else. His history-only approach, she wrote, was “wrong twice over”: Thomas both botched the relevant history and failed to make a persuasive case for its use in the first place. Start with “the court’s evidence.” Thomas’ law-office history , Barrett explained, consists of “loosely related cases from the late-19th and early-20th centuries” that do not “establish a historical analogue for the names clause.” His analysis of these cases is shallow and often dubious; Barrett highlighted unfounded inferences in Thomas’ skim of the historical record, questioning his generalizations from a handful of archaic decisions. She also noted that Thomas declined to “fully grapple with countervailing evidence,” citing old decisions that cut against his conclusory assertions.
Clearly, Barrett is growing tired of her colleague’s bogus originalism: She also criticized his highly selective frolic through the archives in last term’s Samia v. U.S. , questioning his reliance on a somewhat random “snapshot” of history to cut back protections of the Sixth Amendment. “The court overclaims,” the justice wrote then, risking “undermining the force of historical arguments when they matter most.”
But this time, Barrett’s critique cuts much deeper: Thomas, she wrote, “never explains why hunting for historical forebears on a restriction-by-restriction basis is the right way to analyze the constitutional question.” The majority “presents tradition itself as the constitutional argument,” as though it is “dispositive of the First Amendment issue,” without any “theoretical justification.” In a passage that must have made the liberal justices proud, Barrett continued: “Relying exclusively on history and tradition may seem like a way of avoiding judge-made tests. But a rule rendering tradition dispositive is itself a judge-made test. And I do not see a good reason to resolve this case using that approach rather than by adopting a generally applicable principle.” Plucking out historical anecdotes, ad libbing some connective tissue, then presenting the result as a constitutional principle “misses the forest for the trees.” When applying “broadly worded” constitutional text, “courts must inevitably articulate principles to resolve individual cases.” This approach brings sorely needed “clarity to the law.”
Barrett sketched out a better path: assessing the “names clause” within a framework “grounded in both trademark law and First Amendment precedent.” When the government “opens its property to speech,” she wrote, restrictions are permissible so long as they aren’t cover for the “official suppression of ideas.” Thus, courts should uphold trademark laws if they “are reasonable in light of the trademark system’s purpose.”
Why did Barrett spill so much ink repudiating Thomas’ opinion when the two justices landed in the same place? Her opinion reads like a rebuttal of Bruen , Thomas’ 2022 decision establishing a novel right to carry guns in public—which Barrett joined in full. Bruen marked a sea change because it upended the way courts looked at firearm restrictions. Previously, the courts of appeals applied heightened scrutiny to gun laws, asking whether the regulation was carefully drawn to further public safety. SCOTUS applies this test in countless other contexts, including the First Amendment and equal protection. It requires judges to balance the interests on both sides, a well-worn tool of judicial review. Yet Thomas spurned this “means-ends scrutiny,” demanding that courts rely exclusively on the nation’s “history and tradition”: A gun restriction, he wrote, is only constitutional if it has a sufficient number of “historical analogues” from the distant past.
This brand-new test has flummoxed the lower courts and led to ludicrous outcomes —partly because judges are not historians and have no reliable way to produce a complete historical record, and also because American society has evolved to the point that a great deal of “tradition” now looks barbaric . This term, the Supreme Court has been confronted with the fallout from Bruen in a follow-up called Rahimi , which asks whether domestic abusers have a right to bear arms . During oral arguments in Rahimi , Barrett sounded deeply uncomfortable with what her court had wrought. Rahimi has not yet been decided. But Barrett’s concurrence in Elster reads like a preview of her opinion in that case. The justice seems to have second thoughts about pinning constitutional interpretation entirely on a court’s amateur historical analysis; she now seems to see the immense value in “adopting a generally applicable principle” that courts can apply across cases.
The liberal justices were right there alongside Barrett in Elster , gladly signing on to her more sensible approach to the case. Justice Sonia Sotomayor also wrote a separate concurrence raising many of Barrett’s objections, taking more explicit aim at Bruen and the “confusion” it has caused. And some of Barrett’s Elster concurrence echoes a recent opinion by Justice Elena Kagan—which Barrett notably joined—that offered an alternative to Thomas’ rigid focus on founding-era history in a case upholding the constitutionality of the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau.
This shadowboxing foreshadows a bitter split in Rahimi , though with Barrett and the liberals appear poised to wind up on the winning side. There’s no doubt that Barrett is still a Second Amendment enthusiast , but with one more vote, this bloc is well positioned to walk back the excesses of Bruen . What’s certain right now is that the justice, at a minimum, has serious doubts about the legitimacy and workability of this Supreme Court’s sloppy, results-oriented originalism . That doesn’t mean Barrett has abandoned her broader commitment to the conservative legal movement’s cause. But it does signal a disillusionment with conservative orthodoxies that could put her vote up for grabs in cases much more important than a trademark dispute.
Official websites use .gov
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS

Department Press Briefing- June 20, 2024
Matthew Miller, Department Spokesperson
June 20, 2024
Article Index
- ISRAEL / PALESTINIAN TERRITORIES / LEBANON / REGION
- ISRAEL / PALESTINIAN TERRITORIES
- UKRAINE / RUSSIA
- NORTH KOREA / RUSSIA
- VIETNAM / RUSSIA
- SOUTH KOREA / UKRAINE
- NATO / UKRAINE
- INDIA / PAKISTAN
- ISRAEL / PALESTINIAN TERRITORIES / REGION
2:09 p.m. EDT
MR MILLER: Good afternoon.
QUESTION: Good afternoon.
MR MILLER: At the risk of disappointing everyone, I don’t have any opening comments. So Matt is first.
QUESTION: Why – disappointing us, really?
MR MILLER: That was a bit facetious on my part perhaps.
QUESTION: Okay. All right. So let’s just start in the Middle East. One, can you tell us what you’re expecting out of this meeting from Dermer and the Secretary?
MR MILLER: Yeah. So later this afternoon the Secretary will meet with Ron Dermer, Minister for Strategic Affairs for the Government of Israel and Tzachi Hanegbi, the National Security Advisor. He will discuss our ongoing work to try to reach a ceasefire that will secure the release of all hostages, would surge humanitarian assistance. They will discuss the situation in the north of Lebanon – or, I’m sorry – in the north of Israel along the border with Lebanon. They will discuss our ongoing work, even absent trying to secure a ceasefire to get humanitarian assistance into Gaza, and work that needs to be done to accelerate and prove that process, among, of course, a host of other issues that we discuss every time we meet with people from the Government of Israel.
QUESTION: Okay. Well, when it relates to the quote, unquote, north of Lebanon —
MR MILLER: Israel. I believe I corrected it.
QUESTION: Well, I know. The north of Israel, yes. But you want to talk about the north of —
MR MILLER: South of Lebanon.
QUESTION: We can talk about the north of Lebanon if you want.
MR MILLER: Sure. (Laughter.)
QUESTION: But let’s talk about —
MR MILLER: You can probably tell me your trips to it. I’m sure you’ve been. (Laughter.)
