- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources

How to Make a Literature Review in Research (RRL Example)
What is an RRL in a research paper?
A relevant review of the literature (RRL) is an objective, concise, critical summary of published research literature relevant to a topic being researched in an article. In an RRL, you discuss knowledge and findings from existing literature relevant to your study topic. If there are conflicts or gaps in existing literature, you can also discuss these in your review, as well as how you will confront these missing elements or resolve these issues in your study.
To complete an RRL, you first need to collect relevant literature; this can include online and offline sources. Save all of your applicable resources as you will need to include them in your paper. When looking through these sources, take notes and identify concepts of each source to describe in the review of the literature.
A good RRL does NOT:
A literature review does not simply reference and list all of the material you have cited in your paper.
- Presenting material that is not directly relevant to your study will distract and frustrate the reader and make them lose sight of the purpose of your study.
- Starting a literature review with “A number of scholars have studied the relationship between X and Y” and simply listing who has studied the topic and what each scholar concluded is not going to strengthen your paper.
A good RRL DOES:
- Present a brief typology that orders articles and books into groups to help readers focus on unresolved debates, inconsistencies, tensions, and new questions about a research topic.
- Summarize the most relevant and important aspects of the scientific literature related to your area of research
- Synthesize what has been done in this area of research and by whom, highlight what previous research indicates about a topic, and identify potential gaps and areas of disagreement in the field
- Give the reader an understanding of the background of the field and show which studies are important—and highlight errors in previous studies
How long is a review of the literature for a research paper?
The length of a review of the literature depends on its purpose and target readership and can vary significantly in scope and depth. In a dissertation, thesis, or standalone review of literature, it is usually a full chapter of the text (at least 20 pages). Whereas, a standard research article or school assignment literature review section could only be a few paragraphs in the Introduction section .
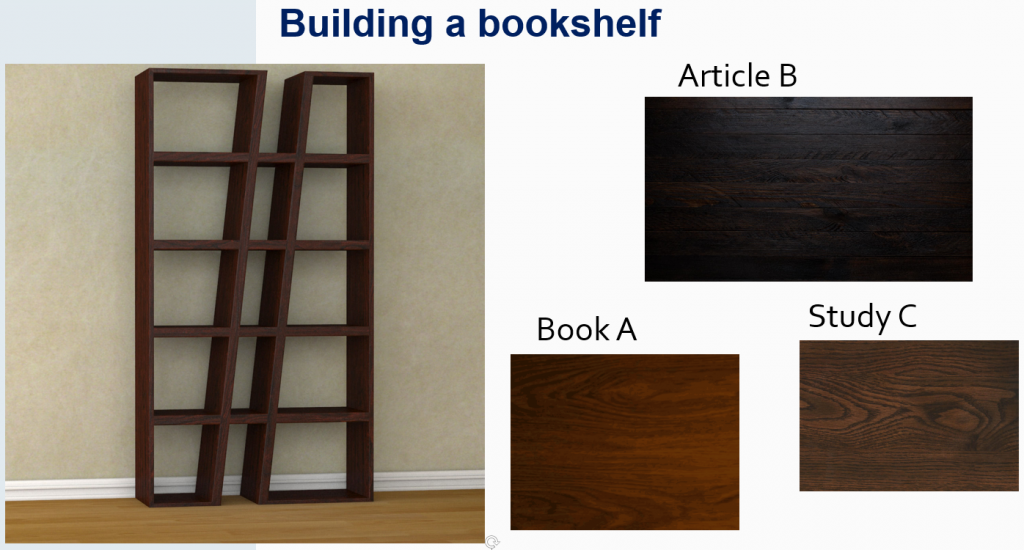
Building Your Literature Review Bookshelf
One way to conceive of a literature review is to think about writing it as you would build a bookshelf. You don’t need to cut each piece by yourself from scratch. Rather, you can take the pieces that other researchers have cut out and put them together to build a framework on which to hang your own “books”—that is, your own study methods, results, and conclusions.
What Makes a Good Literature Review?
The contents of a literature review (RRL) are determined by many factors, including its precise purpose in the article, the degree of consensus with a given theory or tension between competing theories, the length of the article, the number of previous studies existing in the given field, etc. The following are some of the most important elements that a literature review provides.
Historical background for your research
Analyze what has been written about your field of research to highlight what is new and significant in your study—or how the analysis itself contributes to the understanding of this field, even in a small way. Providing a historical background also demonstrates to other researchers and journal editors your competency in discussing theoretical concepts. You should also make sure to understand how to paraphrase scientific literature to avoid plagiarism in your work.
The current context of your research
Discuss central (or peripheral) questions, issues, and debates in the field. Because a field is constantly being updated by new work, you can show where your research fits into this context and explain developments and trends in research.
A discussion of relevant theories and concepts
Theories and concepts should provide the foundation for your research. For example, if you are researching the relationship between ecological environments and human populations, provide models and theories that focus on specific aspects of this connection to contextualize your study. If your study asks a question concerning sustainability, mention a theory or model that underpins this concept. If it concerns invasive species, choose material that is focused in this direction.
Definitions of relevant terminology
In the natural sciences, the meaning of terms is relatively straightforward and consistent. But if you present a term that is obscure or context-specific, you should define the meaning of the term in the Introduction section (if you are introducing a study) or in the summary of the literature being reviewed.
Description of related relevant research
Include a description of related research that shows how your work expands or challenges earlier studies or fills in gaps in previous work. You can use your literature review as evidence of what works, what doesn’t, and what is missing in the field.
Supporting evidence for a practical problem or issue your research is addressing that demonstrates its importance: Referencing related research establishes your area of research as reputable and shows you are building upon previous work that other researchers have deemed significant.
Types of Literature Reviews
Literature reviews can differ in structure, length, amount, and breadth of content included. They can range from selective (a very narrow area of research or only a single work) to comprehensive (a larger amount or range of works). They can also be part of a larger work or stand on their own.
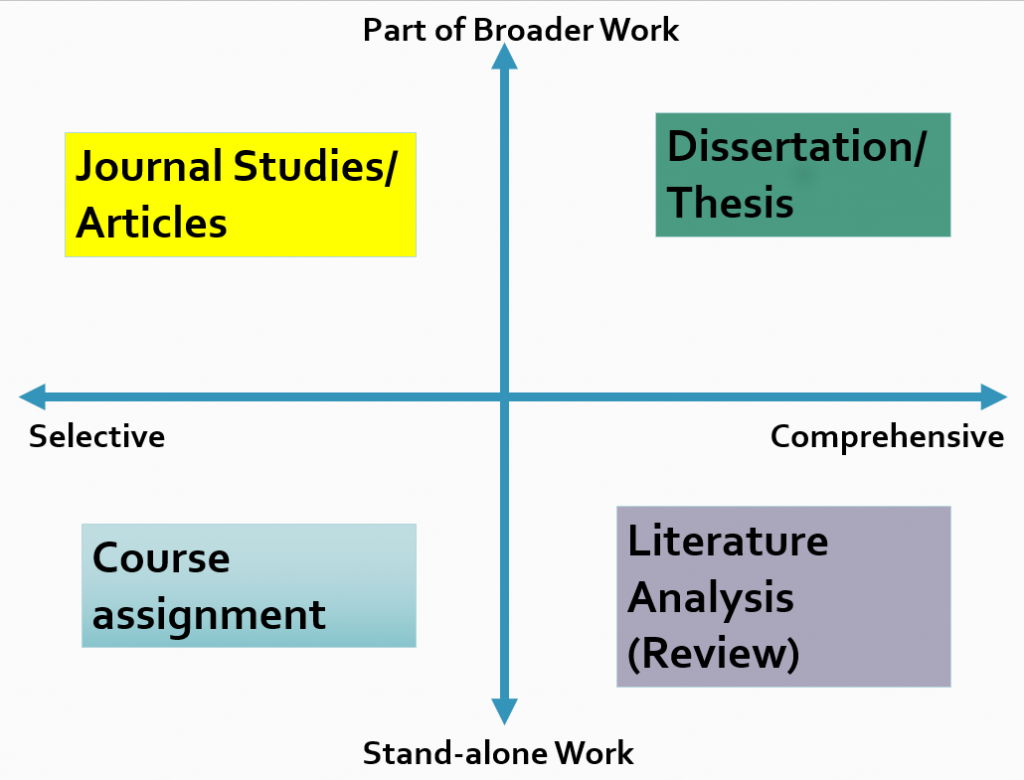
- A course assignment is an example of a selective, stand-alone work. It focuses on a small segment of the literature on a topic and makes up an entire work on its own.
- The literature review in a dissertation or thesis is both comprehensive and helps make up a larger work.
- A majority of journal articles start with a selective literature review to provide context for the research reported in the study; such a literature review is usually included in the Introduction section (but it can also follow the presentation of the results in the Discussion section ).
- Some literature reviews are both comprehensive and stand as a separate work—in this case, the entire article analyzes the literature on a given topic.
Literature Reviews Found in Academic Journals
The two types of literature reviews commonly found in journals are those introducing research articles (studies and surveys) and stand-alone literature analyses. They can differ in their scope, length, and specific purpose.
Literature reviews introducing research articles
The literature review found at the beginning of a journal article is used to introduce research related to the specific study and is found in the Introduction section, usually near the end. It is shorter than a stand-alone review because it must be limited to very specific studies and theories that are directly relevant to the current study. Its purpose is to set research precedence and provide support for the study’s theory, methods, results, and/or conclusions. Not all research articles contain an explicit review of the literature, but most do, whether it is a discrete section or indistinguishable from the rest of the Introduction.
How to structure a literature review for an article
When writing a literature review as part of an introduction to a study, simply follow the structure of the Introduction and move from the general to the specific—presenting the broadest background information about a topic first and then moving to specific studies that support your rationale , finally leading to your hypothesis statement. Such a literature review is often indistinguishable from the Introduction itself—the literature is INTRODUCING the background and defining the gaps your study aims to fill.
The stand-alone literature review
The literature review published as a stand-alone article presents and analyzes as many of the important publications in an area of study as possible to provide background information and context for a current area of research or a study. Stand-alone reviews are an excellent resource for researchers when they are first searching for the most relevant information on an area of study.
Such literature reviews are generally a bit broader in scope and can extend further back in time. This means that sometimes a scientific literature review can be highly theoretical, in addition to focusing on specific methods and outcomes of previous studies. In addition, all sections of such a “review article” refer to existing literature rather than describing the results of the authors’ own study.
In addition, this type of literature review is usually much longer than the literature review introducing a study. At the end of the review follows a conclusion that once again explicitly ties all of the cited works together to show how this analysis is itself a contribution to the literature. While not absolutely necessary, such articles often include the terms “Literature Review” or “Review of the Literature” in the title. Whether or not that is necessary or appropriate can also depend on the specific author instructions of the target journal. Have a look at this article for more input on how to compile a stand-alone review article that is insightful and helpful for other researchers in your field.