QUESTION: Let’s talk about the north of Israel on the Lebanese border. What is the situation there, as you understand it? Is there some kind of – is there some kind of operation that’s going to be mounted any time soon? And if there is, what do you think of it?
MR MILLER: So we have made quite clear that we do not want to see escalation of this conflict. Hizballah has increased the number of cross-border attacks over the past few weeks. You’ve seen dramatic attacks targeting civilian communities.
Matt, I hate to interrupt. There’s a big cockroach on the wall over your head there. So maybe need a – we’ll defer that to – (laughter) – it’s not – no insecticide or roach-icide in the briefing, Matt.
QUESTION: Well, I’ll go get it as soon as you finish.
MR MILLER: Yeah. I’m sorry to be distracted, but that’s a rather large one. (Laughter.)
QUESTION: Do we – do I have to get rid of it now?
MR MILLER: No, no.
QUESTION: All right.
MR MILLER: Let me go ahead and finish. We’ve seen a number – a dramatic increase in attacks across the border. I shouldn’t have said anything because now the room’s going to have a hard time focusing on what – on the very important messages I have to deliver here. Back to where we were.
QUESTION: I’m worried. Is it still alive?
MR MILLER: Back to where we were. We’ve been extremely concerned about the situation in the north of Israel. As I said, we don’t want to see the conflict escalate. We have seen a dramatic increase in strikes by Hizballah across the border targeting Israeli villages, civilian infrastructure. And so we have been pursuing a diplomatic resolution to try to make clear that there should be no further escalation, and that’s what we’ll continue to pursue.
QUESTION: Well, yeah. But I mean, have you told them, the Israelis or the Lebanese, that the – that – have you – well, have you told them anything?
MR MILLER: So we’ve had intensive conversations with both governments about this. In our conversations with the Government of Israel, which I’ll speak to – and I’m sure the Secretary will go over with the two representatives from the government who are here today – we have made clear that our preference is to see a diplomatic resolution. And they have said to us that they want to see a diplomatic resolution to this conflict, and that’s what we’re going to continue to try to pursue.
QUESTION: Have the Israelis told you that they’re about to launch some kind of a strike and —
MR MILLER: They have not.
(The cockroach was taken care of.) (Applause.)
MR MILLER: Solves that problem. (Laughter.)
QUESTION: Right. I mean, is that the —
MR MILLER: I’m not going to engage in any metaphors related here, which I think –(laughter) – I think where you’re going to —
QUESTION: No. Well, I mean, I – so have you told the Israelis that you’re going to – that you will support them or help them if they decide to go in?
MR MILLER: We have made clear that we want to see a diplomatic resolution. I think I’ll leave –
QUESTION: Well, that’s not what I’m asking.
MR MILLER: I think I will leave it at that.
QUESTION: All right. Thanks.
QUESTION: Matt.
MR MILLER: Yeah, Michel.
QUESTION: After Mr. Hochstein’s visit to Israel and Lebanon, is it fair to say that the diplomatic solution has failed?
MR MILLER: No, I don’t think so. I think we continue to pursue very active diplomacy to try to keep this conflict from escalating. You’ve heard me say this before, and I’ll say it again because it remains the case. The best way to unlock the possibility of a resolution along the Israel-Lebanese border would be achieving a ceasefire in Gaza.
And we continue to actively pursue a ceasefire in Gaza, primarily for – to alleviate the suffering of the Palestinian people in Gaza and to secure the return of hostages. But a very important side effect, we assess, would be making it much easier to achieve a ceasefire and diplomatic resolution along the Israel-Lebanon border. That said, we’re not waiting for a ceasefire in Gaza. We’re continuing to pursue diplomacy because it’s important to do. But, again, it’s very difficult to reach such a resolution while the conflict in Gaza continues at the pace it is today.
QUESTION: And do you have any comments on Hizballah secretary general’s speech yesterday and his threat to Cyprus? And did the Secretary discuss this topic with Cyprus foreign minister in their call yesterday?
MR MILLER: So the meeting that he had with the Government of Cyprus was actually two days ago. So it was before the speech that – the Hizballah speech that you referred to. So no, they obviously didn’t discuss because it hadn’t happened yet. But obviously those comments are extremely unproductive, and Hizballah should cease making threats against anyone, and our preference would be for Hizballah to pursue a diplomatic resolution. I think that’s the most productive. And certainly making threats at other countries that aren’t involved in this conflict at all are not a productive step for them to be taking.
QUESTION: Thank you.
MR MILLER: Yeah. Go ahead.
QUESTION: Just on – keep on the Lebanon border issue. Is it fair to say that this has now become, like, a greater focus of your diplomacy, like in the meetings this afternoon, than the situation in Gaza? This seems to have really heightened in terms of the rhetoric coming from both sides. Do you see this as a sort of – the priority is now avoiding a broader conflict in the north?
MR MILLER: No, they continue to be equally important priorities, and they have been from the beginning. We have been incredibly focused on the situation in Gaza since right after October 7th. But if you go back and look at what the Secretary said in his first visit to the region and what we said in really every trip, keeping the conflict from escalating has been one of our overriding strategic goals. And there have been times when it looked like there was more of a chance of the conflict escalating than others. Obviously, we had the time when there was direct fire against the state of Israel from inside Iran. We’ve seen the pace of attacks across the Lebanese border kind of rise and fall over time, but that overriding strategic objective has been there from the beginning for us. We continue to focus on both.
This is not what you were saying, but I would just say that I wouldn’t – the number of questions we get about any one topic is not always indicative of the actual work that’s going on inside the government. We continue to work to pursue a ceasefire. There are conversations going on between our government and the Government of Israel – the governments of Israel, Egypt, and Qatar about how best to achieve that ceasefire in a way that protects Israel’s security interests, gets the hostages home, alleviates the suffering of the Palestinian people. But no, I wouldn’t rank them in any kind of order.
QUESTION: And also on the relationship with the Israeli Government, there’s been this fallout from the video that Prime Minister Netanyahu made talking about what Secretary Blinken said to him in their meeting. There’s obviously – the administration has spoken about this and said some parts of it are not true. I just wanted to get your response, because there’s the latest comment from the prime minister; he’s saying he’s willing to absorb personal attacks – he calls them “personal attacks” apparently in a reference to the way that the administration has responded to this video – in order to get the weapons that Israel needs for its survival. So how do you respond to this kind of – there seems to be a continuing discord between the way you’re talking about this, and specifically on the issue of whether you’re providing Israel with everything it needs?
MR MILLER: So I’m not exactly sure what the prime minister is talking about or what he was trying to accomplish. All I can tell you is what the Secretary told the prime minister directly in his meeting in Israel last week, which is that our commitment to Israel’s security is sacrosanct. We have proved that not just with words, but with deeds, and I don’t think it’s productive to engage in an intense public back and forth about this. So we will just let our actions continue to speak for themselves as they have since October 7th.
QUESTION: Israel?
MR MILLER: Yeah.
QUESTION: Staying on Lebanon. You and other U.S. officials have made clear that you don’t want a second front to open, but how likely at this stage do you believe that a new confrontation between Hizballah in Lebanon and Israel is?
MR MILLER: I’m not going to give you any kind of assessment of likelihood. I will say it is an intense concern of ours. It has been for some time. As I said, there are times where we have been more concerned about it. It has never gone away as a concern, but whenever you see an increase in strikes across the border, that magnifies our concern at any given moment. So of course, we have intense concerns about it right now, which is why we are pursuing diplomacy to try to achieve a resolution.
QUESTION: A U.S. official told us today that Israel hasn’t come close to achieving their stated objective of destroying Hamas in Gaza. Its defense minister made similar comments publicly. Does the U.S. believe that Israel is militarily capable of succeeding militarily against Hizballah, with or without American support?
MR MILLER: Against Hizballah? I just don’t want to offer any kind of assessment about a conflict that we hope never happens in the first place.
QUESTION: Well, you may be more persuasive if you point out that it’s not one that Israel can win.
MR MILLER: We will have – we have conversations about that sort of thing behind closed doors, but I don’t think it’s helpful for me to offer that kind of assessment publicly.
QUESTION: Okay. And then just – just because so much of this has also been predicated or has been accompanied by the U.S. diplomatic push to achieve a ceasefire in Gaza, where do those talks stand? Have mediators engaged – re-engaged with Hamas to get a read on what the bridgeable gaps are at this stage?
MR MILLER: We are engaging in conversations, as I said a moment ago, with the governments of Egypt, Israel, and Qatar about how to move forward, responding to the proposal that Hamas made last week, to try to come to a resolution that is consistent with what the United Nations Security Council endorsed and what countries across the world have signed up to. But I don’t think at this point it’s helpful for me to talk about those conversations in detail.
QUESTION: Just to – there’s been no re-engagement with Hamas, either their political representatives or their military wing?
MR MILLER: I don’t want to get into that publicly right now.
QUESTION: All right, one more on Ukraine and then I’ll —
MR MILLER: Okay. We’ll come back.
QUESTION: While we’re on Hizballah, can I just ask if you can kind of give us an up-to-date assessment as to where the U.S. – how the U.S. is viewing Iran’s backing of Hizballah at this moment in time? Has it increased? Is it the same steady state that it’s been? Just where that stands.
MR MILLER: So I can’t give you a minute-to-minute assessment, but Iran has been one of the primary backers of Hizballah going back years, as they are a primary backer of Hamas going back years, and other terrorist organizations in the region, and that has in no way changed.
QUESTION: Okay. And so there’s no further support that they’re providing to them?
MR MILLER: They are providing ongoing support to them at all times. And what I mean is I can’t give you a daily kind of run-by-run of what they’re doing, but they have been one of Hizballah’s chief backers going back years and that hasn’t changed; it’s been consistent. It’s one of the reasons we’ve been so concerned about Iran’s destabilizing activities.
QUESTION: And then just – just one question on the Secretary previewed last week that the department was going to be rolling out plans for – day-after plans in Gaza. I just wonder if you can give us an update as to where those efforts stand, how many plans you guys are going to roll out, if a few weeks is still kind of the time frame that we’re dealing with here.
MR MILLER: I think I’m going to have to give you the “stay tuned” answer on this one. There are conversations we are engaging with our partners in the region about. We do look forward to moving those conversations forward and, as the Secretary said, having something to say, but I’m not ready to preview it today.
QUESTION: Okay.
QUESTION: Can I follow up?
MR MILLER: Yeah, Said, go – sorry, you’ll be next.
QUESTION: Thank you. Just to where you were responding to Olivia I guess on the path forward, I mean, a lot of – according to Politico, U.S. officials see no path forward to resolving the Gaza war anytime soon or coming up with a ceasefire that can endure. So I just want – perhaps if you elaborate on this.
MR MILLER: So —
QUESTION: Where are we – where are we with the talks?
MR MILLER: So first of all, I have no idea who those U.S. officials are. As I’ve said on previous occasions, you have thousands of people who serve in the government and have U.S. – who are U.S. officials, and they have a wide diversity of opinions. They’re not all – the opinions that you see quoted from U.S. officials are not universally shared. I think everyone understands that.
I will say that we very much see a path forward to a ceasefire. There was a way to get a ceasefire last week – in fact, even before last week – if Hamas had agreed to the proposal that Israel had put forward and that had been endorsed, as I said, by the United Nations Security Council and countries around the world. And had Hamas accepted that proposal, we would have a ceasefire today and the suffering of the people inside Gaza could have been dramatically alleviated and we would have seen a massive surge in humanitarian assistance. So it remains incredibly unfortunate that they didn’t accept that proposal, but we think they ought to accept that – they ought to agree to a ceasefire. We are engaged in conversations with the mediators about how to get to a ceasefire that protects Israel’s security interests, that alleviates the suffering of the Palestinian people. We very much do think it’s possible to achieve one, but as you heard the Secretary say, just because it’s possible doesn’t mean that we will get there. But we’re going to keep trying.
QUESTION: Well, since you mentioned the humanitarian aid, I mean, today marks the 43rd day of the closure of the Rafah crossing and Karem Abu Salem and so on. There is virtually no aid, and the pier is not functioning, obviously. The situation is very dire. Why can’t – why can’t the U.S. put forth an idea or a way to increase under the current circumstances before you even get the ceasefire, because the situation is very bad? I mean, people – literally children are starving —
MR MILLER: We are absolutely —
QUESTION: — to death.
MR MILLER: We are – sorry to interrupt you. We are absolutely putting forward ways to improve the humanitarian situation in Gaza. And it was because of U.S. advocacy that we saw Israel institute these humanitarian pauses that they announced on Sunday or Monday. We continue to engage with our partners on the ground about how to increase the number of trucks that go in, but more importantly right now, because there are a number of trucks that have made it to Kerem Shalom that are sitting in Kerem Shalom unable to then distribute the aid that they’re holding inside Gaza, we’re working for ways to resolve the security and logistical challenges that made it difficult to distribute aid inside Gaza. We continue to be incredibly focused on that as well —
QUESTION: Do you —
MR MILLER: And I should say as well as reaching an agreement between Israel and Egypt about how to safely reopen the Rafah border crossing.
QUESTION: Although Israel has destroyed it completely. They’re saying that it is now rendered completely inoperable. But let me ask you about the – what Navi Pillay, the chairperson of the Independent International Commission of Inquiry on the Occupied Palestinian Territory, announced yesterday that Israel did indeed commit war crimes. Do you have any comment? Have you seen the report and do you have any comment on that?
MR MILLER: We did see the report. We saw that Israel said it is reviewing the report. I can just give you what our assessment has been. You saw us put out a report last month where we said it is reasonable to assess that there have been violations of international humanitarian law, and we’re continuing to look at specific incidents to draw final determinations.
MR MILLER: Yeah, go ahead.
QUESTION: On Iran – pardon me – there’s reporting that Iran’s undergoing a major extension at the Fordow facility that would triple production of enriched uranium there. I wanted to get your comment on that and the separate reporting that the Iranians could now be using computer modeling that could be used in their development of nuclear weapons.