How to Write a Literature Review in 6 Steps
So how do authors turn a network of articles into a coherent review of relevant literature?
Writing a literature review is not usually a linear process—authors often go back and check the literature while reformulating their ideas or making adjustments to their study. Sometimes new findings are published before a study is completed and need to be incorporated into the current work. This also means you will not be writing the literature review at any one time, but constantly working on it before, during, and after your study is complete.
Here are some steps that will help you begin and follow through on your literature review.
Step 1: Choose a topic to write about—focus on and explore this topic.
Choose a topic that you are familiar with and highly interested in analyzing; a topic your intended readers and researchers will find interesting and useful; and a topic that is current, well-established in the field, and about which there has been sufficient research conducted for a review. This will help you find the “sweet spot” for what to focus on.
Step 2: Research and collect all the scholarly information on the topic that might be pertinent to your study.
This includes scholarly articles, books, conventions, conferences, dissertations, and theses—these and any other academic work related to your area of study is called “the literature.”
Step 3: Analyze the network of information that extends or responds to the major works in your area; select the material that is most useful.
Use thought maps and charts to identify intersections in the research and to outline important categories; select the material that will be most useful to your review.
Step 4: Describe and summarize each article—provide the essential information of the article that pertains to your study.
Determine 2-3 important concepts (depending on the length of your article) that are discussed in the literature; take notes about all of the important aspects of this study relevant to the topic being reviewed.
For example, in a given study, perhaps some of the main concepts are X, Y, and Z. Note these concepts and then write a brief summary about how the article incorporates them. In reviews that introduce a study, these can be relatively short. In stand-alone reviews, there may be significantly more texts and more concepts.
Step 5: Demonstrate how these concepts in the literature relate to what you discovered in your study or how the literature connects the concepts or topics being discussed.
In a literature review intro for an article, this information might include a summary of the results or methods of previous studies that correspond to and/or confirm those sections in your own study. For a stand-alone literature review, this may mean highlighting the concepts in each article and showing how they strengthen a hypothesis or show a pattern.
Discuss unaddressed issues in previous studies. These studies that are missing something you address are important to include in your literature review. In addition, those works whose theories and conclusions directly support your findings will be valuable to review here.
Step 6: Identify relationships in the literature and develop and connect your own ideas to them.
This is essentially the same as step 5 but focused on the connections between the literature and the current study or guiding concepts or arguments of the paper, not only on the connections between the works themselves.
Your hypothesis, argument, or guiding concept is the “golden thread” that will ultimately tie the works together and provide readers with specific insights they didn’t have before reading your literature review. Make sure you know where to put the research question , hypothesis, or statement of the problem in your research paper so that you guide your readers logically and naturally from your introduction of earlier work and evidence to the conclusions you want them to draw from the bigger picture.
Your literature review will not only cover publications on your topics but will include your own ideas and contributions. By following these steps you will be telling the specific story that sets the background and shows the significance of your research and you can turn a network of related works into a focused review of the literature.
Literature Review (RRL) Examples
Because creating sample literature reviews would take too long and not properly capture the nuances and detailed information needed for a good review, we have included some links to different types of literature reviews below. You can find links to more literature reviews in these categories by visiting the TUS Library’s website . Sample literature reviews as part of an article, dissertation, or thesis:
- Critical Thinking and Transferability: A Review of the Literature (Gwendolyn Reece)
- Building Customer Loyalty: A Customer Experience Based Approach in a Tourism Context (Martina Donnelly)
Sample stand-alone literature reviews
- Literature Review on Attitudes towards Disability (National Disability Authority)
- The Effects of Communication Styles on Marital Satisfaction (Hannah Yager)
Additional Literature Review Format Guidelines
In addition to the content guidelines above, authors also need to check which style guidelines to use ( APA , Chicago, MLA, etc.) and what specific rules the target journal might have for how to structure such articles or how many studies to include—such information can usually be found on the journals’ “Guide for Authors” pages. Additionally, use one of the four Wordvice citation generators below, choosing the citation style needed for your paper:
Wordvice Writing and Academic Editing Resources
Finally, after you have finished drafting your literature review, be sure to receive professional proofreading services , including paper editing for your academic work. A competent proofreader who understands academic writing conventions and the specific style guides used by academic journals will ensure that your paper is ready for publication in your target journal.
See our academic resources for further advice on references in your paper , how to write an abstract , how to write a research paper title, how to impress the editor of your target journal with a perfect cover letter , and dozens of other research writing and publication topics.