MR MILLER: So with respect to the first question, Iran continues to expand its nuclear program in ways that have no credible peaceful purpose. We remain deeply concerned with Iran’s nuclear activities and will continue to vigilantly monitor them. As we said in a joint statement we put out with the G7 on Friday, Iran must cooperate with the IAEA without further delay. As it relates to this report on commuter modeling – computer modeling, I’ve seen the article; I’m not going to comment, obviously, on intelligence matters. As you have heard us say before, we do not see indications that Iran is currently undertaking the key activities that we would – that would be necessary to produce a testable nuclear device, but of course this is something we continue to monitor very closely.
QUESTION: Follow-up? Iran?
MR MILLER: Yeah. Oh, Guita, go ahead. Yes. Yeah, stick with Iran.
QUESTION: (Off-mike.)
QUESTION: Earlier when you were talking about Hizballah, its activities, you referenced Iran, its support for Hizballah, terrorism. Canada just designated the IRGC as a terrorist group. I was wondering if you have any comment?
MR MILLER: So we welcome the decision by Canada to designate the IRGC as a terrorist group. It’s something the United States has done. The IRGC’s terrorism and lethal plotting threatens the entire world, and we stand ready to provide support as countries – other countries consider designating the IRGC as a terrorist organization.
QUESTION: How can you support other countries in doing this?
MR MILLER: Well, we can provide information to them about activities that they have undertaken, something we often do in sharing intelligence information and other information with our allies and partners about activities that we have seen any supporters of terrorists – terrorism take around the world.
MR MILLER: Yeah, Tom.
QUESTION: Just to come back to the Netanyahu video, I mean, the White House has said today that what the Israeli prime minister said was, quote, “incorrect.” So I’m just trying to – there were a few things he said, but I’m trying to understand which part was incorrect.
MR MILLER: So I think the part that is incorrect is that there are bottlenecks that need to be overcome. So obviously, there is one shipment of high-payload munitions that we have put under review and that remains under review. That’s not a bottleneck; that’s a policy review. Other shipments of weapons have been moving regularly to Israel, because we are committed to Israel’s long-term defense, and that includes things that have nothing to do with the war in Gaza but are capabilities related to Israel’s long-term security, defending itself against, for example, the threat from Iran.
QUESTION: He also said that the Secretary told him that the administration was working day and night to overcome the bottlenecks. Is that incorrect?
MR MILLER: So I’m not going to get into a word-for-word parsing of what the prime minister said, because as I said a moment ago, I don’t think it’s really productive to have this kind of conversation in public. But there are – but there are no bottlenecks. And the Secretary made clear in the – in his conversation that we are continuing to flow security assistance – other than the one that is publicly known, that we have made clear to them and we’ve said publicly are under review—other things continue to flow. So there are – there just are no bottlenecks.
QUESTION: So he didn’t – he didn’t say that the administration was working to overcome that particular block of the 2000-pound bombs?
MR MILLER: No.
QUESTION: He didn’t say that?
QUESTION: Okay. And —
QUESTION: Can I just follow up on that, Tom?
QUESTION: Yeah, sure.
QUESTION: On that (inaudible). You say the – it’s not for public exchanges, back and forth and all this. But I mean, the White House this morning went quite strongly against Netanyahu’s comments. And so is the State Department not at the same line as the White House?
MR MILLER: No, I – I made clear that we didn’t think – I didn’t think the comments – I didn’t know what the prime minister was talking about or what he was trying to accomplish. And I’m happy to make the record clear, as I think the White House was doing, but none of us think it’s productive to have a extended public debate about – that’s not – there’s no daylight between me in the White House. I think they would agree with that. But of course, when it comes to defending our record, we’re going to defend our record.
QUESTION: Well, why don’t you tell them that?
QUESTION: I mean, it seems to have a little bit of a different take than the White House on this.
MR MILLER: I – not at all. Not at all.
QUESTION: Why don’t you tell them that?
MR MILLER: No – no —
QUESTION: No?
MR MILLER: The White House? We have the exact same —
QUESTION: No, not the White House – the Israelis.
MR MILLER: I think I just did.
QUESTION: Did you? Did you?
QUESTION: All right. Okay.
QUESTION: Yeah, I mean, but – I mean, you’re saying it’s not productive to have a back and forth, but you are having a back and forth with them right now. So —
QUESTION: Exactly.
QUESTION: — what purpose do you think that serves? Because in the end —
MR MILLER: I don’t – so I don’t think it serves any purpose. That – no, that is my overall point.
QUESTION: In the end, you could sort of not engage with this, and yet you’re still signing the checks, right. So —
MR MILLER: Hold on. No – I don’t think it serves any purpose, but if someone – if someone comes out and says something about the actions by the United States Government that we – that are not accurate, we’re going to correct the record. I don’t think it’s necessarily —
QUESTION: But you’re —
MR MILLER: I don’t think it’s necessarily productive to have this exchange in public, especially about things that we don’t understand and can’t comprehend because they don’t reflect reality, but we will defend our record a hundred percent.
QUESTION: So you’re saying it’s not productive to have the exchange in public, but you will still have the exchange in public?
MR MILLER: I’m saying we’ll defend our record when we have to, yeah.
QUESTION: Sorry – sorry, but you have daily contacts with the Israelis. So what are you saying to them? Netanyahu, the prime minister, is lying or not saying correct things or —
MR MILLER: As I just said, we don’t understand what he was talking about when it comes to talking about bottlenecks because we’ve continued to provide, absent – outside of this one shipment that is under review, we continue to provide them the equipment they need to defend themselves.
QUESTION: And his staff hasn’t explained to you what he was talking about, since you’re in daily contact with them?
MR MILLER: So we have very direct exchanges with them. They can be quite candid at time, and I think I’ll leave it at that.
Alex, go ahead.
QUESTION: Thank you, Matt. I want to shift to Ukraine, but before that, anything you can tell us about another arrested U.S.-Russian citizen, Ksenia Karelina, who is facing trial in Yekaterinburg. Basically Russia is trying to jail another American citizen for experiencing her First Amendment rights in the U.S.
MR MILLER: Yeah, so first of all, as you – as we always make clear, we take seriously our commitment to assist U.S. citizens abroad and provide all appropriate assistance. Oftentimes, there’s a limit to what I can say for privacy reasons just based on the law, and that is the case here. I will say generally, when a U.S. citizen is detained abroad, consular officers seek to provide them with all appropriate assistance. Russia has long taken the position that when it comes to dual nationals, they don’t have to respond to those requests for appropriate assistance. But that said, we continue to actively seek access to any individuals in this situation.
And then I do have to just reiterate, as I always do in these situations, that no American citizen for any reason should travel to Russia. And I know this is – sometimes comes down to a very painful choice for Americans who have family members in Russia sometimes family members with health problems, that they want to see. But you run a tremendous risk by traveling to Russia of being detained, being imprisoned, being convicted. And so we continue to make clear to every American: Do not for any reason travel to Russia.
QUESTION: Thank you. Moving to Ukraine, on today’s decision to reprioritize arms sales to Ukraine, anything you can tell us about what triggered the decision?
MR MILLER: So we have been engaged with the – when conversations with the Government of Ukraine about what they need. We’ve seen the Russia military targeting Ukrainian cities. We’ve seen them targeting energy infrastructure, making clear that they want to turn the lights off and turn the heat off when winter rolls back around. And so it has been clear to us that we needed to do something to increase Ukraine’s air defense capabilities, and we have been engaged with our allies and partners about how to do that.
That includes sourcing additional systems from around the world to improve Ukraine’s air defense, but it also includes supplying the systems that they have already been provided, and so that’s the decision that the President took, which is to re-sequence some of the deliveries of Patriot interceptors – the missiles that go up and intercept missiles that have been fired by Russia – to re-sequence them from other countries, because of the dire need that Ukraine has and the dire threat that Ukraine faces, to make sure that Ukraine is getting what it needs now to defend itself from this intense Russian air bombardment.
QUESTION: Is it fair also to expect reprioritizing F-16 training slot?
MR MILLER: So I’m not going to get into any future decisions, but the Secretary has always made clear that we always adapt and adjust our policy based on the battlefield realities. And so we look at what Ukraine needs and then we look at how we can meet those needs – whether through actions that the United States is taking or whether actions that our allies and partners are taking. And we look to provide them the best equipment, the best of training – best training that we can as quickly as we can provide it. And when the United States can’t do it or when there’s another country that can do it better, we look to another country to do it.
QUESTION: Thank you. One more from me. On Putin’s trip to North Korea, any concern on your end – first on this – its potential implications for Ukraine? And also any concern on your end that unified UN response to North Korea’s nuclear issues might be irrelevant?
MR MILLER: So a few things. First of all on the deepening cooperation between Russia and the DPRK, we have been warning about this for some time. You recall that we first made public that the DPRK was providing Russia with military equipment that would show up on the battlefield in Ukraine, has showed up on the battlefield in Ukraine. We’ve seen them provide thousands of artillery shells and other munitions that they have been using to shell Ukrainian cities, Ukrainian villages, and kill Ukrainian civilians.
We have been taking this quite seriously. And I will say it’s one of the reasons why we have been prioritizing strengthening our ties with allies and partners in the Indo-Pacific throughout this administration, including through the historic trilateral agreement we had with the Republic of Korea and Japan, through AUKUS, through other work because of the potential for deepening cooperation between these two countries. That said, it should also be concerning for the – for your second question, which is anyone who cares about maintaining peace and stability on the Korean Peninsula – if you look at the – what was contained in the agreements that they made public, it would include Russia violating UN Security Council resolutions that it voted for. So it continues to be a problem, and we’re going to work on it with our allies and partners, including those in the region.
QUESTION: And just – I said – I know I said it was final, but any – that being said, any connection between tomorrow’s – assistant secretary’s —
MR MILLER: I think I can go to someone else. You said it was final already. (Laughter.) Go ahead. Sorry.
QUESTION: Assistant secretary’s trip to Vietnam and Putin’s visit – any connection between the two?
MR MILLER: Between the Secretary’s trip?
QUESTION: Assistant secretary —
MR MILLER: Oh, the assistant secretary.
QUESTION: Yeah.
MR MILLER: Oh, Assistant Secretary Kritenbrink, who is there – no, we were planning that trip well before this visit by President Putin.
QUESTION: (Inaudible.)
MR MILLER: Who —
QUESTION: No, that’s okay. It was on Kritenbrink.
MR MILLER: Decide amongst yourselves. I don’t care.
QUESTION: (Laughter.) All right. Thank you. All right, so Putin’s visit to Vietnam comes after President Biden’s visit last year where the U.S.-Vietnam relationship was upgraded to Comprehensive Strategic Partnership. I was wondering what your take is on Putin’s trip to Vietnam.
MR MILLER: So obviously Russia and Vietnam have had longstanding close ties. That said, we expect that any country, when it engages in conversations with the Government of Russia and especially when it hosts leaders from the Government of Russia, will make clear their respect for the principles of the UN Charter, including sovereignty and territorial integrity, and convey that those principles must be upheld across the world.
QUESTION: Since Assistant Secretary Kritenbrink will be there tomorrow in Hanoi, will Vietnam be sharing maybe the conversation they had with Putin?
MR MILLER: I don’t know. Ask me tomorrow after the meeting.
QUESTION: Okay. One last one on —
MR MILLER: I’m unable – I’m unable to predict the future.
QUESTION: Okay. One last one on this. Is there any indication that Vietnam companies or Vietnamese companies are supplying material to – or financial support to Russia in its war against Ukraine? And has the U.S. talked to Vietnam about this subject?
MR MILLER: Let me – I don’t have an assessment. Let me take that back and get you an answer.
QUESTION: Okay. My one question turned into two now, just on the basis of all of this stuff. On the heels of this pact between Russia and DPRK, South Korea – reports from South Korea indicate its government is considering sending arms to Ukraine. Does the U.S. have a view on that?
MR MILLER: That is a decision for South Korea to make, just as its in – it’s – that is a decision for every country to make in terms of whether they are going to supply weapons to Ukraine. We welcome any support for Ukraine in its fight against Russian aggression, but I – that’s ultimately a decision for South Korea.
QUESTION: So you would welcome that scenario and not view it as destabilizing to the Indo-Pacific?
MR MILLER: I’m just not going to – it is a decision – we welcome any country that wants to support Ukraine in this fight, but as for the specific decision, it’s one for South Korea to make.
QUESTION: Okay. And then somewhat separately but still on Ukraine, we’ve heard the Secretary say that next month at the NATO summit – he hopes it will lead to a well-lit bridge for Ukraine joining NATO. There’s been discussion of other characterizations of its pathway. The UK and the secretary general of – of NATO have used the word “irreversible.” Does the U.S. oppose using the word “irreversible” to characterize Ukraine’s path to NATO?
MR MILLER: So I’m not going to get into what the eventual words might be in a NATO communique for a summit that hasn’t actually happened, but the important thing is this: NATO’s future is in – I’m sorry, Ukraine’s future is in NATO. It will become a member of NATO. We have made that clear. And we will continue to work with our Allies in NATO about the exact bridge to membership and what that looks like and what Ukraine has to do, but what the actual words are in a communique, we will resolve that diplomatically with our Allies.
QUESTION: I don’t expect you to give us the final language that’s going to be used. I’m just asking you if you oppose a given word appearing in a communique, which is “irreversible.”
MR MILLER: And I think we will handle this through diplomatic discussions with the members of NATO. You are not a member, Olivia, so sorry. (Laughter.)
MR MILLER: Did you have one, Simon?
QUESTION: Just to come back to the North Korea – Putin’s presence there.
QUESTION: So Putin himself has said that Russia may deliver weapons to North Korea as part of this. What about that side of it? What are your concerns regarding the potential for Russia to be destabilizing in that sense?
MR MILLER: It is incredibly concerning. It would destabilize the Korean Peninsula, of course, and potentially give it – depending on the type of weapons they provide might violate UN Security Council resolutions that Russia itself has supported, which is why we will continue to work with our allies in the region – South Korea, Japan, others – to respond to the threat posed by North Korea.