Review of Related Literature (RRL)
Ai generator.
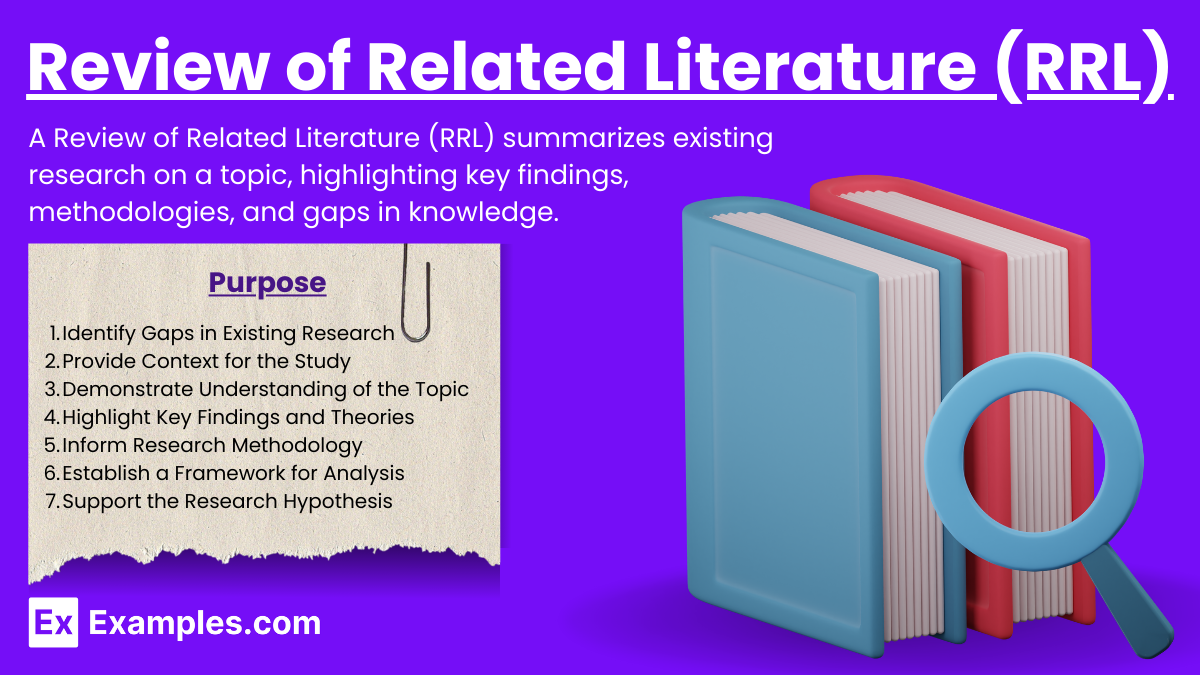
The Review of Related Literature (RRL) is a crucial section in research that examines existing studies and publications related to a specific topic. It summarizes and synthesizes previous findings, identifies gaps, and provides context for the current research. RRL ensures the research is grounded in established knowledge, guiding the direction and focus of new studies.
What Is Review of Related Literature (RRL)?
The Review of Related Literature (RRL) is a detailed analysis of existing research relevant to a specific topic. It evaluates, synthesizes, and summarizes previous studies to identify trends, gaps, and conflicts in the literature. RRL provides a foundation for new research, ensuring it builds on established knowledge and addresses existing gaps.
Format of Review of Related Literature (RRL)
The Review of Related Literature (RRL) is a critical part of any research paper or thesis . It provides an overview of existing research on your topic and helps to establish the context for your study. Here is a typical format for an RRL:
1. Introduction
- Purpose : Explain the purpose of the review and its importance to your research.
- Scope : Define the scope of the literature reviewed, including the time frame, types of sources, and key themes.
2. Theoretical Framework
- Concepts and Theories : Present the main theories and concepts that underpin your research.
- Relevance : Explain how these theories relate to your study.
3. Review of Empirical Studies
- Sub-theme 1 : Summarize key studies, including methodologies, findings, and conclusions.
- Sub-theme 2 : Continue summarizing studies, focusing on different aspects or variables.
- Sub-theme 3 : Include any additional relevant studies.
4. Methodological Review
- Approaches : Discuss the various methodologies used in the reviewed studies.
- Strengths and Weaknesses : Highlight the strengths and weaknesses of these methodologies.
- Gaps : Identify gaps in the existing research that your study aims to address.
5. Synthesis and Critique
- Integration : Integrate findings from the reviewed studies to show the current state of knowledge.
- Critique : Critically evaluate the literature, discussing inconsistencies, limitations, and areas for further research.
6. Conclusion
- Summary : Summarize the main findings from the literature review.
- Research Gap : Clearly state the research gap your study will address.
- Contribution : Explain how your study will contribute to the existing body of knowledge.
7. References
- Citation Style : List all the sources cited in your literature review in the appropriate citation style (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago).
Review of Related Literature (RRL) 1. Introduction This review examines research on social media’s impact on mental health, focusing on anxiety and depression across various demographics over the past ten years. 2. Theoretical Framework Anchored in Social Comparison Theory and Uses and Gratifications Theory, this review explores how individuals’ social media interactions affect their mental health. 3. Review of Empirical Studies Adolescents’ Mental Health Instagram & Body Image : Smith & Johnson (2017) found Instagram use linked to body image issues and lower self-esteem among 500 high school students. Facebook & Anxiety : Brown & Green (2016) showed Facebook use correlated with higher anxiety and depressive symptoms in a longitudinal study of 300 students. Young Adults’ Mental Health Twitter & Stress : Davis & Lee (2018) reported higher stress levels among heavy Twitter users in a survey of 400 university students. LinkedIn & Self-Esteem : Miller & White (2019) found LinkedIn use positively influenced professional self-esteem in 200 young professionals. Adult Mental Health General Social Media Use : Thompson & Evans (2020) found moderate social media use associated with better mental health outcomes, while excessive use correlated with higher anxiety and depression in 1,000 adults. 4. Methodological Review Studies used cross-sectional surveys, longitudinal designs, and mixed methods. Cross-sectional surveys provided large data sets but couldn’t infer causation. Longitudinal studies offered insights into long-term effects but were resource-intensive. Mixed methods enriched data through qualitative insights but required careful integration. 5. Synthesis and Critique The literature shows a complex relationship between social media and mental health, with platform-specific and demographic-specific effects. However, reliance on self-reported data introduces bias, and many cross-sectional studies limit causal inference. More longitudinal and experimental research is needed. 6. Conclusion Current research offers insights into social media’s mental health impact but leaves gaps, particularly regarding long-term effects and causation. This study aims to address these gaps through comprehensive longitudinal analysis. 7. References Brown, A., & Green, K. (2016). Facebook Use and Anxiety Among High School Students . Psychology in the Schools, 53(3), 257-264. Davis, R., & Lee, S. (2018). Twitter and Psychological Stress: A Study of University Students . Journal of College Student Development, 59(2), 120-135. Miller, P., & White, H. (2019). LinkedIn and Its Effect on Professional Self-Esteem . Journal of Applied Psychology, 104(1), 78-90. Smith, J., & Johnson, L. (2017). The Impact of Instagram on Teen Body Image . Journal of Adolescent Health, 60(5), 555-560. Thompson, M., & Evans, D. (2020). The Relationship Between Social Media Use and Mental Health in Adults . Cyberpsychology, Behavior, and Social Networking, 23(4), 201-208.
Review of Related Literature (RRL) Examples
Review of related literature in research, review of related literature in research paper, review of related literature qualitative research.

Review of Related Literature Quantitative Research

More Review of Related Literature (RRL) Examples
- Impact of E-learning on Student Performance
- Effectiveness of Mindfulness in Workplace
- Green Building and Energy Efficiency
- Impact of Technology on Healthcare Delivery
- Effects of Nutrition on Cognitive Development in Children
- Impact of Employee Training Programs on Productivity
- Effects of Climate Change on Biodiversity
- Impact of Parental Involvement on Student Achievement
- Effects of Mobile Learning on Student Engagement
- Effects of Urban Green Spaces on Mental Health
Purpose of the Review of Related Literature (RRL)
The Review of Related Literature (RRL) serves several critical purposes in research:
- Establishing Context : It situates your research within the broader field, showing how your study relates to existing work.
- Identifying Gaps : It highlights gaps, inconsistencies, and areas needing further exploration in current knowledge, providing a clear rationale for your study.
- Avoiding Duplication : By reviewing what has already been done, it helps ensure your research is original and not a repetition of existing studies.
- Building on Existing Knowledge : It allows you to build on the findings of previous research, using established theories and methodologies to inform your work.
- Theoretical Foundation : It provides a theoretical basis for your research, grounding it in existing concepts and theories.
- Methodological Insights : It offers insights into the methods and approaches used in similar studies, helping you choose the most appropriate methods for your research.
- Establishing Credibility : It demonstrates your familiarity with the field, showing that you are well-informed and have a solid foundation for your research.
- Supporting Arguments : It provides evidence and support for your research questions, hypotheses, and objectives, strengthening the overall argument of your study.
How to Write Review of Related Literature (RRL)
Writing a Review of Related Literature (RRL) involves several key steps. Here’s a step-by-step guide:
1. Define the Scope and Objectives
- Determine the Scope : Decide on the breadth of the literature you will review, including specific themes, time frame, and types of sources.
- Set Objectives : Clearly define the purpose of the review. What do you aim to achieve? Identify gaps, establish context, or build on existing knowledge.
2. Search for Relevant Literature
- Identify Keywords : Use keywords and phrases related to your research topic.
- Use Databases : Search academic databases like Google Scholar, PubMed, JSTOR, etc., for relevant articles, books, and papers.
- Select Sources : Choose sources that are credible, recent, and relevant to your research.
3. Evaluate and Select the Literature
- Read Abstracts and Summaries : Quickly determine the relevance of each source.
- Assess Quality : Consider the methodology, credibility of the authors, and publication source.
- Select Key Studies : Choose studies that are most relevant to your research questions and objectives.
4. Organize the Literature
- Thematic Organization : Group studies by themes or topics.
- Chronological Organization : Arrange studies in the order they were published to show the development of ideas over time.
- Methodological Organization : Categorize studies by the methods they used.
5. Write the Review
- State the purpose and scope of the review.
- Explain the importance of the topic.
- Theoretical Framework : Present and discuss the main theories and concepts.
- Summarize key studies, including their methodologies, findings, and conclusions.
- Organize by themes or other chosen organizational methods.
- Methodological Review : Discuss the various methodologies used, highlighting their strengths and weaknesses.
- Synthesis and Critique : Integrate findings, critically evaluate the literature, and identify gaps or inconsistencies.
- Summarize the main findings from the literature review.
- Highlight the research gaps your study will address.
- State how your research will contribute to the existing knowledge.
6. Cite the Sources
- Use Appropriate Citation Style : Follow the required citation style (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago).
- List References : Provide a complete list of all sources cited in your review.
What is an RRL?
An RRL summarizes and synthesizes existing research on a specific topic to identify gaps and guide future studies.