QUESTION: And also on the visit to Vietnam – so you’ve kind of expressed your concerns, but more broadly, is this a – how do you see the relationship with Vietnam given that in recent – only a few months ago the President went there to sign this upgrade in ties? Is this a failure of the policy to try to bring a country in – out of the orbit of those more authoritarian countries and to be a U.S. partner in the region?
MR MILLER: No, I think two things can be true. First of all, it was a major achievement to significantly upgrade the ties between the United States and Vietnam, especially when you look at the history between our two countries and as a key part of our Indo-Pacific Strategy. That said, Vietnam has had longstanding very close ties with Russia, so our only expectation is that when they have conversations with Russia – as China does, as other countries in the region do – we would hope that they would express their support for the principles of the UN Charter everywhere in the world.
QUESTION: And there’s an ongoing process – it’s based in the Commerce Department – to decide whether to recognize Vietnam as a market economy. Does the State Department have a view on whether it is? And I guess you would be involved in some way in advising for that process.
MR MILLER: I will have to take that back and get you an answer on that. I don’t have an answer today.
QUESTION: Sorry, can I just —
QUESTION: On this, you talk about the UN Charter and the territory – sovereignty and territorial integrity. What’s the U.S. record on that with regard to Vietnam?
MR MILLER: So obviously we have – were involved in a conflict in Vietnam many years ago, ancient history, and we are glad to see the —
QUESTION: It’s not so ancient. I mean, I was alive during it.
MR MILLER: We – we are – yeah —
QUESTION: I don’t know, maybe not others were, but I – but it’s not ancient. It’s not ancient history, and —
MR MILLER: I wasn’t trying to insult you, Matt, just to be clear. That said, we have —
QUESTION: But look, I mean, in the early 1960s, the U.S. actually went into Vietnam and stayed there until 1975, so —
MR MILLER: I am full aware of the long historical record between our two countries, and in the years since you have seen a broad reconciliation between our countries and between our two peoples.
QUESTION: Okay, but when you say that you want the Russians to respect the UN Charter as it relates to Vietnam and —
MR MILLER: I was speaking as it respects to Ukraine – with respect to Ukraine.
QUESTION: Well, anywhere.
QUESTION: As it relates to Vietnam, you don’t exactly have the best record, right?
MR MILLER: So as usual, I’m not going to litigate the full history of American foreign policy —
QUESTION: You don’t have to litigate it.
MR MILLER: Foreign policy from the podium, especially as the representative of an administration that has been charged – in charge for three and a half years, and I think I’ll leave it at that.
MR MILLER: Go ahead.
QUESTION: Thanks, Matt. So just in relation to the UN —
MR MILLER: I was calling on you, but that’s fine. Go ahead. (Laughter.) Go ahead.
QUESTION: Okay, well, I’m – I started, so I’ll finish, as they used to say. So the UN Human Rights High Commissioner’s report, one of our colleagues – I don’t recall who asked you about that, and you noted the State Department report and you said we’re continuing to look at specific incidents to draw final determinations as to whether international humanitarian law was broken.
QUESTION: Are the incidents the six incidents mentioned in the UN report among the specific incidents that the U.S. (inaudible)?
MR MILLER: I have never spoken to and am not going to today speak to specific incidents that are under review, but there is a broad number of incidents that we are looking at.
QUESTION: But, I mean, in this case – like, I can’t go through all six of them, take too long, but one instance, a strike on the Taj3 Tower in Gaza City, the UN says was caused by several thousand-pound bombs, killing 105 people, including 32 women and 47 children. I mean, should it take eight months to make a final determination as to whether that was within international law?
MR MILLER: So as we have said before it is very difficult to draw fact specific conclusions when we don’t have someone on the ground and we’re in the middle of an active conflict. So what we do is we gather information. We talk to independent organizations to try to gather information and then we make our assessments. Those assessments are compounded by the sheer scale of this conflict and the number of incidents that we have to review and the limited resources that we have to make those assessments. But I can tell you there are people working hard on it day and night.
QUESTION: But how does it come – I don’t want to belabor the point, Matt, but how is to come that —
MR MILLER: I think you do.
QUESTION: — UN, Human Rights Watch, Amnesty, International Criminal Court, can all find compelling evidence of war crimes by Israel, and the United States with its enormous powers of intelligence and direct contact with Israel can’t find those things.
MR MILLER: I would say that different organizations have difference burdens, different responsibilities and we take ours very seriously, and are taking these assessments very seriously, and want to finish them as soon as possible, but it’s important that we get them right. Go ahead.
QUESTION: Talking about people on the ground, UNICEF Global Spokesperson James Elder report an incident that he witnessed in Gaza when Israeli forces struck two fisherman and then denied them medical care until they both died. Do you know about this incident? Do you have any comment?
MR MILLER: I have read the reports about – of the incident and I’m not able to verify them, obviously.
QUESTION: Okay. And Haaretz published a story on Tuesday about another Palestinian doctor dying after being detained and tortured in Israeli prison. His name is Dr. Iyad Rantisi. Do you have any answer of why doctors are being detained for – in the first place?
MR MILLER: I don’t have an answer with respect to this specific incident or with the overall policy. What we have made clear, as a general matter, is that we expect Israel in carrying out its detention policies and carrying out similar operations to fully respect human rights, fully respect the laws of war and allow people to have due process.
QUESTION: And lastly, there’s a picture circulating of Israeli soldier displaying Zionist plan of the greater Israeli – Israel on their uniform. This is the picture. So the badge shows a map, including Egypt, Saudi Arabia, Iraq, parts of them, Syria and all of Lebanon. Do you have any comment on that and does this serve the long-lasting peace agenda that you guys talk about?
MR MILLER: I haven’t seen that photo and I’ll admit that my eyes are not good enough to view it on your —
QUESTION: I can send it to you.
MR MILLER: I appreciate that. To view it on your phone from here, but we have made quite clear how we want to see this conflict resolved and we have made quite clear what we believe the future ought to be, and that’s the establishment of an independent Palestinian state.
QUESTION: Thank you, sir. Pakistani Prime Minister Shehbaz Sharif congratulated Indian Prime Minister Narendra Modi for securing a third term. We have seen messages on social media and many experts believe that both the prime minister have the ability to initiate the peace process and normalize the relationship. Do you have any comment on that?
MR MILLER: So we value our important relationships with both India and Pakistan. As we have said, we support direct discussions between India and Pakistan, but the pace, scope and character should be determined by those two countries, not by us.
QUESTION: Sir, Pakistani Ambassador (inaudible) Masood Khan has said that Pakistan needs modern American weapons to fight with the TTP, as they are using American weapons against Pakistani military forces that were left by U.S. forces in Afghanistan. So is the U.S. going to consider provide more U.S. military equipment to Pakistani security forces?
MR MILLER: So the United States and Pakistan have a shared interest in combating threats to regional security. We partner with Pakistan on security through our high-level counterterrorism dialogue, including several counterterrorism capacity building programs, and we support a series of U.S.-Pakistan military-to-military engagements. We are regular – in regular communication with the Pakistani leaders as a part of our partnership on CT issues, and we will continue to discuss regional security in detail, including through our annual counterterrorism dialogue and other bilateral consultations.