Why is RRL important?
It provides context, highlights gaps, and ensures new research builds on existing knowledge.
How do you write an RRL?
Organize by themes, summarize studies, evaluate methodologies, identify gaps, and conclude with relevance to current research.
What sources are used in RRL?
Peer-reviewed journals, books, conference papers, and credible online resources.
How long should an RRL be?
Length varies; typically 10-20% of the total research paper.
What are common RRL mistakes?
Lack of organization, insufficient synthesis, over-reliance on outdated sources, and failure to identify gaps.
Can an RRL include non-scholarly sources?
Primarily scholarly, but reputable non-scholarly sources can be included for context.
What is the difference between RRL and bibliography?
RRL synthesizes and analyzes the literature, while a bibliography lists sources.
How often should an RRL be updated?
Regularly, especially when new relevant research is published.
Can an RRL influence research direction?
Yes, it identifies gaps and trends that shape the focus and methodology of new research.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

- My Library Account
- Articles, Books & More
- Course Reserves
- Site Search
- Advanced Search
- Sac State Library
- Research Guides
- Writing a Literature Review
- Organizing Your Literature Review
- What is a Literature Review?
- Literature Review Examples
- Managing your Citations
- Further Reading on Lit Reviews
How to Organize Your review
- << Previous: Literature Review Examples
- Next: Managing your Citations >>
- Last Updated: Jun 6, 2024 9:36 AM
- URL: https://csus.libguides.com/litreview
404 Not found
Review of Related Literature: Format, Example, & How to Make RRL
A review of related literature is a separate paper or a part of an article that collects and synthesizes discussion on a topic. Its purpose is to show the current state of research on the issue and highlight gaps in existing knowledge. A literature review can be included in a research paper or scholarly article, typically following the introduction and before the research methods section.

This article will clarify the definition, significance, and structure of a review of related literature. You’ll also learn how to organize your literature review and discover ideas for an RRL in different subjects.
🔤 What Is RRL?
- ❗ Significance of Literature Review
- 🔎 How to Search for Literature
- 🧩 Literature Review Structure
- 📋 Format of RRL — APA, MLA, & Others
- ✍️ How to Write an RRL
- 📚 Examples of RRL
🔗 References
A review of related literature (RRL) is a part of the research report that examines significant studies, theories, and concepts published in scholarly sources on a particular topic. An RRL includes 3 main components:
- A short overview and critique of the previous research.
- Similarities and differences between past studies and the current one.
- An explanation of the theoretical frameworks underpinning the research.
❗ Significance of Review of Related Literature
Although the goal of a review of related literature differs depending on the discipline and its intended use, its significance cannot be overstated. Here are some examples of how a review might be beneficial:
- It helps determine knowledge gaps .
- It saves from duplicating research that has already been conducted.
- It provides an overview of various research areas within the discipline.
- It demonstrates the researcher’s familiarity with the topic.
🔎 How to Perform a Literature Search
Including a description of your search strategy in the literature review section can significantly increase your grade. You can search sources with the following steps:
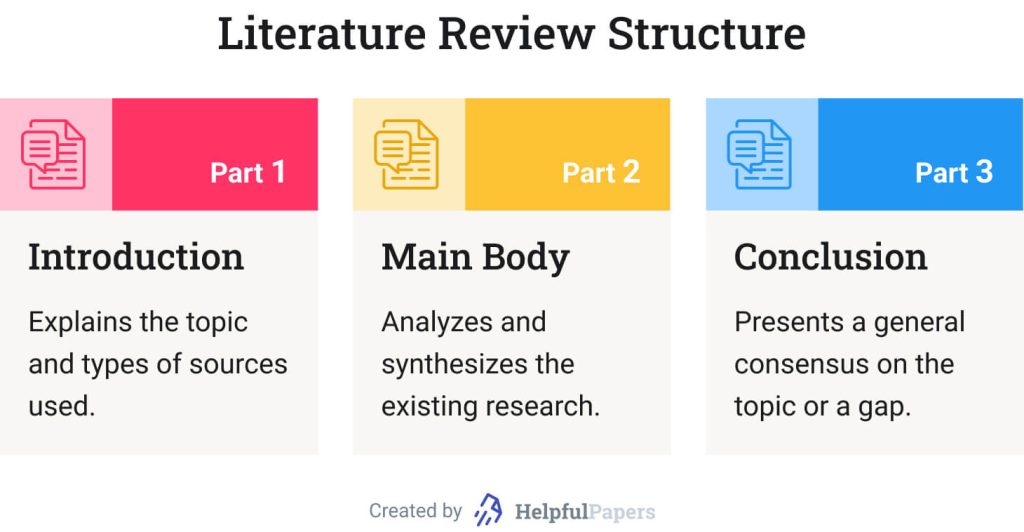
🧩 Literature Review Structure Example
The majority of literature reviews follow a standard introduction-body-conclusion structure. Let’s look at the RRL structure in detail.
Introduction of Review of Related Literature: Sample
An introduction should clarify the study topic and the depth of the information to be delivered. It should also explain the types of sources used. If your lit. review is part of a larger research proposal or project, you can combine its introductory paragraph with the introduction of your paper.
Here is a sample introduction to an RRL about cyberbullying:
Bullying has troubled people since the beginning of time. However, with modern technological advancements, especially social media, bullying has evolved into cyberbullying. As a result, nowadays, teenagers and adults cannot flee their bullies, which makes them feel lonely and helpless. This literature review will examine recent studies on cyberbullying.
Sample Review of Related Literature Thesis
A thesis statement should include the central idea of your literature review and the primary supporting elements you discovered in the literature. Thesis statements are typically put at the end of the introductory paragraph.
Look at a sample thesis of a review of related literature:
This literature review shows that scholars have recently covered the issues of bullies’ motivation, the impact of bullying on victims and aggressors, common cyberbullying techniques, and victims’ coping strategies. However, there is still no agreement on the best practices to address cyberbullying.
Literature Review Body Paragraph Example
The main body of a literature review should provide an overview of the existing research on the issue. Body paragraphs should not just summarize each source but analyze them. You can organize your paragraphs with these 3 elements:
- Claim . Start with a topic sentence linked to your literature review purpose.
- Evidence . Cite relevant information from your chosen sources.
- Discussion . Explain how the cited data supports your claim.
Here’s a literature review body paragraph example:
Scholars have examined the link between the aggressor and the victim. Beran et al. (2007) state that students bullied online often become cyberbullies themselves. Faucher et al. (2014) confirm this with their findings: they discovered that male and female students began engaging in cyberbullying after being subject to bullying. Hence, one can conclude that being a victim of bullying increases one’s likelihood of becoming a cyberbully.
Review of Related Literature: Conclusion
A conclusion presents a general consensus on the topic. Depending on your literature review purpose, it might include the following:
- Introduction to further research . If you write a literature review as part of a larger research project, you can present your research question in your conclusion .
- Overview of theories . You can summarize critical theories and concepts to help your reader understand the topic better.
- Discussion of the gap . If you identified a research gap in the reviewed literature, your conclusion could explain why that gap is significant.
Check out a conclusion example that discusses a research gap:
There is extensive research into bullies’ motivation, the consequences of bullying for victims and aggressors, strategies for bullying, and coping with it. Yet, scholars still have not reached a consensus on what to consider the best practices to combat cyberbullying. This question is of great importance because of the significant adverse effects of cyberbullying on victims and bullies.
📋 Format of RRL — APA, MLA, & Others
In this section, we will discuss how to format an RRL according to the most common citation styles: APA, Chicago, MLA, and Harvard.
Writing a literature review using the APA7 style requires the following text formatting:
- When using APA in-text citations , include the author’s last name and the year of publication in parentheses.
- For direct quotations , you must also add the page number. If you use sources without page numbers, such as websites or e-books, include a paragraph number instead.
- When referring to the author’s name in a sentence , you do not need to repeat it at the end of the sentence. Instead, include the year of publication inside the parentheses after their name.
- The reference list should be included at the end of your literature review. It is always alphabetized by the last name of the author (from A to Z), and the lines are indented one-half inch from the left margin of your paper. Do not forget to invert authors’ names (the last name should come first) and include the full titles of journals instead of their abbreviations. If you use an online source, add its URL.
The RRL format in the Chicago style is as follows:
- Author-date . You place your citations in brackets within the text, indicating the name of the author and the year of publication.
- Notes and bibliography . You place your citations in numbered footnotes or endnotes to connect the citation back to the source in the bibliography.
- The reference list, or bibliography , in Chicago style, is at the end of a literature review. The sources are arranged alphabetically and single-spaced. Each bibliography entry begins with the author’s name and the source’s title, followed by publication information, such as the city of publication, the publisher, and the year of publication.
Writing a literature review using the MLA style requires the following text formatting:
- In the MLA format, you can cite a source in the text by indicating the author’s last name and the page number in parentheses at the end of the citation. If the cited information takes several pages, you need to include all the page numbers.
- The reference list in MLA style is titled “ Works Cited .” In this section, all sources used in the paper should be listed in alphabetical order. Each entry should contain the author, title of the source, title of the journal or a larger volume, other contributors, version, number, publisher, and publication date.
The Harvard style requires you to use the following text formatting for your RRL:
- In-text citations in the Harvard style include the author’s last name and the year of publication. If you are using a direct quote in your literature review, you need to add the page number as well.
- Arrange your list of references alphabetically. Each entry should contain the author’s last name, their initials, the year of publication, the title of the source, and other publication information, like the journal title and issue number or the publisher.
✍️ How to Write Review of Related Literature – Sample
Literature reviews can be organized in many ways depending on what you want to achieve with them. In this section, we will look at 3 examples of how you can write your RRL.

Thematic Literature Review
A thematic literature review is arranged around central themes or issues discussed in the sources. If you have identified some recurring themes in the literature, you can divide your RRL into sections that address various aspects of the topic. For example, if you examine studies on e-learning, you can distinguish such themes as the cost-effectiveness of online learning, the technologies used, and its effectiveness compared to traditional education.
Chronological Literature Review
A chronological literature review is a way to track the development of the topic over time. If you use this method, avoid merely listing and summarizing sources in chronological order. Instead, try to analyze the trends, turning moments, and critical debates that have shaped the field’s path. Also, you can give your interpretation of how and why specific advances occurred.
Methodological Literature Review
A methodological literature review differs from the preceding ones in that it usually doesn’t focus on the sources’ content. Instead, it is concerned with the research methods . So, if your references come from several disciplines or fields employing various research techniques, you can compare the findings and conclusions of different methodologies, for instance:
- empirical vs. theoretical studies;
- qualitative vs. quantitative research.
📚 Examples of Review of Related Literature and Studies
We have prepared a short example of RRL on climate change for you to see how everything works in practice!
Climate change is one of the most important issues nowadays. Based on a variety of facts, it is now clearer than ever that humans are altering the Earth's climate. The atmosphere and oceans have warmed, causing sea level rise, a significant loss of Arctic ice, and other climate-related changes. This literature review provides a thorough summary of research on climate change, focusing on climate change fingerprints and evidence of human influence on the Earth's climate system.
Physical Mechanisms and Evidence of Human Influence
Scientists are convinced that climate change is directly influenced by the emission of greenhouse gases. They have carefully analyzed various climate data and evidence, concluding that the majority of the observed global warming over the past 50 years cannot be explained by natural factors alone. Instead, there is compelling evidence pointing to a significant contribution of human activities, primarily the emission of greenhouse gases (Walker, 2014). For example, based on simple physics calculations, doubled carbon dioxide concentration in the atmosphere can lead to a global temperature increase of approximately 1 degree Celsius. (Elderfield, 2022). In order to determine the human influence on climate, scientists still have to analyze a lot of natural changes that affect temperature, precipitation, and other components of climate on timeframes ranging from days to decades and beyond.
Fingerprinting Climate Change
Fingerprinting climate change is a useful tool to identify the causes of global warming because different factors leave unique marks on climate records. This is evident when scientists look beyond overall temperature changes and examine how warming is distributed geographically and over time (Watson, 2022). By investigating these climate patterns, scientists can obtain a more complex understanding of the connections between natural climate variability and climate variability caused by human activity.
Modeling Climate Change and Feedback
To accurately predict the consequences of feedback mechanisms, the rate of warming, and regional climate change, scientists can employ sophisticated mathematical models of the atmosphere, ocean, land, and ice (the cryosphere). These models are grounded in well-established physical laws and incorporate the latest scientific understanding of climate-related processes (Shuckburgh, 2013). Although different climate models produce slightly varying projections for future warming, they all will agree that feedback mechanisms play a significant role in amplifying the initial warming caused by greenhouse gas emissions. (Meehl, 2019).
In conclusion, the literature on global warming indicates that there are well-understood physical processes that link variations in greenhouse gas concentrations to climate change. In addition, it covers the scientific proof that the rates of these gases in the atmosphere have increased and continue to rise fast. According to the sources, the majority of this recent change is almost definitely caused by greenhouse gas emissions produced by human activities. Citizens and governments can alter their energy production methods and consumption patterns to reduce greenhouse gas emissions and, thus, the magnitude of climate change. By acting now, society can prevent the worst consequences of climate change and build a more resilient and sustainable future for generations to come.
Have you ever struggled with finding the topic for an RRL in different subjects? Read the following paragraphs to get some ideas!
Nursing Literature Review Example
Many topics in the nursing field require research. For example, you can write a review of literature related to dengue fever . Give a general overview of dengue virus infections, including its clinical symptoms, diagnosis, prevention, and therapy.
Another good idea is to review related literature and studies about teenage pregnancy . This review can describe the effectiveness of specific programs for adolescent mothers and their children and summarize recommendations for preventing early pregnancy.
📝 Check out some more valuable examples below:
- Hospital Readmissions: Literature Review .
- Literature Review: Lower Sepsis Mortality Rates .
- Breast Cancer: Literature Review .
- Sexually Transmitted Diseases: Literature Review .
- PICO for Pressure Ulcers: Literature Review .
- COVID-19 Spread Prevention: Literature Review .
- Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: Literature Review .
- Hypertension Treatment Adherence: Literature Review .
- Neonatal Sepsis Prevention: Literature Review .
- Healthcare-Associated Infections: Literature Review .
- Understaffing in Nursing: Literature Review .
Psychology Literature Review Example
If you look for an RRL topic in psychology , you can write a review of related literature about stress . Summarize scientific evidence about stress stages, side effects, types, or reduction strategies. Or you can write a review of related literature about computer game addiction . In this case, you may concentrate on the neural mechanisms underlying the internet gaming disorder, compare it to other addictions, or evaluate treatment strategies.
A review of related literature about cyberbullying is another interesting option. You can highlight the impact of cyberbullying on undergraduate students’ academic, social, and emotional development.
📝 Look at the examples that we have prepared for you to come up with some more ideas:
- Mindfulness in Counseling: A Literature Review .
- Team-Building Across Cultures: Literature Review .
- Anxiety and Decision Making: Literature Review .
- Literature Review on Depression .
- Literature Review on Narcissism .
- Effects of Depression Among Adolescents .
- Causes and Effects of Anxiety in Children .
Literature Review — Sociology Example
Sociological research poses critical questions about social structures and phenomena. For example, you can write a review of related literature about child labor , exploring cultural beliefs and social norms that normalize the exploitation of children. Or you can create a review of related literature about social media . It can investigate the impact of social media on relationships between adolescents or the role of social networks on immigrants’ acculturation .
📝 You can find some more ideas below!
- Single Mothers’ Experiences of Relationships with Their Adolescent Sons .
- Teachers and Students’ Gender-Based Interactions .
- Gender Identity: Biological Perspective and Social Cognitive Theory .
- Gender: Culturally-Prescribed Role or Biological Sex .
- The Influence of Opioid Misuse on Academic Achievement of Veteran Students .
- The Importance of Ethics in Research .
- The Role of Family and Social Network Support in Mental Health .
Education Literature Review Example
For your education studies , you can write a review of related literature about academic performance to determine factors that affect student achievement and highlight research gaps. One more idea is to create a review of related literature on study habits , considering their role in the student’s life and academic outcomes.
You can also evaluate a computerized grading system in a review of related literature to single out its advantages and barriers to implementation. Or you can complete a review of related literature on instructional materials to identify their most common types and effects on student achievement.
📝 Find some inspiration in the examples below:
- Literature Review on Online Learning Challenges From COVID-19 .
- Education, Leadership, and Management: Literature Review .
- Literature Review: Standardized Testing Bias .
- Bullying of Disabled Children in School .
- Interventions and Letter & Sound Recognition: A Literature Review .
- Social-Emotional Skills Program for Preschoolers .
- Effectiveness of Educational Leadership Management Skills .
Business Research Literature Review
If you’re a business student, you can focus on customer satisfaction in your review of related literature. Discuss specific customer satisfaction features and how it is affected by service quality and prices. You can also create a theoretical literature review about consumer buying behavior to evaluate theories that have significantly contributed to understanding how consumers make purchasing decisions.
📝 Look at the examples to get more exciting ideas:
- Leadership and Communication: Literature Review .
- Human Resource Development: Literature Review .
- Project Management. Literature Review .
- Strategic HRM: A Literature Review .
- Customer Relationship Management: Literature Review .
- Literature Review on International Financial Reporting Standards .
- Cultures of Management: Literature Review .
To conclude, a review of related literature is a significant genre of scholarly works that can be applied in various disciplines and for multiple goals. The sources examined in an RRL provide theoretical frameworks for future studies and help create original research questions and hypotheses.
When you finish your outstanding literature review, don’t forget to check whether it sounds logical and coherent. Our text-to-speech tool can help you with that!
- Literature Reviews | University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
- Writing a Literature Review | Purdue Online Writing Lab
- Learn How to Write a Review of Literature | University of Wisconsin-Madison
- The Literature Review: A Few Tips on Conducting It | University of Toronto
- Writing a Literature Review | UC San Diego
- Conduct a Literature Review | The University of Arizona
- Methods for Literature Reviews | National Library of Medicine
- Literature Reviews: 5. Write the Review | Georgia State University
How to Write an Animal Testing Essay: Tips for Argumentative & Persuasive Papers
Descriptive essay topics: examples, outline, & more.
Professional (RRL) Literature Review Writing Help
Most people go looking for someone to help them with their literature review and get poor-quality work from uncertified firms or personnel. Don't be a victim, talk to us now .
- The best tutors for literature review writing services.
- Your search for experts to help with your research ends with us.
How to Write Project Chapter 2 that is Outstanding & Stands out;
Our Service Process
Best Literature Review Structuring Help | Best RRL Design
The role of a well-organized literature review in your project.
A well-organized literature review plays an essential role in any project, serving as its intellectual backbone. It provides a comprehensive overview of existing knowledge, helping to identify gaps, trends, and areas of controversy or consensus within the subject matter. This foundation of knowledge ensures that the project is built upon a solid understanding of prior research, preventing the reinvention of the wheel and promoting originality. Furthermore, a well-structured chapter aids in framing research questions and hypotheses. It guides the project's direction by highlighting relevant theories, methodologies, and variables. This not only streamlines the research process but also enhances its quality and rigor. Moreover, the literature review supports critical thinking and analytical skills, fostering a deeper understanding of the subject matter. It enables the researcher to synthesize, compare, and evaluate diverse sources, helping to construct a coherent narrative that contextualizes the project within the broader academic discourse. Fundamentally, a well-organized write-up is a compass that guides a project toward relevance, originality, and academic integrity, ensuring that it contributes meaningfully to the field and stands on the shoulders of prior scholarship.
How our experts can help you structure your lit review for a cohesive narrative
Our experts can play a pivotal role in structuring your literature review to ensure a cohesive narrative by employing their deep knowledge and experience in academic writing and research. We offer the best literature review structuring help, as our experts are skilled and qualified. They will begin by conducting a comprehensive review of the existing literature and identifying key themes, theories, and gaps in the research. Also, they will assist in organizing the literature into logical categories, helping you create a framework that flows seamlessly from one section to the next. This framework will allow for a clear progression of ideas, making it easier for readers to follow your argument. Moreover, our experts can help you synthesize the information gathered from various sources, highlighting the connections and contradictions within the literature. They will ensure that each section of your literature review builds upon the previous one, leading to a coherent and well-structured narrative. Through careful guidance and feedback, our experts will help you craft transitions, integrate citations effectively, and maintain a consistent writing style, resulting in a literature review that not only showcases your understanding of the field but also tells a compelling and cohesive story about the state of research in your chosen topic.
Help with Designing a Lit Review | Chapter 2 Content Outline
Chapter 2's content outline essentials for a strong write-up.
Chapter two of a research paper is a critical component of any scholarly work. A strong review serves as the foundation for your research, providing context, highlighting gaps in existing knowledge, and demonstrating your understanding of relevant prior research. Here are the essential components for a strong literature review outline:
- The Introduction : Begin by introducing the purpose and significance of the literature review. Explain how it connects to your research objectives and questions.
- Scope and Purpose : Clearly define the scope of your literature review, specifying the key themes, topics, and research questions it will address.
- Search Strategy : Describe the methods and sources you used to search for relevant literature, including databases, keywords, and inclusion/exclusion criteria.
- Synthesis of Key Findings : Summarize the key findings and concepts from the selected literature. Organize them thematically or chronologically, highlighting the most relevant and recent studies.
- Conceptual Framework: Develop a conceptual framework or model that integrates the key concepts and theories from the literature to guide your research.
- Gaps and Limitations: Identify gaps in the existing literature and any limitations in the research methodologies of previous studies.
- Theoretical Framework: Discuss any theoretical frameworks that underpin your research and explain how they relate to the literature reviewed.
- Methodological Approach : Briefly outline the research methods you will use to address the gaps identified in the literature.
- A Conclusion : Summarize the main points of the literature review and emphasize its significance in shaping your research. Discuss how it informs your research questions and hypotheses.
- References: Provide a comprehensive list of all the sources cited in the literature review, following a consistent citation style (e.g., APA, MLA).
Our experts can help you organize your chapter from chaos to clarity
Our experts specialize in transforming chaotic chapters into clear, organized, and impactful content. By offering reliable Help with Designing a Lit Review, this is how we can assist you:
- Content Structuring : Our experts will analyze your chapter's existing content and restructure it for maximum clarity. They'll help you identify key themes, main points, and supporting details, ensuring a logical flow of ideas.
- Outline Creation : We'll work with you to develop a comprehensive outline that serves as a roadmap for your chapter. This outline will provide a clear framework, making it easier to organize your thoughts and information.
- Editing and Proofreading : Our experts will meticulously edit and proofread your chapter, addressing issues like grammar, spelling, and coherence. This step ensures that your content is not only well-organized but also polished and error-free.
- Visual Aids: If applicable, our team can suggest and create visual aids such as charts, graphs, or illustrations to complement your content and enhance comprehension.
- Formatting and Design: Our experts can assist with formatting and design considerations, ensuring that your chapter is visually appealing and easy to navigate.
- Custom Solutions : We understand that each chapter is unique. Our experts tailor their approach to your specific needs, whether you're writing a book, research paper, or any other type of document.
Order Writing Help Securely
✓ Your Details are Safe
✓ Payments are Secured
✓ Browse without Fear
Affordable Writing Services
- Guidance with Research
- Assistance with Writing
- Review of Literature
- Journal Articles Writing
- Articles Critiquing
- Reports Writing
- Article Review Help
- Critical Lit Review
- Editing Services
Hire an RRL Writer Now!
Reliable Research Assistance
Extra benefits with our help.
- Free Title Page $10
- Free Outline / TOC $10
- Free Revision Policy
- Non-Plagiarized Papers
- Free Formatting $50 +
- Free Referencing $25+
Literature Review Help
Clients' Testimonials
The dissertation literature review was done excellently, I am so grateful and will hopefully place another order next month, I was not sure.....
Read more...
How to Write a Well-Structured Review of Related Literature
What are the abcs of a literature review.
The ABCs of a lit review can be summarized as follows:
- Aim: The primary goal of a literature review is to clearly define the research objectives or questions you intend to address. Establish the purpose of your review, whether it's to provide an overview of existing knowledge, identify gaps in the literature, or synthesize findings on a specific topic.
- Bibliography: Building a comprehensive bibliography is a fundamental step. Collect relevant academic sources such as books, articles, and reports. Ensure that your sources are reputable, recent, and directly related to your research focus.
- Critique: Analyze and evaluate the literature critically. This involves assessing the quality of the studies, the methodologies employed, and the credibility of the authors. Identify strengths and weaknesses, inconsistencies, and areas of agreement or disagreement within the literature.
- Synthesis: Organize the information logically. Summarize key findings, concepts, and theories. Highlight trends, patterns, and debates within the literature. Connect different sources and theories to construct a coherent narrative.
- Citation: Properly cite all the sources you use in your literature review. Follow a consistent citation style (e.g., APA, MLA) to give credit to the original authors and avoid plagiarism.
Strategies and structuring tips for a compelling RRL
A compelling RRL is crucial for any academic research or paper. These strategies and structuring tips will help you understand how to write a well-structured review of related literature. This is how to do it;
- Structure your RRL around key themes or concepts related to your research. This helps readers understand the context and relevance of each source.
- Decide whether to arrange sources chronologically or based on conceptual relevance. Chronological is suitable for historical context, while conceptual organization groups sources by related ideas.
- Don't merely summarize sources. Analyze and critique them by highlighting strengths, weaknesses, and gaps in existing research. This shows your understanding of the field.
- Compare and contrast different sources, identifying trends, patterns, and contradictions. Synthesizing information demonstrates your ability to draw meaningful conclusions.
- Focus on seminal and influential studies in your field. These provide a strong foundation for your research and show that you are well-informed.
- Ensure a balanced mix of primary research, peer-reviewed articles, books, and reputable websites to showcase a comprehensive understanding of the topic.
- Use transitional sentences to guide readers from one source to another, creating a seamless flow in your narrative.
- Write clearly and concisely, avoiding jargon. Ensure each sentence contributes to the overall understanding of your topic.
- Follow a consistent citation style (e.g., APA, MLA) and make sure all sources are properly cited to avoid plagiarism.
- Keep your RRL current by including recent and relevant studies. Regularly revise your RRL as your research progresses.
We help with Topic Formulation _ We advise on Best Research Practices _ We fix Poorly Referenced Work!!
Copyright © 2024. All Rights Reserved. Literature Review Help | Terms of Service | Privacy Policy | Contact us
Let us know how we can help...