QUESTION: Sir, one last question. FBI and military officials and former CIA chief warn that the United States faces a serious threat of a terrorist attack in the months ahead. Have you seen their report? Do you have any comments?
MR MILLER: I have seen that report and I’ll say that we obviously take counterterrorism matters very seriously. It’s something that we work on across the inter-agency. The full suite of national security and law enforcement agencies work to detect terrorism plots, disrupt them and hold people accountable for them. Go ahead.
QUESTION: (Inaudible) follow up?
QUESTION: Sir, Senator Cardin recently said that Congress has taken steps to make sure the President can’t withdraw from a treaty or any of our commitments abroad. And following up on Ukraine and those diversion of foreign military sales, does this speak to not just the situation on the ground but like a renewed sense of tension and urgency around a possible Trump administration and like that destabilizing Ukrainian security?
MR MILLER: So I’m just not going to speak to something that relates to the election at all. I will make clear what our policy is with respect to Ukraine, and our commitment to Ukraine that we have made very clear, including through the signing of the bilateral security agreement, which is a long-term commitment by the United States of America. But when it comes to speculating about the effects of the election, I don’t think it’s appropriate for me to do. Yeah.
QUESTION: Thank you, sir. Two questions, please. One, as far as U.S.-India relations are concerned comparing with the Prime Minister Modi two and now Prime Minister Modi three, third time he’s the Prime Minister of India. And a lot is going on now between U.S. and India because the NSA – Mr. Sullivan in India, and also at the G7 prime minister was there, of course; the President, among others. So where do we stand now as far as under Modi three, relations between the two countries and military – I mean, diplomatically and also culture and many other things going on?
MR MILLER: India continues to be a close partner of the United States, not just at the government level but at the people-to-people level. We do share close economic ties, close cultural ties. They continue to be a partner that we work with on our Indo-Pacific strategy, and we will look forward to continue to do that with the government – with Prime Minister Modi’s government.
QUESTION: And second, if I may – sorry. America well-known for its football. But now cricket – USA is known around the globe, household name, is now there. And this is the first time that a U.S. cricket team, who are created here in this area, in Washington – and beating top T20 or top cricket teams, including Pakistan, many other nations also by the U.S. cricket team. My question is how this diplomacy will play – cricket diplomacy – around around the globe as far as – and not only the cricket team was created here, but also U.S. is also the hosting country for the Cricket World Cup.
MR MILLER: Yeah. So I would say that we are very proud of the United States cricket team and its recent success, just as we are proud of the U.S. men’s and women’s soccer team. The U.S. men’s soccer team is about to kick off the Copa America on Sunday, so we’ll be pulling for them, as we pulled for the United States cricket team. And it is true that sports plays a powerful role in diplomacy, in connecting people, including people from countries where governments have disputes or have longstanding historical disagreements. And so we continue to see sports as an important way to bring peoples together all around the world.
QUESTION: So what is the future of the U.S. cricket team?
MR MILLER: What’s that?
QUESTION: What is the future of the world – or U.S. cricket team.
MR MILLER: Well, I hope they’ll continue – I hope they’ll continue to be successful.
QUESTION: Thank you, sir.
QUESTION: How many cricket matches have you actually watched, Matt?
MR MILLER: I’m going to take that one back, Matt. (Laughter.)
QUESTION: Thank you so much. So Saudi crown prince calls for Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu to be held criminally accountable for his actions against Palestinians. He’s maybe hinting, like, with the Netanyahu-led Israeli state, maybe he will not ready for U.S.-led peace process with Israel – Saudi Arabia and Israel. How do you see that?
MR MILLER: So when it comes to the establishment of an independent Palestinian state, which is I think where ultimately that question goes, we’ve made quite clear that at the end of this conflict we you need to have plans for – we need to have political plans as well as military plans. We need to have plans for security in Gaza; we need to have plans for reconstruction in Gaza. And ultimately, we need to give the Palestinian people a path forward to their own self-determination, to present an alternative vision of the world to the one that Hamas has presented.
QUESTION: And secondly, India just surpasses Pakistan in nuclear arms race, standing at 172 where Pakistan at 170. And meanwhile, China is also accelerating, like, it have 500 nukes. So meanwhile, like, NATO members are in talks about to make standby their nuclear weapons regarding the Russian threats. And at the same time, some reports suggest that Chinese officials are showing concerns. It said, like, undermining nuclear disarmament and nonproliferation regimes and it should stop doing it – some of the Chinese officials quoted. With this timeline, do U.S. have some concerns on China and India nuclear acceleration?
MR MILLER: I’m just not going to comment from – I’m not going to comment on that here. I don’t think it’s productive to do so publicly.
Go ahead, in the back and then we’ll wrap.
QUESTION: Yes, thank —
QUESTION: Thank you —
MR MILLER: No, next to you. Go ahead. Sorry.
QUESTION: Okay. Hello. Thank you. After Israel took control of the Philadelphi route and the Rafah crossing, Egypt expressed its reservation and refused to coordinate with Israel regarding the operation of the Rafah crossing. How did Egypt address this issue in the conversation with the United States?
MR MILLER: So I’m not going to get into private conversations. But we have made clear in – that we want to see Rafah crossing reopen, and we have been engaged in conversations between Egypt and Israel. It’s something that they need to work on together, and so we’re trying to facilitate that process, and it’s one that remains ongoing.
QUESTION: Okay, another question, please. The – last month, the Israeli Broadcasting Authority published statements referring to the IDF Minister Gallant in which he said that Israel – there is no Palestinian state and the American understand this, adding the American public statement are not important. At the same time, the price of the Saudi Arabia peace includes the establishment of Palestinian state. What’s your comment, please, for this?
MR MILLER: Comment is the same that we have had said for some time, that we think ultimately the only way to resolve the longstanding tension in the region, the longstanding disputes between Israel and the Palestinian people, is the establishment of a Palestinian state. And we are working on not just day-after plans for the conflict in Gaza, but long-term plans to achieve that.
Go ahead, and then we’ll wrap for today.
QUESTION: Thank you, Matt. Yes, thank you. As you know that the head of Hizballah, like, threatened Cyprus yesterday, that he’s ready to attack the island. And any comment, please, sir, since this is the first time that Nasrallah threatened Cyprus?
And also, can you tell us how was the meeting between the Secretary and the foreign minister of Cyprus today?
MR MILLER: So let me take it kind of in reverse order. It was an incredibly productive meeting. The Secretary thanked the – thanked the Government of Cyprus for all the work that they have done to facilitate the delivery of humanitarian assistance to the people of Gaza. And I just want to highlight that, again, that Cyprus has really played a key role as a staging area for delivering humanitarian assistance that makes it to Gaza, that helps innocent Palestinians, that feeds innocent Palestinians. And why Hizballah would attack a country in the middle of that important humanitarian role it’s playing, why they would launch this kind of verbal attack, is just beyond me.
And with that, we’ll wrap for today.
Oh yeah – yeah.
QUESTION: Can I just ask one – one quick question on the Dermer and Hanegbi meeting. Does the Secretary plan to reiterate that there are no bottlenecks in U.S. weapons going to Israel, despite Netanyahu’s comments?
MR MILLER: So I don’t want to preview a meeting before it happens, but that has been something that we have consistently made clear to the Government of Israel. So —
QUESTION: So you don’t think you have to make clear that perception again?
MR MILLER: I just don’t want to speak to the meeting that’s starting in a few minutes. We’ll be happy to talk about it afterwards.
(The briefing was concluded at 2:58 p.m.)
U.S. Department of State
The lessons of 1989: freedom and our future.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Start before you say the first word. Don't think of your presentation opener only as the actual words you're gonna say. Your opener starts before you even open your mouth: it's the way you enter the stage, the way you smile at the audience, the way you're dressed, your voice and body language. So prepare yourself, stand tall, smile, be ...
Tip: An easy way to make your writing more concise is to start your sentences with the subject. Also, try to limit the number of adverbs and adjectives you use. 3. Tailor your writing to your audience. Being aware of your audience while you're writing will help you craft a more persuasive message.
Conclusion. Mastering a persuasive speech is about connection, clarity, and conviction. Remember the essentials: a well-structured argument supports your message and engaging topics capture attention. Outline each argument with care, making it easy for listeners to follow, then balance facts with stories that stir emotions.
The purpose of a persuasive speech is to convince your audience to agree with an idea or opinion that you present. First, you'll need to choose a side on a controversial topic, then you will write a speech to explain your position, and convince the audience to agree with you. You can produce an effective persuasive speech if you structure your ...
Preview. This is the easiest piece of the introduction to write because, at its core, it's the same for every speech. Give the audience a roadmap, or signposts, of the next three big points you'll be discussing. In a persuasive speech, your signposts are typically the problems, causes, and solutions. Example: "Let's first learn more ...
Step 2: After the Story, Now, Give Your Advice. When most people write a persuasive presentation, they start with their opinion. Again, this makes the listener want to play Devil's advocate. By starting with the example, we give the listener a simple way to agree with us.
If you make a mistake, don't let it derail your whole speech. This might be an opportunity to use a little humor. Then, move on. 4. Involve your audience. If there is something specific you'd like your audience to do, provide them with any resources you can to make it easier.
Ideas for your persuasive speech outline 1. Structure of your persuasive speech. The opening and closing of speech are the most important. Consider these carefully when thinking about your persuasive speech outline. A strong opening ensures you have the audience's attention from the start and gives them a positive first impression of you.
Keep your introduction short, and not more than 10-15% of your speech. If your speech is 2000 words, then your introduction should be a maximum of 200-250 words. Or if you are presenting for 10 minutes, your introduction should be a maximum of 2 minutes. This will give you time to state your main points and help you manage your time effectively.
An essential part of putting together a good persuasive speech is finding credible evidence to support your argument. Seek out reputable, reliable, quotable sources to back the points you make. Without them your speech will fail its purpose. Persuasion is a synthesis of emotional as well as intellectual appeal.
Analyze their response and tweak the joke accordingly if necessary. Starting your speech with humour means your setting the tone of your speech. It would make sense to have a few more jokes sprinkled around the rest of the speech as well as the audience might be expecting the same from you. 4. Mohammed Qahtani.
Here are 26 different techniques for beginning your speech: 1. Use a quote. One method of starting a speech and gaining the audience's attention is to use a famous or relatable quote. This approach can give your audience context for your topic and connect it to something they recognize. For instance, if you plan to give a speech on a political ...
In your speech outline, you want to touch on several key elements. Pick your fight: Start by zeroing in on what you really want to change or influence with this speech. Support your claim with evidence: Identify those key points that back up your stance to appeal to your audience's rational side. The emotional hook: Weave in stories or facts ...
Step 2 - Select a good persuasive speech topic to accomplish the goal and choose a position. How to write a persuasive speech. Step 3 - Locate credible and reliable sources and identify evidence in support of the topic/position. Revisit Step 2 if there is a lack of relevant resources. Step 4 - Identify the audience and understand their ...
Opening Lines of the Top 10 Greatest Speeches of All Time. #1: Socrates - "Apology". "How you, men of Athens, have been affected by my accusers. I do not know.". #2: Patrick Henry - "Give Me Liberty or Give Me Death". "Mr. President, it is natural to man to indulge in the illusions of hope.".
1) Thank the Organizers and Audience. You can start by thanking the audience for coming and thanking the organization for inviting you to speak. Refer to the person who introduced you or to one or more of the senior people in the organization in the audience. This compliments them, makes them feel proud and happy about your presence, and ...
Start your persuasive speech with a strong introduction, grabbing the attention of your audience. This can be emotional, shocking, or funny - as long as it is powerful. After you have your audience's attention, you should clearly introduce the topic of your speech. You now need to distil your research into a few key arguments.
Avoid awkward constructions that might cause a speaker to stumble. Tip: Read the speech aloud as you're writing. If you do it enough, you'll start hearing the words when you type them. 2. Tell ...
Not sure where to start with writing a persuasive speech? With these six steps, learn how to write a persuasive speech easily and captivate your audience.
112 Engaging Persuasive Speech Topics. Tips for Preparing Your Persuasive Speech. Writing a stellar persuasive speech requires a carefully crafted argument that will resonate with your audience to sway them to your side. This feat can be challenging to accomplish, but an engaging, thought-provoking speech topic is an excellent place to start.
Read on for six key elements to include at the start of your persuasive speeches. 1. A Strong Hook. Add a powerful opener (hook) to get the audience emotionally engaged from the get-go. This could be a shocking statistic, a thought-provoking quote, an emotive short story, or a rhetorical question.
The right emotional appeal can make an audience start to see things your way. Logos: Logic seals the deal. A well-reasoned argument backed by solid facts? ... Good persuasive speeches do more than wade through facts. They spark engaging dialogues, challenge people's beliefs, and maybe even alter their viewpoints.
In many ways, a persuasive speech is structured like an informative speech. It has an introduction with an attention-getter and a clear thesis statement. It also has a body where the speaker presents their main points and it ends with a conclusion that sums up the main point of the speech. The biggest difference is that the primary purpose of ...
5. Melissa Butler. Speech Ending: When you go home today, see yourself in the mirror, see all of you, look at all your greatness that you embody, accept it, love it and finally, when you leave the house tomorrow, try to extend that same love and acceptance to someone who doesn't look like you. 6.
You've written a good speech. You feel more confident about giving a speech in public, and you've practiced. You're ready to actually give the speech. There are some tips and tricks you can use on the day of your speech to make it go more smoothly, though.
His history-only approach, she wrote, was "wrong twice over": Thomas both botched the relevant history and failed to make a persuasive case for its use in the first place. Start with "the ...
2:09 p.m. EDT MR MILLER: Good afternoon. QUESTION: Good afternoon. MR MILLER: At the risk of disappointing everyone, I don't have any opening comments. So Matt is first. QUESTION: Why - disappointing us, really? MR MILLER: That was a bit facetious on my part perhaps. QUESTION: Okay. All right. So let's just start in […]