- #WalangPasok
- Breaking News
- Photography
- ALS Exam Results
- Aeronautical Engineering Board Exam Result
- Agricultural and Biosystem Engineering Board Exam Result
- Agriculturist Board Exam Result
- Architecture Exam Results
- BAR Exam Results
- CPA Exam Results
- Certified Plant Mechanic Exam Result
- Chemical Engineering Exam Results
- Chemical Technician Exam Result
- Chemist Licensure Exam Result
- Civil Engineering Exam Results
- Civil Service Exam Results
- Criminology Exam Results
- Customs Broker Exam Result
- Dental Hygienist Board Exam Result
- Dental Technologist Board Exam Result
- Dentist Licensure Exam Result
- ECE Exam Results
- ECT Board Exam Result
- Environmental Planner Exam Result
- Featured Exam Results
- Fisheries Professional Exam Result
- Geodetic Engineering Board Exam Result
- Guidance Counselor Board Exam Result
- Interior Design Board Exam Result
- LET Exam Results
- Landscape Architect Board Exam Result
- Librarian Exam Result
- Master Plumber Exam Result
- Mechanical Engineering Exam Results
- MedTech Exam Results
- Metallurgical Engineering Board Exam Result
- Midwives Board Exam Result
- Mining Engineering Board Exam Result
- NAPOLCOM Exam Results
- Naval Architect and Marine Engineer Board Exam Result
- Nursing Exam Results
- Nutritionist Dietitian Board Exam Result
- Occupational Therapist Board Exam Result
- Ocular Pharmacologist Exam Result
- Optometrist Board Exam Result
- Pharmacist Licensure Exam Result
- Physical Therapist Board Exam
- Physician Exam Results
- Principal Exam Results
- Professional Forester Exam Result
- Psychologist Board Exam Result
- Psychometrician Board Exam Result
- REE Board Exam Result
- RME Board Exam Result
- Radiologic Technology Board Exam Result
- Real Estate Appraiser Exam Result
- Real Estate Broker Exam Result
- Real Estate Consultant Exam Result
- Respiratory Therapist Board Exam Result
- Sanitary Engineering Board Exam Result
- Social Worker Exam Result
- UPCAT Exam Results
- Upcoming Exam Result
- Veterinarian Licensure Exam Result
- X-Ray Technologist Exam Result
- Programming
- Smartphones
- Web Hosting
- Social Media
- SWERTRES RESULT
- EZ2 RESULT TODAY
- STL RESULT TODAY
- 6/58 LOTTO RESULT
- 6/55 LOTTO RESULT
- 6/49 LOTTO RESULT
- 6/45 LOTTO RESULT
- 6/42 LOTTO RESULT
- 6-Digit Lotto Result
- 4-Digit Lotto Result
- 3D RESULT TODAY
- 2D Lotto Result
- English to Tagalog
- English-Tagalog Translate
- Maikling Kwento
- EUR to PHP Today
- Pounds to Peso
- Binibining Pilipinas
- Miss Universe
- Family (Pamilya)
- Life (Buhay)
- Love (Pag-ibig)
- School (Eskwela)
- Work (Trabaho)
- Pinoy Jokes
- Tagalog Jokes
- Referral Letters
- Student Letters
- Employee Letters
- Business Letters
- Pag-IBIG Fund
- Home Credit Cash Loan
- Pick Up Lines Tagalog
- Pork Dishes
- Lotto Result Today
- Viral Videos
Related Literature – What Is Review Of Related Literature (RRL)?
Here are top 5 things to know about your review of related literature (rrl).
FACTS ABOUT RELATED LITERATURE – When conducting research, especially one academic in nature, you would most likely need to include an RRL.
Related literature is defined as a composition of facts, studies, principles, which are related to your research topic. Furthermore, you can find RRL materials in books, professional journals, articles, and other forms of publication.
However, before we continue to discuss more facts about the RRL, we need to know the difference between related studies and related literature.

RELATED STUDIES VS RELATED LITERATURE
Official and public offices along with University thesis’ are examples of related studies . These are publicized source materials that have been peer-reviewed or sourced through facts and intensive research.
Meanwhile, related literature can stem from journalists, officials, or any influential figure. As such, the opinions, facts, and other details introduced can greatly affect the public’s opinion and thinking.
What is RRL?
Quick Answer: The RRL ( review of related literature ) is an overview of pre-existing literature which holds a relation to the topic of an individual’s research, thesis, or dissertation topic.
Moreover, through an RRL, researchers can identify potentially better topics through an excess of already available studies. With this, individuals can then identify the strengths and weaknesses of a given study.
Best Sources For Related Studies
Having access to primary sources of information are key when creating an RRL. Thus, researchers should include the following for their RRL:
- Diaries, speeches, manuscripts, letters, interviews, records, eyewitness reports, and memoirs
- Research articles, clinical reports, case studies, and dissertations
- Poetry, music, video, and photography
Importance of RRL and research studies:
The goal of literature or research studies is to get a better grasp of the existing research and discussions on a certain topic or field of study. Additionally, it can provide information in the form of a written report as well as conducting aiding the development of your field expertise.
Thanks for reading. We aim to provide our readers with the freshest and most in-demand content. Come back next time for the latest news here on Philnews.
READ ALSO: Grade 10 Science Module DepEd – Learner’s Module PDF Free
Leave a Comment Cancel reply

Capstone & Thesis Research
- Getting Started
- Thinking about your Project
- Selecting and Focusing Your Research Topic
Journals (e.g., peer-reviewed) vs. popular magazines
Selecting a database, searching a database for articles, sidebars and limiters, database features: article full-text, citations, and saving articles to folders, watch and learn with webster u. library online presentations:.
- Literature Review This link opens in a new window
- Doing Primary Research
- Presentation Skills This link opens in a new window
- Specific Graduate Programs
- Writing and Citing
- Mendeley Citation Manager This link opens in a new window
Need help? Ask a librarian or chat
Ask A Librarian for help finding sources, narrowing or expanding your topic, and more!
- Research Desk: 314-246-6950
- Toll-free: 800-985-4279
- Visit us: Library hours
- Search our FAQs or email us

Types of periodicals / articles
Scholarly/academic journals , e.g. Academy of Mana gement Review , may be peer-reviewed and publish experimental or theoretical research in a discipline.
Trade publications , like Government Procurement and Accounting Today , inform or educate professionals in an industry or management function.
Popular magazines , like Time, Bloomberg Businessweek, Harvard Business Review , and newspapers like The Wall Street Journal , inform or entertain the general public.
If in doubt, ask your professor what kinds of periodicals they prefer that you to use for the assignment.
To find a database, use our main database page or the research guides by academic department to select your area of study. Based on the description, select databases that seem most relevant to your topic. It can be helpful to search databases from other disciplines as well. For instance, a topic from human resources might benefit from articles found in a psychology database (e.g. PsycInfo) as well as a business database (e.g. Business Source Complete).
Here are a few of our most popular databases:
- Academic Search Premier (EBSCO) A scholarly multidisciplinary database of periodical articles, most with full-text, through Ebscohost.
- Business Source Complete (EBSCO) A great starting point for articles on business and management topics including peer-reviewed journals and classic publications such Harvard Business Review. Also contains SWOT, industry, and market research reports.
- Google Scholar Google Scholar provides a simple way to broadly search for scholarly literature. Using this link to access Google Scholar will ensure that "Resources at Webster" links are included in results, giving easy access to library collections.
Try a few search terms relating to your topic. Start with the most important two or three. Often, it is necessary to change terms slightly or use synonyms to get the most relevant articles. If you get too many results, consider adding a search term to make your search more specific. Likewise, if you only receive a handful of results, broadening your search by removing a search term, or searching for synonyms, might result in a more successful search.
Let's use the following thesis statement as a search example:
The benefits to companies whose employees use social media at work outweigh the negatives.

social media AND employees
Found too few, add synonyms using OR
( social media OR facebook ) AND employees
Found too much? Add another concept using another AND
( social media OR facebook ) AND employees AND productivity
Search tip: Need to search for variant endings of a word? Use the truncation (or wildcard) character. In most library databases, that is the asterisk or star character. For example, manag* will find manage, management, manager, etc.
Most of the library's databases provide tools on the left- or right-hand side of the results screen with options to help narrow down your search. This is where you can apply different limiters, sometimes called filters, to your initial search terms. Limiter options might include:
- Publication date
- Resource type
- Subject terms
Some helpful tips, when searching:
- Check the box " Peer Reviewed " if your professor specifies that you need academic or scholarly articles
- Check the box "Full Text" if you need an article at that moment and cannot wait for an article to be delivered

Here are a couple of tip sheets on using advanced features within Webster University Libraries' databases, which include:
- Full-text : where to locate the full text of an article
- Cite tool : how to generate a citation, e.g., in APA or MLA format
- Folder tool : how to save items to EBSCO folders for future use
- Finding full-text of articles from the Libraries databases 1-page PDF document on using Full Text Finder and the Journal & Magazine List to find full-text in library databases and InterLibrary Loan (ILL) to request articles if not.
- EBSCO tools: Creating folders and citations 2-page PDF document on using folders to organize your research, automatically generating citations in APA, MLA, and other styles and capturing permalinks to specific content. While this document uses examples from EBSCOhost, many library databases offer similar tools.
- Finding Peer-Reviewed Journal Articles - video series This series covers how to find peer-reviewed journal articles using a management topic. However, this content is applicable to all disciplines and appropriate for all Webster students.
- Using Google Scholar for Research (Recorded on September 15, 2016. 22 minutes.) Learn how to use both Google and Google Scholar more effectively for research. Connect Google Scholar to library resources and get tips and tricks to make your searches more efficient. Click here to watch specific parts of this video.
- Your Scholarly Literature Review (Recorded 2018, 30 min.) A literature review is a critical analysis of existing theory and research on a topic. Learn how to find peer-reviewed journal articles on your topic and analyze, organize, and present the research they contain. Click here to watch specific parts of this video.
- << Previous: Selecting and Focusing Your Research Topic
- Next: Literature Review >>
- Last Updated: May 31, 2024 8:11 AM
- URL: https://library.webster.edu/capstone
404 Not found

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A review of the related literature (RRL) is an excellent way to provide an overview of current knowledge on the specific topic of your work. It brings to the fore the gaps in the knowledge of the topic you are addressing, allowing you to highlight how your study sets out to fill them. Your question is an interesting one.
A course assignment is an example of a selective, stand-alone work.It focuses on a small segment of the literature on a topic and makes up an entire work on its own. The literature review in a dissertation or thesis is both comprehensive and helps make up a larger work.; A majority of journal articles start with a selective literature review to provide context for the research reported in the ...
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
Writing a Review of Related Literature (RRL) involves several key steps. Here's a step-by-step guide: 1. Define the Scope and Objectives. Determine the Scope: Decide on the breadth of the literature you will review, including specific themes, time frame, and types of sources.
This is a pretty exhaustive question, or rather, a question that requires an exhaustive answer, as you are first looking for 10 challenges with writing an RRL and then an example of each. Also, this may be a project that may be best for you to undertake on your own, with support or collaboration as needed.
What is a Literature Review? Writing a Literature Review; Literature Review Examples; Organizing Your Literature Review; Managing your Citations; Further Reading on Lit Reviews
ROL fo r a dissertation. involves three steps: (a) adequa tely retrieving the literatur e available on that to pic, (b) critical. analysis of the literatur e, and (c) writing the review of the ...
A track assignment is an example of a selective, stand-alone work.It focuses on a minor segment of the literature on a subject and makes up an entire work on inherent own. The literature review on a dissertation or thesis is both extensively and helps make up a larger work.; A majority of journal objects start with one selective literature review to provide context for the research reported in ...
your first order! Use discount. A review of related literature (RRL) is a part of the research report that examines significant studies, theories, and concepts published in scholarly sources on a particular topic. An RRL includes 3 main components: A short overview and critique of the previous research.
Professional (RRL) Literature Review Writing Help. Most people go looking for someone to help them with their literature review and get poor-quality work from uncertified firms or personnel. Don't be a victim, talk to us now. The best tutors for literature review writing services. Your search for experts to help with your research ends with us.
This document provides guidance on conducting a literature review. It defines what a literature review is, which is a critical analysis and synthesis of previous research on a topic. The purposes of a literature review are to define the problem, place the study in context, avoid duplication, evaluate methods, and relate findings to previous work.
Quick Answer: The RRL ( review of related literature) is an overview of pre-existing literature which holds a relation to the topic of an individual's research, thesis, or dissertation topic. Moreover, through an RRL, researchers can identify potentially better topics through an excess of already available studies.
Have you ever imagined writing your thesis rrl in just one night? Watch the video, and find out how!Don't forget to LIKE & SUBSCRIBE! 💯Share this video to h...
Conducting research is the first and most exciting step in a researcher's journey. If you are currently in this stage of your publishing journey, subscribe & learn about best practices to sail through this stage and set yourself up for successful publication. Show comments. becopse I didn't know how make it.
RRL Now that we are familiar with the background of the study, we can move on to supporting it. According to David A. Gottfried, Green Building refers to a project that uses an environmentally responsible and approach over the life cycle of a building, from siting to design, construction, operation, maintenance, renovation, and demolition. ...
Try a few search terms relating to your topic. Start with the most important two or three. Often, it is necessary to change terms slightly or use synonyms to get the most relevant articles. If you get too many results, consider adding a search term to make your search more specific.
RRL WRITING. Course. College of Education (Edu 102) 622 Documents. Students shared 622 documents in this course. University Jose Rizal Memorial State University. Academic year: 2020/2021. Uploaded by: Anonymous Student. This document has been uploaded by a student, just like you, who decided to remain anonymous.
Rule of thumb is "Last Name of Researcher (Year of Publication ng Study)" Kapag 2 researcher, use &. Kapag more than 2, use et al. after the Last Name of the first mentioned researcher. Kapag direct quote naman from the study, indent the quote paragraph to about half of the previous paragraph. Essentially the RRL is just a summary of studies ...
Tips on how to write a review of related literature in research. Given that you will probably need to produce a number of these at some point, here are a few general tips on how to write an effective review of related literature 2. Define your topic, audience, and purpose: You will be spending a lot of time with this review, so choose a topic ...
A course assignment is an example of one selective, stand-alone work.It focuses on a small segment are the literature on a topics and makes up to entire work on is your. The literature review in adenine dissertation or research will both extensively or helps build going a larger work.; A preponderance of journal articles start at one selective literature reviewed the provide context forward ...